What is infectious pericarditis
Author Ольга Кияница
2019-02-28
Infectious pericarditis (PI) is an inflammation of the infectious origin of the serous membrane, which consists of visceral and parietal sheets and fits the heart. The disease can occur acutely or chronically, and in some cases there is a recurrence (renewal) of the pathological process.
According to the International Classification of Diseases 10 revision (ICD-10), infectious pericarditis corresponds to code I30.1.
Examination of patients with infectious pericarditis is almost the same as with other cardiovascular diseases. The only thing that is of particular importance is the determination of the pathogen that caused the pathology, since, as a result, more effective treatment may be prescribed.
Video: Pericarditis
Description of Infectious Pericarditis
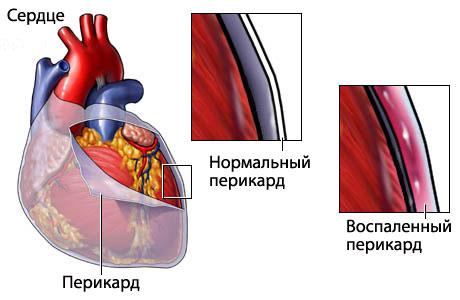
The pericardium is anatomically a thin layer that surrounds and protects the heart from external damage. Inflammation of this serous layer leads to pericarditis and if any infection is the main cause, then infectious pericarditis is diagnosed.
Infectious pericarditis varies due to illness. Most often, the following forms of PI are distinguished:
- Parasitic
- Bacterial
- Viral
- Fungal.
This classification allows you to subsequently conduct a more targeted treatment, which gives the best results.
Additionally, by the nature of the course, infectious pericarditis can be acute, chronic or recurrent.
- Acute pericarditis lasts no more than 6 weeks and, depending on the amount and nature of the pericardial effusion, is dry (fibrinous) and exudative. In the latter case, pus, blood, or fibrinous inclusions can be determined, then they speak of purulent, hemorrhagic, or serous-fibrinous pericarditis, respectively.
- Subacute pericarditis lasts from 6 weeks and not more than 6 months. Its characteristics are the same as those of acute pericarditis.
- Chronic pericarditis . Its duration is from 6 months. He, like acute, may be exudative, but additionally allocate more adhesive and constrictive pericarditis.
- Recurrent pericarditis . Re-develops after previously cured pericardial inflammation.
There are still non-inflammatory forms of pericarditis, like pneumopericardium, hydropericardium, hiloperikard and hemopericardum, but they are not so characteristic of infectious pericarditis.

Features of the development of infectious pericarditis:
- May develop due to invasion of protozoa, such as malarial or amebic pericarditis.
- Parasitic pericarditis is most often caused by echinococcus.
- Bacterial pericarditis are specific and nonspecific. An example of the former is tuberculous and syphilitic pericarditis, the latter is various bacterial pericarditis, mainly cocci.
- Non-bacterial infectious pericarditis are rickettsial and viral diseases, mainly developing against the background of influenza, infectious mononucleosis, etc.
- Fungal infectious pericarditis is most often associated with candidiasis and actinomycosis.
The pathogen can enter directly into the pericardial cavity, but if it is present in the body, infectious-allergic reactions can be triggered and if the link between allergization and the microbial pathogen is proven, then they also talk about infectious pericarditis. An example of this condition is rheumatic pericarditis.
Infectious pericarditis: symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease mainly depends on the etiological factor, that is, the pathogen. The main distinctive features will be given for bacterial pericarditis, viral pericarditis, parasitic pericarditis.
Common signs of infectious pericarditis:
Fever (characteristic of infectious diseases by type of flu). A fever over 38.5 ° C often indicates a more serious infection (for example, tuberculosis, a bacterial infection).
2. Pericardial friction noise (a symptom characteristic of pericarditis). Its main characteristics:
a. Rarely heard with pericarditis, despite the fact that it occurs in 85% of cases (usually transient forms of pericarditis)
b. Determined by a high-pitched, creaky or crisp sound, like when walking through the snow.
c. Auscultation of the left border of the chest with the patient leaning forward and holding the breath allows us to distinguish pericardial friction from pleural friction.
d. In the presence of a pericardial effusion, pericardial friction is almost inaudible.

Additionally, distant heart sounds can be detected. With the development of cardiac tamponade, a symptom of Kussmaul, paradoxical pulse (pulsus paradoxicus), expansion of the jugular veins is detected. Children may have more delicate signs (eg, eyelid swelling, sinus tachycardia).
Clinic of viral pericarditis. Most often develops within a few weeks after the determination of respiratory or gastrointestinal syndromes. Sometimes symptoms appear during the course of an infectious disease itself. A viral PI manifests itself with the common symptoms indicated above. Additionally, the detection of cardioselective enzymes in the assays may indicate a Coxsackie B virus.
Clinic of bacterial pericarditis . Symptoms most often appear with lightning speed, their duration is short. Additionally determined by the clinic of the main acute infectious disease. If, against the background of a bacterial infection, acute purulent pericarditis develops, then the following symptoms are determined:
- Temperature above 39 ° C.
- Frequent pulse.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Feeling unwell.
- Pain and tightness in the region of the heart.
If a pericardial effusion significantly disrupts the heart, then the patient's cyanotic lips, marked shortness of breath and a rare decrease in blood pressure can be determined.
Video: Histopathology Heart --Pericarditis, bacterial
Infectious pericarditis: treatment
Effective therapy for the elimination of infectious pericarditis, as a rule, is applied taking into account the etiological factor.
General principles of pericarditis therapy
When determining the symptoms of an infectious pericarditis patient, it is desirable to lay with a raised head. It also requires access to fresh air, so if possible, indoors open windows or doors. Additionally, before the arrival of the doctor or ambulance, it is advisable to measure blood pressure, calculate the pulse.
In the conditions of a medical institution in such cases the following actions are performed:
- The head end of the bed is raised.
- Provide access to humidified oxygen.
- Conduct cardiac monitoring.
- Pulse oximetry is performed.
- Do intravenous access.
In an unstable condition, the patient is provided with emergency care in the form of pericardiocentesis , which is done by an experienced doctor. In the absence of the proper effect, subsyphoid pericardial drainage and biopsy areperformed, followed by histology and bacterial examination.
Indications for pericardiocentesis:
- Suspected bacterial pericarditis.
- Tamponade of the heart.
Treatment of infectious bacterial pericarditis
For purulent bacterial pericarditis, empirical antibiotics are usually prescribed. Then, pericardiocentesis is performed and the fluid taken during the study is examined for bacterial microflora and drug sensitivity.
First-line antibiotic treatment (drugs are used together):
- Vancomycin
- Ceftriaxone or
- Cefepime
An alternative combination of drugs is the scheme of vancomycin and ciprofloxacin.
Treatment of infectious viral pericarditis
Anti-inflammatory drugs are primarily used, to which, depending on the cause of the disease, specific drugs can be added.
- When cytomegalovirus pericarditis is most often used: hyperimmunoglobulin.
- Pericarditis caused by the Coxsackie virus is mainly treated with interferon-α, which is injected subcutaneously.
- Perimiocarditis caused by adenovirus or parvovirus is eliminated with immunoglobulin.
It is important to remember that the lack of treatment for infectious pericarditis significantly increases the development of complications, and in some cases mortality. In particular, with bacterial infectious pericarditis, mortality is 100%.
Conclusion
Specific prophylactic measures of infectious pericarditis are absent; therefore, it is necessary to adhere to general recommendations on general hygiene, strengthening immunity and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This will not get any infection, and thus avoid the development of pericarditis.
Video: Pericarditis - Overview (signs and symptoms, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment)
Similar articles
With many diseases associated with infection, allergies, or autoimmune reactions, pericarditis develops which can have acute and chronic flow. In case of timely treatment for health, there is no danger. In a number of cases it may be complicated by adhesions and other pathological conditions.

Different forms of pericarditis can develop in different ways, but purulent pericarditis is noted the most unfavorable course. When it is high risk of mortality, especially in the absence of timely treatment. Therefore, operative diagnosis with subsequent thorough therapy is extremely important.

Pericardial inflammation can occur at any age. This pathology is often secondary to another active disease. There are certain differences between pericarditis in children and adults, so the characteristic features of children's pericarditis will be noted in the material.

