Ventricular tachycardia
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-10
All types of tachycardia are manifested with a rapid heartbeat, when the heart rate is more than 90 times per minute.Depending on the localization of the focal point that has become the cause of arrhythmia, supraventricular (atrial), ventricular (ventricular) and nodal tachycardia are secreted.With such attacks, the heart rate is between 150 and 300 times per minute.
The most disadvantageous of all types of paroxysmal tachycardia is the ventricular form, so when it occurs, medical care should be provided without delay.
The disease develops more often on the background of cardiovascular pathology and leads to serious hemodynamic disorders. Also, the cardiac muscle is a myocardium, therefore, it is accompanied, in general, by severe clinical signs. In some cases, even minor heart disease may be complicated by ventricular tachycardia, is the disease dangerous? It is clear that yes, since for one year dies about 300 thousand. people from this pathology of the heart. This is about half of the cases of total cardiac mortality.
Video: VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (V Tach,VT) Causes,Symptoms & Management
Description of ventricular tachycardia
The heart muscle in the normal state conducts electrical impulses regularly and in order, with a frequency of 60-90 times per minute. At the same time, the atrium is first reduced, and then the impulse enters the atrioventricular node in the ventricle, which is also reduced for several milliseconds later. This process passes so fast that the person is practically not felt, and in medicine is defined as sinus rhythm.
With a ventricular tachycardia, the sinus node is not the main driver of the rhythm, since it is not able to control the contractile capacity of the heart.
Ventricular tachycardia (ZT) is a violation of the normal (sinus) heart rhythm, characterized by an increase in the number of reductions in the ventricles. The similar occurs due to the broken structure of the myocardium, which results in the transmission of electrical impulses by the fibers. If it passes normally through the atrium and through the AV node, it begins to interrupt and circulate in a closed circle in the ventricles. Or, in the ventricles itself, ectopic foci are formed, which become complementary and extraordinary generators of the excitation signal. As a result of their activity chaotic contraction of ventricular myocardium begins at a crazy pace.
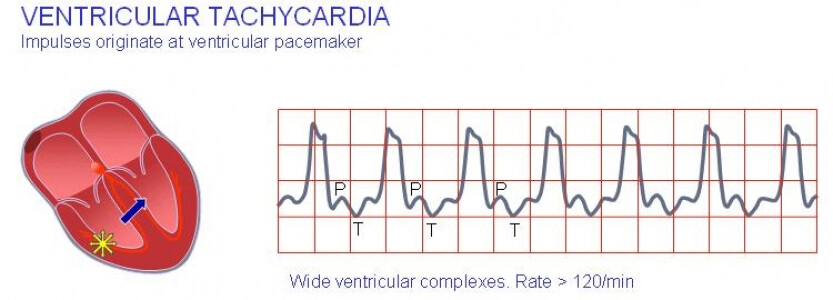
With ZT the hemodynamics are violated. This is due to the influence of two factors:
- with an increase in the frequency of ventricular contractions, the discharge of blood into the small and large circle of blood circulation decreases, which negatively affects the general condition of the patient.
- Discoordination of the heart reduces its functionality, which also affects hemodynamics.
Symptoms of ventricular tachycardia
Clinical picture directly depends on the complexity of hemodynamic disturbances. As a rule, the main symptoms of arrhythmia are added symptoms of the disease, on the background of which developed lung cancer.
Signs characteristic of all paroxysmal tachycardia:
- sudden development of the attack;
- increased number of heart contractions (with the ventricular form of CSS is, as a rule, 150-180 times per minute);
- a strong pulsation of vessels located on the neck can be felt.
The work of the ventricles is closely related to the central circulatory system, therefore, often with symptoms of abnormal hemodynamics: weakness, dizziness, pain in the heart, low blood pressure. In extremely complex cases, swelling develops, shortness of breath appears, it becomes difficult to breathe, which indicates acute cardiac failure.
The disease in 2% of cases is asymptomatic and with minimal organic damage to the heart.
Causes of ventricular tachycardia
ZH is directly related to cardiac pathology, but practical experience shows that the risk of developing a pathology increases in patients with the following diseases:
- Ischemic heart disease leads to the development of QT in 90-95% of cases. Basically, the pathology is associated with infarction changes, which lead to tachycardia in 1-2% of cases and develop in the first hours after organic lesions. It was noted that postinfarction LV lasts for a short time and passes independently. They can also play a negative role in the appearance of myocarditis, which significantly alter the structure of the heart muscle.
- Causes of heart caused by congenital and rheumatic factors. Failure of the valve structure prevents the blood from being thrown out of the heart properly. Especially severe attacks are taking place against the backdrop of long untreated stenosis and deficiencies of the valves that cause decompensation of the left ventricle.
- Medicinal effects can adversely affect the activity of the heart. In 20% of cases ventricular tachycardia is caused by cardiac glycosides. ZH may be a complication of treatment with drugs such as aspartic acid, quinidine, adrenaline.psychotropic drugs, some anesthetics.

In the etiopathogenesis of the disease there are provocative factors contributing to the development of QT. It can be frequent stress and psychoemotional stresses, increased physical activity, surgical interventions on the heart and hormonal imbalance in the body, which occurs in pheochromocytoma.
Types of ventricular tachycardia
In view of various factors, luminosity can occur in several forms: unstable and persistent. Also, the types of ventricular tachycardia are potentially dangerous because of the high risk of developing ventricular fibrillation.
In a small amount, about 2%, tachycardia of the ventricular form develops in young people. At the same time in their health there are no special violations. In such cases, talk about idiopathic zhtha.
Persistent and unstable ventricular tachycardia
The unstable type of ZT is characterized by unstable flow. On an electrocardiogram the paroxysms with periodicity in half a minute are fixed. Their number is more than three for a certain period. Hemodynamic disorders are occurring, but the mortality outlook is negligible. Unstable ventricular tachycardia is a frequent complication of ventricular extrasystoles, therefore, when combined, they are diagnosed as "extrasystole with run-offs of ventricular tachycardia."

Sustainable type of ZT is not prognostically more favorable. The resulting paroxysm lasts at least 30 seconds, determined by the ECG. Ventricular complexes in this case have been greatly changed. Due to the increased risk of sudden cardiac death on the background of developed fibrillation, this type of tachycardia is considered life-threatening.
Classification of ventricular tachycardia
According to this division, types of ZT, potentially dangerous due to the possible development of fibrillation, are determined.
- Monomorphic ZT, which often occur as a result of organic lesion of the heart.

- Polymorphic, or multivariate, zhT are different in amplitude and directions of the ventricular complexes formed as a result of the action of two or more ectopic foci. Generally, there are no structural changes in the heart, although in some cases, organic changes are determined. Distinguish bi-directional-spindle-like polymorphic ZT and polythyne or multifocal.
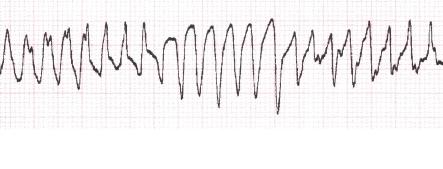
Sometimes a tachycardia occurs in the form of a "pirouette" when the QRS complexes progressively change and repeat against the background of an elongated QT interval.
Complications with ventricular tachycardia
The most dangerous complication is arrhythmia with a complete cessation of the heart's work. This is due to the developing fibrillation of the heart.
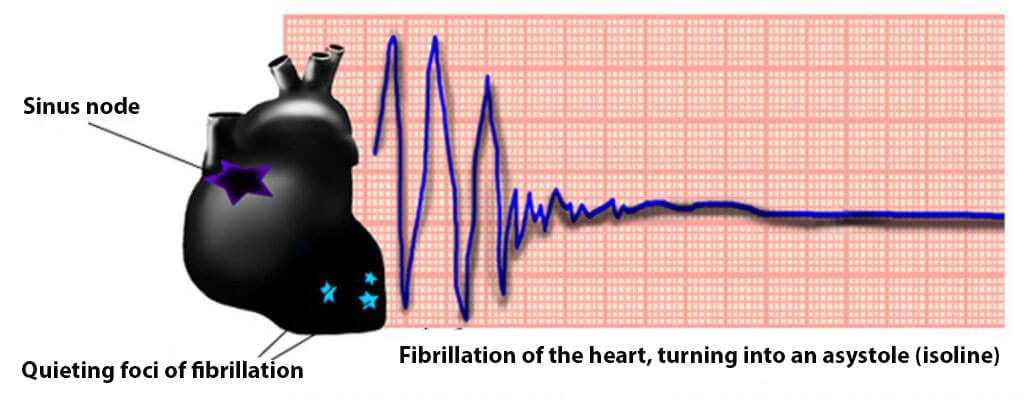
If paroxysms occur periodically for a long time, it is possible to form blood clots, which then pass into large vessels.Therefore, in patients with urolithiasis, the risk of thromboembolism in the arteries of the brain, the lungs, the gastrointestinal tract and the extremities increases.
Without treatment, the prognosis of ZT with organic changes is unfavorable. At the timely appointment of therapy and restoration of normal functioning of the heart changes in the positive side.
A good prognosis is considered when determining LV in children under one year of age. In some cases, tachycardia, which appeared in infancy, is maintained in children from a month or two to 10 years.
Diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia
At the first appearance of a sharp and rapid heartbeat, you should contact a doctor, because only with the help of ECG can be established accurate diagnosis. In some cases, patients suffer from disease on their legs, then it is more appropriate to use daily ECG monitoring. In the absence of a result from this method of research, a stress test is prescribed, during which, in most cases, the pathology of the heart is detected.
Characteristic features of ventricular tachycardia on ECG:
- QRS complexes expand and can deform, vary in amplitude and directions.
- Heart rate from 100 beats per minute.
- The electric axis of the heart (EOS) deviates to the left.
Additional diagnostic methods are used:
- An electrophysiological study that reveals different types and forms of tachycardia. It is well suited for accurate diagnosis of changes occurring in the bundles of Guillaume.
- Echocardiography - Investigates various areas of the heart, helps to determine the location of the pathological focus and its prevalence in the myocardium.
- Coronography - for the most part is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis of ischemic heart disease.
Of importance are laboratory tests (general, biochemistry) that help to detect concomitant pathology, as well as to determine the electrolyte composition, the level of sugar, and cholesterol in the blood.
Treatment of ventricular tachycardia
There are currently no techniques that would give 100% improvement in the clinical picture. As a rule, the treatment of uT begins with the introduction of medication. First of all, lidocaine or novocainamide. Drugs can sharply reduce the pressure, which should be taken into account when administered to patients who are prone to hypotension. In the presence of contraindications to the above drugs used sotalol.
In some cases, the use of antiarrhythmic drugs is indicated:
- seizures occur frequently or poorly tolerated;
- Due to seizures, the blood circulation is very severe;
- the prognosis of the disease is defined as dysfunctional or arrhythmia proceeds malignantly.
The ineffectiveness of medication therapy is an indication of cardioversion. The initial dose is determined at a rate of 1 W per kg.
Treatment of ventricular tachycardia of the malignant course and resistant to medical therapy is carried out by amiodarone. In the absence of effect, propanolol is added to the proposed monotherapy. A combination of two drugs is successful in 80% of cases. Medicines are prescribed for both adults and children, including newborns, who have life-threatening HRT.
Operative treatment is to improve the quality of life of the patient with stable forms of ovarian syndrome developed in the background of IBS. Other organic disorders may also be observed. During surgery, a cardiologic device that prevents cardiac arrest is implanted. Such an operation is costly, therefore, it is rarely practiced. There is some technique for doing it:
- defibrillator implantation;
- some paths conducting an electrical impulse and considered pathological are intersected;
- An electrical pacemaker is installed.
Emergency care with QT
Must be provided until the doctor or medical brigade approaches the patient. An attack can occur anywhere and in all circumstances, so it is advisable for every informed citizen to know the first-aid measures that will help save the sick life:
- If a man grabbed his heart, he began to tremble, leaned forward or fell, he should be sewn as far as possible or placed on a flat surface.
- If a person is conscious, it is necessary to ask him to squeeze and squeeze the muscles of the abdomen, arms and legs.
- Ask the patient to make a sharp exhalation.
- Massage movements rub the area of the carotid arteries around the neck from one side and the other in turn.
- If possible, attach to the forehead and temples something cold, you can wet the towel or handkerchief.
The most important thing when rendering first aid is to call an ambulance, because only the nursing staff with the necessary medicines and equipment will be able to stop the attack of the ventricular tachycardia.
Secondary prophylaxis of ventricular tachycardia
In case of attacks for the first time, it is necessary to diagnose and treat the disease that caused the lung in the shortest possible time. Afterwards, the individual therapy is selected, which is essentially a secondary prophylaxis of the ventricular tachycardia.
With the development of frequent paroxysms, which are difficult to stop and noticeably affect the quality of life of the patient, the doctor may be given a direction for implantation of the defibrillator.
In order to prevent relapses, it is useful to follow general recommendations for adjusting the usual way of life:
- Regularly monitor blood pressure, blood glucose, body weight.
- It is right to eat, with the inclusion of products useful for the heart.
- Bad habits must be eliminated as a matter of necessity.
- To engage in curative physical education and perform the permissible physical activity.
Video: Ventricular tachycardia (VT) - an Osmosis Preview
Similar articles
Any form of ventricular tachycardia requires urgent hospitalization. If the patient is diagnosed with tachycardia stable or with hemodynamic disorders then defibrillation is performed. Ventricular tachycardia may be complicated by heart failure, and in this case, an adrenalin solution is administered intracardiacly. Amiodarone and lidocaine may also be used in the process of compression of the attack. The occurrence of paroxysms more than twice a month is an indication for implantation of an electrical pacemaker in the form of a defibrillator cardioverter.
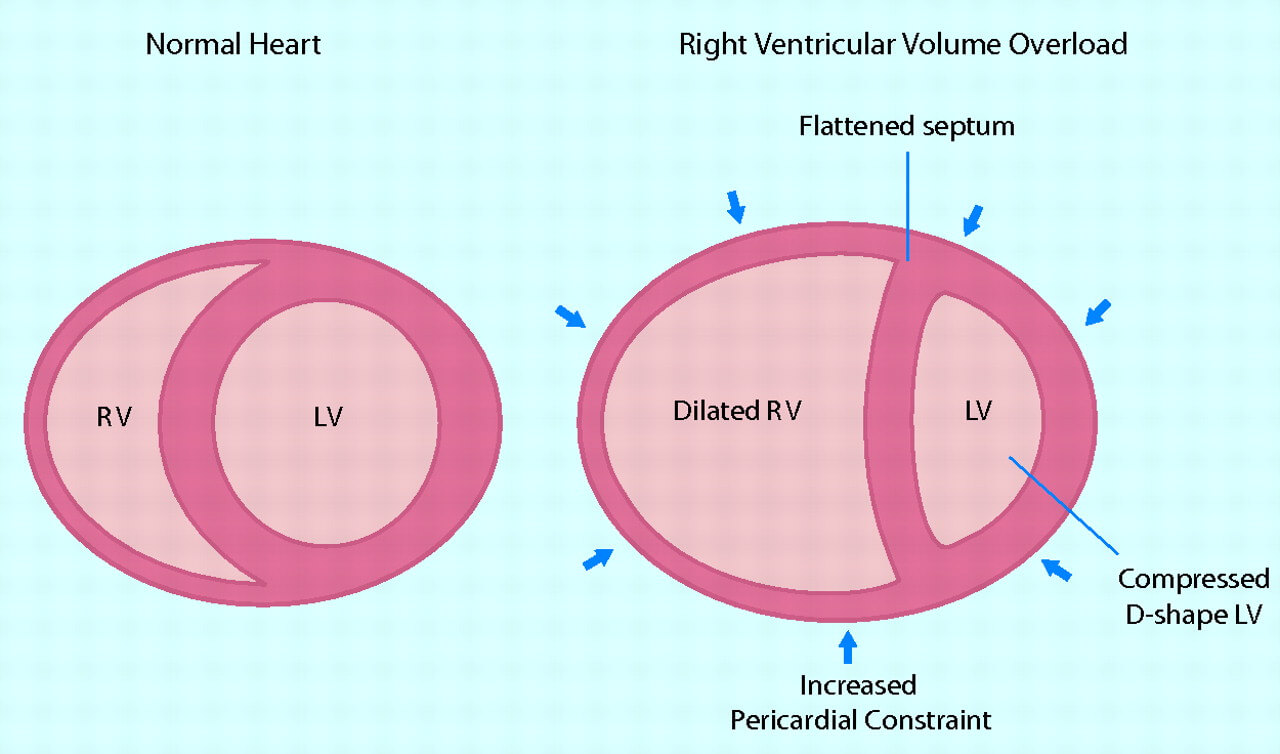
While left ventricular failure has been the subject of intensive discussion for decades, right ventricular heart failure, as a rule, remained with minimal attention. Indeed, the right half of the heart for a long time was considered relatively passive channel for blood flow between systemic and pulmonary blood circulation, respectively, its frustration was considered relatively not difficult.

In the human body, everything is interconnected, so one disease often contributes to the development of another. If necessary, during treatment all the patient's pathologies, including the gastrointestinal tract and the heart, are taken into account. Sometimes an improvement in the course of the underlying disease makes it possible to reduce the clinical signs of another.
