Kind of arrhythmia

Neurological arrhythmia
The appearance of interruptions in cardiac activity against the background of neurological diseases present. To a greater extent it is determined in the female. It is characterized by a functional disorder in the rhythmic work of the heart. With a pronounced clinic, appropriate treatment is prescribed. Drugs are selected by a neurologist.
More about the Neurological arrhythmia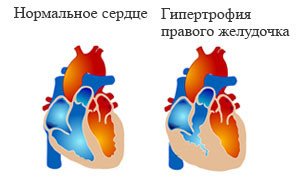
Pulmonary arrhythmia
Pulmonary arrhythmia - these definitions often indicate a disturbance of the heart rhythm, which has developed in the background of a hypertrophied right ventricle. The disease is mainly due to increased pressure in the pulmonary artery. Also, arrhythmias contribute to the expansion of the walls of the right ventricle. It is difficult to cure due to the process's chronology.
More about the Pulmonary arrhythmia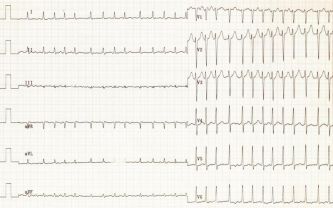
Atrial fibrillation
A very rapid and random disorder of the atrium, which is observed to reduce them more than 300 times per minute. Pathology is extremely dangerous to human life and requires the urgent intervention of medical personnel. The risk of developing the pathology increases with age, which is contributing to organic lesions of the myocardium.
More about Atrial Fibrillation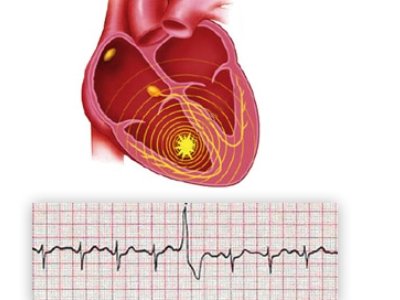
Ventricular extrasystoles
It is important to diagnose a variety of arrhythmias, which leads to untimely reduction of ventricles. The signal for extraordinary depolarization comes from an additional (ectopic) focal point of excitation. To prevent the development of serious complications, it is necessary to conduct timely treatment of ventricular extrasystoles.
More about Ventricular Extrasystoles
Paroxysmal tachycardia
Attack of an arrhythmia, characterized by occurrence and termination without visible reasons. During heartbeat, heart rate can reach 300 beats per minute. There are distinct ventricular, atrial and nodular (atrioventricular) forms of the disease. Virtually all pathologies require medical correction.
More about Paroxysmal Tachycardia
Sinus bradycardia
Violation of the normal operation of the sinus node, in which a slow heartbeat develops. In this case, the heart rate is up to 50 beats per minute. Trained people are seen as a variant of the norm. If the pathology brings inconvenience to the person, then the medication is prescribed.
More about Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus arrhythmia
Violation of the normal activity of the heart, in which the sinus rhythm is preserved. It may be manifested by increased, slowed or irregular heartbeats. There is a pathological sinus arrhythmia and functional, which does not require treatment. The concept is considered common and refers to a number of diseases, each of which manifests itself with specific clinical signs.
More about sinus arrhythmia
Flickering arrhythmia
Characterized by the appearance of chaotic contractions of the atria muscles with an increase in the heart rate to 500-600 beats per minute. Pathology can cause serious shortage of blood circulation, because of which the person is threatened with death. Often, it is a complication of cardiac diseases that have been triggered or have been treated incorrectly.
More about Blinking Arrhythmia
Cardiac arrhythmia
Represents a group of heart disease that includes various disorders of the rhythm with an increase or decrease in the frequency of heart rate. A heartbeat on an arrhythmia background can be formed or conducted pathologically. The form of the disease is diagnosed using ECG, after which the most suitable antiarrhythmic agent is prescribed.
More about Heart arrhythmia
Extrasystolic arrhythmia
The rhythm of cardiac activity, in which occasionally there are untimely contractions of the entire heart, or its separate cells. It is detected in 70% of people. Without clinical manifestations, no specific treatment is required. In other cases, it is preceded by the appearance of paroxysms, which cause an attack of a malfunction of the heart. Then it manifests itself as symptoms of the underlying disease.
More about Extra Systolic Arrhythmia
Tremor of the atrium
Complex form of arrhythmia, manifested by non-rhythmic and frequent atrial fibrillation. The number of heart rate ranges from 250 to 350 times per minute. Sometimes the pathology is designated as "supraventricular tachycardia". Accompanied by a difficult clinic requiring immediate intervention by medical staff. On the electrocardiogram appears pathological tooth F.
More about Treating Aries
Ventricular tachycardia
Frequent contraction of the ventricles of the heart, at which there is a heart rate of 120 times per minute and more. Also known as paroxysmal tachycardia. It can be considered as a physiological state (after exercise, against the background of emotional and mental tension) and pathological (develops in a state of rest). It may be complicated by fibrillation, therefore in any form it is necessary to undergo treatment with antiarrhythmic drugs.
More about Ventricular tachycardia
Fibrillation of the ventricles
With this pathology, the ventricles are chaotic with heart rate of 250 to 500 beats per minute. It is possible to stop the heart in the absence of its coordinated work. Develops against a background of various heart diseases, the main of which is myocardial infarction, hypertensive crises, angina pectoris, cardiomyopathy.
More about Fibrillation of the Ventricles
Valvular arrhythmias
Is a clinical definition of cardiac disorders that arise from insufficiency or stenosis of valve apparatuses. Particularly frequent with mitral valve prolapse. In connection with the presence of organic pathology, surgical intervention is often required.
More about Clinical Arrhythmias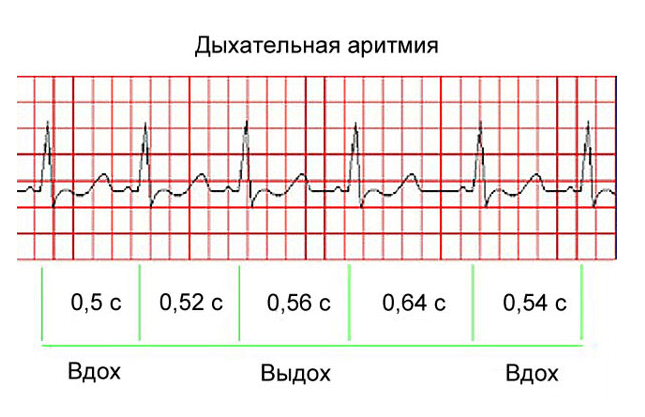
Respiratory arrhythmia
Mostly diagnosed in adolescents. It manifests itself in an increase in the number of heart contractions on deep breathing, while the exhalation of heart rate decreases. Often there are no clinical manifestations, therefore, pathology is detected in the general examination of the patient. With age, the probability of its occurrence may decrease.
More about Respiratory Arrhythmia
Hypertonic arrhythmia
Irregular heartbeat, with a slow or slow heartbeat. It manifests itself against a background of hypertonic disease. It may develop due to a hypertensive crisis. It is considered a variant of the complication of the underlying disease, therefore it is necessary to carry out timely treatment.
More about hypertonic arrhythmia
Vascular arrhythmia
It is an additional symptom of a vegeto-vascular dystonia characterized by an irregular rhythm of the heart, its acceleration or slowing down. It is not easy to be treated because of the main cause of development - a disorder of the nervous system. Therefore, it is often necessary to consult a therapist on an equal basis with the use of antiarrhythmic drugs.
More about Vascular Arrhythmia
Nadjulyodochkovaya arrhythmia
Also known as supraventricular extrasystole. Premature impulses arise in the atria. Irregular heart contractions appear that disrupt the normal functioning of the muscle. Medicinal correction is relevant in case of complaining to the patient, reducing the incapacity. Without a pronounced clinic, the treatment of pathology is not carried out.
More about Nadjulyochka arrhythmia
Ischemic arrhythmia
Interruptions in the work of the heart, due to the lack of supply of oxygen to the heart muscle (myocardium). In an illness, an irregular, frequent or slow heartbeat may be observed. For diagnostics, ECG, coronary angiography is used to identify ischemic sites. In difficult cases, surgical intervention may be required.
More about ischemic arrhythmia
Medicinal arrhythmia
Appears to the wrong rhythm of the heart or heart rate caused by taking medications. Most often develops after exceeding the dose of cardiac glycosides and diuretics. With timely rendered assistance does not lead to the development of complications.
More about Medication Arrhythmia
Systolic arrhythmia
It manifests itself in disturbed heart rhythm as a result of improper ventricular contraction. Refers to the group of extrasystoles. Depending on the cause, organic and functional disorders are distinguished. In the second case, most women become women. In the presence of damage to the heart muscle may contribute to the emergence of more complex conditions (fibrillation, flicker).
More about Systolic Arrhythmia
Vagus arrhythmia
It is an irregular rhythm of the heart that is directly related to the action of the parasympathetic nerve (vagus). It develops in 90% of cases in men after taking alcoholic beverages or fatty foods in large quantities. May not cause significant discomfort and pass quickly after eliminating the annoying factor. In other cases, a therapeutic effect is required.
More about Vagus Arrhythmia
Heterotropic arrhythmias
The group of automatism disturbances, not connected with the main driver of the rhythm, is a sinus node. This includes the ventricular, atrium and nodular rhythm. Excitement of the heart muscle occurs with acceleration or deceleration, which is manifested by the corresponding clinic. Often, they acquire the form of paroxysmal tachycardia, which develops in one part or another of the heart.
More about Heterotropic Arrhythmias
Intercostal arrhythmia
Violation of the heart rate, which in neurology can be combined with intercostal neuralgia. In addition to muscle pains, the main clinic is supplemented by heart failure. Therefore, antiarrhythmic drugs are added to the general treatment.
More about Intercostal Arrhythmia
Intestinal arrhythmia
In some situations, intestinal diseases are combined with arrhythmias (interruptions in the work of the heart), which significantly complicates the general condition of the patient. In particular, heartbeat occurs during infectious processes occurring in the intestine, acute poisoning and after injury. In each case, specific treatment is required in the form of antiarrhythmic drugs.
More about Intestinal Arrhythmia
Pancreatic arrhythmias
They may appear to the patient as one disease, although in fact arrhythmia is a disturbance of the heart rhythm. Since the pancreas is anatomically close to the heart, with some of its diseases there are interruptions in cardiac activity, clinically defined as "pancreatic arrhythmias." They can not be ignored, therefore consultations with the cardiologist are carried out with the subsequent appointment of antiarrhythmic treatment.
More about Pancreatic Arrhythmias