Nadjulyodochkovaya arrhythmia
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-10
Any form of arrhythmia is a change in the sequence, frequency and rhythmicity of the heart contractions. During supraventricular arrhythmia, a rhythm disturbance is observed directly in the atria. Also, the pathological focus can be located in the atrioventricular septum. Incorrect heart activity is manifested in additional cardiac abbreviations.
The incidence of supraventricular arrhythmia is 65% on average. Such a high incidence is due to the fact that this form of arrhythmia is often observed in clinically healthy people.
The disease is mainly diagnosed in the elderly and adolescents, although it often happens that arrhythmias develop on the background of cardiac pathologies in infancy.Asymptomatic manifestations are mainly determined during the examination of infants or prophylactics of the able-bodied population.
Description of supraventricular arrhythmia
Nadjulyochkovaya arrhythmia (NZH) is still defined as atrial or supraventricular. The source of extraordinary contractions is located in the atria, that is, over the ventricles, hence the name of the pathology.
The basis of NHA formation is the formation of a pathological focal point of trigger activity, which sends periodic extraordinary impulses. In some cases, an electrical signal is transmitted by the atrium or atrioventricular node through the reentry mechanism, then a cyclic propagation of the pulse is observed, leading to acceleration of cardiac activity.
Development of supraventricular arrhythmia can occur on the background of cardiovascular diseases, which is characteristic of the elderly, or without visible clinical signs during the formation of the organism, that is, children and adolescents.
If the pathology is associated with other cardiovascular disorders, then it is important that the cardiologist undergoes regular examinations. Otherwise, it will be necessary to know what is dangerous to supraventricular arrhythmia, on their own experience.
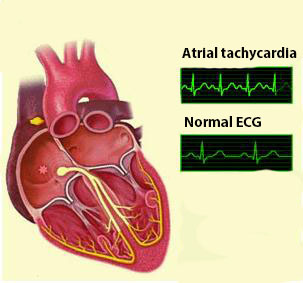
Symptoms of supraventricular arrhythmia
The following common manifestations are characteristic of all species of NSA:
- failures in cardiac activity in the form of rhythm rhythm (tachycardia), rhythm interruptions (extrasystoles) or rhythm (bradycardia);
- discomfort in the sternum;
- feeling heartbeat or turning the heart into your chest, jumping from chest.
Further to the given symptoms are added specific for the main illness of manifestation. With neuroses, panic attacks, or vegetosulmonary dystonia, it may be excessive sweating, a feeling of heat in the body, irritability, the appearance of fear of death and anxiety. Cardiac insufficiency feels weakness, dizziness, cardiac arthritis (cardiac pain). For hypertension characterized by an increase in blood pressure, noise in the ears, "knocking in temples."
Only a physician can make a sound justification for involvement of supraventricular arrhythmia in one or another disease.
Asymptomatic neovascular flow is mainly associated with functional disorders. These may be the same VSD or neuroses.
In particular, arrhythmias that arise in the following cases should be distinguished:
- With hormonal disorders (during pregnancy, climacterism, adolescents), arrhythmia is observed both at rest and in physical or emotional stresses. Also, the thyroid gland pathology, the bronchopulmonary system may contribute to heart failure.
- After the abundant food, the parasympathetic nervous system begins to predominate, and, with its activity, a heart failure occurs. The condition worsens when you receive a horizontal position immediately after eating.
Appealing to a doctor should be not only with pronounced supraventricular arrhythmia. When determining the asymptomatic course of the disease, it is also necessary to undergo periodic examinations of the cardiologist or arrhythmologist.
Causes of supraventricular arrhythmia
It has been noted above that in the development of arrhythmia, the provocative factor that can have a functional or organic origin is played by the primary role.
Functional reasons:
- autonomic dysfunction;
- excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeine-containing beverages;
- unnormal work schedule with insufficient rest;
- hormonal disorders (most often in women and adolescents);
- infectious processes accompanied by high temperature.
Organic causes:
- heart defects;
- myocarditis and endocarditis
- postoperative disorders;
- traumatic heart disease;
- tumor processes located in the heart area;
- pulmonary heart developed against a background of pulmonary hypertension.
Some metabolic disorders, in the form of a lack of potassium, magnesium, and renal insufficiency, can also contribute to the development of NSAIDs.
The use of cardiac glycosides, sympathomimetics, theophylline and antiarrhythmic drugs in the wrong dose can cause supraventricular arrhythmia.
The presence of a hypoxia in a patient, which is commonly encountered with anemia, heart failure and bronchopulmonary disease, may be affected by cardiac arrhythmias with localization in the atria.
Classification of supraventricular arrhythmia
The pathology is quite variable, so it is divided into three types according to the nature of manifestation: tachycardia, bradycardia, extrasystole.
All extrasystoles differ in frequency, localization and number of ectopic focuses, as well as at the time of the onset of an attack.
Frequency
The frequency of premature abbreviations that are considered in one minute divides all extrasystoles into:
- unitary - the extrasystole number is not more than five;
- paired - ECG shows two extrasystoles located one after another;
- group - premature contractions go a few times;
- multiple - defined by more than five extrasystoles.
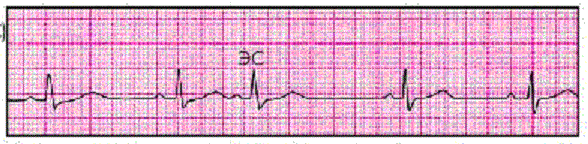
By localization of the focal point
It can be determined directly in the atrium or atrioventricular node. In any case talk about supraventricular arrhythmia.
Atrial arrhythmias are localized in the corresponding department of the heart
Atrioventricular arrhythmias are characterized by the location of an ectopic focal point in the septum located between the atrium and the ventricles.

By the number of foci
When determining with the help of special methods of research of one ectopic focal point, speak of monotonous extrasystoles.
The presence of two or more pathologic foci indicates polyclonal extraordinary cardiac contractions.
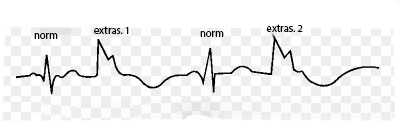
By the time of occurrence
The ECG determines the time interval in which an extraordinary reduction is performed. There are three types of extrasystole, differing in time of formation:
- early - occur at the time when the atrium is reduced;
- interpolated - the location of the localization is at the intersection of the contractions of the atrium and ventricles;
- Late - characteristic for the period of reduction of ventricles, can also be formed during the relaxation of the heart (in diastole).
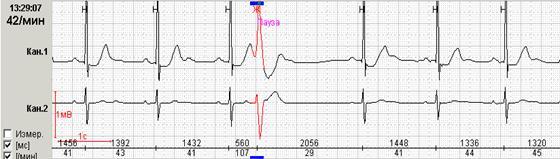
Diagnosis of supraventricular arrhythmia
Electrocardiography - is one of the main methods of studying patients with arrhythmia. Provides detailed data on the nature of rhythm disturbance, the location of the focal point, the frequency of cardiac contractions. The research takes a little time - up to 10 minutes. The safety of the study is very high, so it is allowed to spend it from one month.
ECG decoding allows to reveal practically all forms of supraventricular arrhythmia, the number of focal points, their localization, the time of occurrence of the extracystal. The wide availability of this method of diagnostics makes it indispensable for medical examination and prophylactic examinations, during which a large part of NSA is determined.
Major ECG signs of supraventricular arrhythmia:
- changed tooth P, in the figure it is shown negative, may also be two-humped or otherwise deformed;
- the distance between RR is different, may decrease or vice versa increase;
- Cardiac heart rate is most often increased, more than 100 times per minute.

Daily ECG monitoring - is to apply sick sensors in the breast region that are connected to the recording device. The goal is to write a heart rate for a day or a few days and then decode it using special programs. This makes it possible to detect rare attacks that may not be detected on a standard ECG.
Echocardiography is a modern diagnostic method that works on the basis of ultrasound. When using echocardiography, the organic and functional state of the heart and blood vessels is evaluated. For example, using an ultrasound, the thickness of the atrium is determined, which in the normal state on the left side should be no more than 4 cm.
Treatment and prognosis for supraventricular arrhythmia
In the case of asymptomatic current or in a patient with minimal discomfort, no specific treatment is performed. In such conditions, it is enough to adhere to a healthy lifestyle and eat properly, so that there is no aggravation of the flow of arrhythmia. If the pathology gives the patient a psychological discomfort, then antiarrhythmic drugs can be prescribed - sotalol, amiodarone, propafenone.
In severe cases, when arrhythmia is not corrected by medication, they resort to surgical treatment. The following types of operation can be performed:
- Implantation of the pacemaker - shown with weakness of the sinus node, when the atrium can not be fully reduced or impulse is created chaotic;
- implantation of the defibrillator - is established at prolonged tachycardias, not stopped by medical preparations;
- radiofrequency ablation - is a minimally invasive operation, which in some forms of arrhythmia helps to get rid of pathology by 100%. In particular, good efficacy from RFA is observed in the WPW syndrome.
Prophylaxis of supraventricular arrhythmia
There are certain principles for the prevention of rhythm disturbance, which apply to all forms of arrhythmia, including supraventricular;
- Proper nutrition - should consist of non-lean varieties of meat, fish, in the diet should include a sufficient amount of plant products.
- Physical activity - should be at the level acceptable for the patient so that the heart is supplied with enough oxygen and nutrients.
- Maintenance of indicators of glucose and total cholesterol in the blood within the normal range. Also, the mass of the body should correspond to the age and physiological norms.
Video Therapy of extrasystoles and supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
