Neurological arrhythmia
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-01-18
"All illnesses from nerves" is a well-known saying. And it is not groundless, because the nerve endings are suitable for all organs without exception. Especially sensitive to various types of nervous disorders heart. At strong stresses and emotional stresses it is possible to disrupt its activity and well if everything is formed independently. But in some cases there are neurological arrhythmias that cause tangible discomfort to the person.
In quite healthy people, a few arrhythmias may occur a day. But at the same time, they do not cause any change in the general condition of a person.
Some people have such a psyche that is particularly susceptible to various nervous disorders. Insignificant stresses or experiences make them grasp for the heart. Someone may think that it is nicer. In fact, a person starts an arrhythmia attack and in such cases appropriate help should be provided. Moreover, such a condition can be observed not only in the elderly, but also in young people.
Video Arrhythmia: If I am young, then I can not have arrhythmias?
Description of neurological arrhythmia
Arrhythmia should be understood as a violation of the rhythm, which differs from normal sinus. In healthy condition, it is expressed in the frequency of heart rate in adults from 60 to 90 times per minute, as well as a regular and regular wave of cardiac contractions. If the heart is affected by adverse factors, then the rhythm and frequency are violated and arrhythmia is observed.
By the nature of the severity of arrhythmia, both frequent and rare can be, with an increase or vice versa, a decrease in the frequency of cardiac contractions.When involvement in the pathological process of the conductive system may be blockade of cardiac activity.
The key mechanism of the development of arrhythmias is a violation of the basic functions of the heart: the pulse, the reduction of the myocardium, the excitation and refractoriness of cardiomyocytes. Since the heart abundantly innervates, the increase and decrease in the heartbeat is often associated with the activity of certain nerve fibers:
- wandering nerves slow down cardiac activity;
- The sympathetic nervous system amplifies the ejection and rhythms take on.
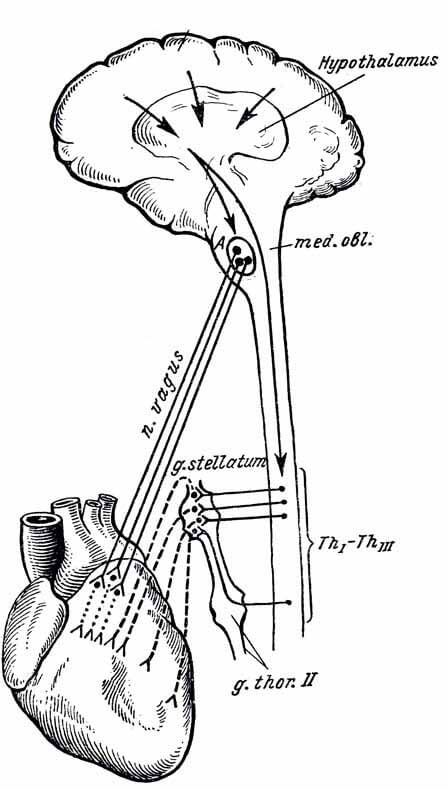
The effect of wandering and sympathetic nerves is interconnected, so when excited first, the activity of the second and the other is reduced.
Symptoms of neurological arrhythmia
Mostly in patients with neurological arrhythmia, symptoms occur suddenly, several times a day, or from time to time. Often, the symptoms of the disease are presented in the following sequence:
- palpitations appear;
- there are interruptions in the work of the heart;
- weakness is felt;
- the heart "jumps out of the chest";
- "Darkens" in the eyes.
Against the background of such feelings, fear develops for their health and life in general, so patients turn to the cardiologist. In fact, such conditions are treated by cardiologists in conjunction with neurologists. Only then can a positive result be achieved in the treatment of neurological arrhythmia.
In 50% of patients with neurologic arrhythmias, there is a disturbed perception of reality when a person indicates, for example, a high-speed pulse, but when checked, such a violation is not determined.
A constant feeling of fear introduces a person into depression. The patient may close in and become little contact. If he still managed to get to the doctor for a reception, then his experiences describe colorfully and as much as possible in detail. In general, arrhythmia brings more psychological discomfort than physical. In the presence of serious disorders associated with organic pathology, neurological arrhythmias arise from the type of fibrillation or flickering that present a hazard to humans.
Causes of neurological arrhythmia
The emotional state of a person directly affects the work of the heart. Under the action of emotions, special vascular nerves change the lumen of the vessels. Therefore, any physical states (fear, anger, intensified work) or pathological disorders of the nervous system (neuritis, neurosis, neuralgia) lead to a change in the activity of the heart.
Neurologic arrhythmia occurs in many diseases associated with the nervous system and, first of all, with the brain:
- acute cerebral pathology (stroke);
- craniocerebral trauma;
- infectious diseases of the nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis);
- tumor processes in the brain;
- autonomic polyneuropathies, often developing against the background of alcoholism and diabetes mellitus.

Neurological arrhythmias may be the first sign of developing epilepsy. With this disease in the brain are formed centers of excitation, which activate the work of cardiac activity. Since seizures of epilepsy occur periodically, on its back, arrhythmia also develops from time to time, but this does not mean that the pathological condition is not dangerous.
Types of neurological arrhythmia
The disease manifests itself in various cardiac rhythm disorders. It all depends on the severity of the pathological process.
- If arrhythmia is associated with organic damage to the brain or conductive system of the heart, then there is a blockade of the heart, fibrillation of the ventricles and tremor / flickering of the atrium. Each of these forms of arrhythmia presents a danger to a person as there is an increased risk of heart failure. Independent resolution of these conditions occurs in very rare cases, so it is best to seek medical attention in a timely manner.
- Disorders of cardiac function of functional origin are most often associated with an emotional state of a person. On the background of emotions, stress, after physical or psychological tiredness, sinus or paroxysmal tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, extrasystole develop most often. These conditions are not considered to be dangerous in themselves, but with their regular and prolonged occurrence, they should contact the cardiologist to thoroughly diagnose the cardiovascular system.
Diagnosis of neurological arrhythmia
Any violation of heart rhythm must be confirmed by the conclusion of an electrocardiographic examination. For each type of arrhythmia specific ECG signs are characteristic:
- sinus tachycardia manifests sinus, right rhythm and heart rate more than age norm;
- sinus bradycardia - sinus, right rhythm and heart rate less than age norm;
- paroxysmal tachycardia - heart rate more than 150 times per minute, the presence of sudden attacks, the ECG is similar to the extrasystoles that go one after the other;
- cardiac blockades - conduction retardation, determined at the level corresponding to the location of the focal point of the defeat, the severity of the pathology is estimated by the occurrence of complexes;
- Atrial flutter is a non-sinusoid rhythm on a F wave background with the same frequency and amplitude, heart rate is up to 350 times per minute;
- atrial flickering - the nonsusoid rhythm is accompanied by the appearance of the wave f and heart rate more than 350 times per minute.Unlike flutter, atrial fibrillation has an irregular ventricular rhythm.

In addition, X-ray, magnetoresonance, and ultrasound studies can be performed to help carry out a comprehensive examination of the patient to identify the underlying cause of the development of not only neurological arrhythmia, but also the underlying disease that caused the autonomic autonomic nervous system dysfunction.
Treatment and prognosis for neurological arrhythmia
Today, neurocardiologists are practicing the appointment of vegetarian correction therapy, which often helps to normalize the balance of the autonomic nervous system. In particular, it is used:
- anaprilin - with sinus tachycardia, supraventricular extrasystole, supraventricular ectopic tachycardia;
- Bollatamine - with sinus bradycardia, sinatrial and atrioventricular blockages.
Drugs reduce the incidence of arrhythmias, reduce the subjective manifestations of the disease. With the use of drugs in patients with organic brain damage, an improvement in the quality of life is observed.
In order to restore electrolyte balance, panangin is prescribed, which proved to be effective in many studies. Today, with the help of this drug quite a good way to get rid of neurological arrhythmias.
To eliminate depressive and asthenic disorders, fluoxetine or alprazolam is used.
In the presence of epilepsy, appropriate therapy is prescribed, which helps to reduce the severity of the attacks or reduce the number of their occurrence. Effective treatment of epilepsy is the main way of preventing the development of rhythm disturbances.
Neurologic arrhythmias in most cases do not present life threats, but can significantly reduce the quality of life. Therefore, one should not neglect even minor symptoms of the disease.
Prevention of neurological arrhythmia
It is concluded in the prevention of the development of psycho-emotional stresses, which are often exposed to modern people. If there is an organic damage to the nervous system or a brain injury, then for preventive purposes it is necessary to take appropriate medicines. Especially cautious in terms of arrhythmia, you need to be ill with epilepsy, since with this disease most often arises neurological arrhythmia.
Arrhythmia or heart rhythm disturbance
Similar articles
With intercostal neuralgia the patient is most concerned with pain, which can be sharp, shooting, sharp, sufficiently pronounced and often troubling. As a rule, the definition of this sign lies at the basis of diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia. The strategy of treatment is mainly aimed at eliminating pain, which allows you to quickly improve the patient's condition.
Neuralgia can occur for various reasons, among which the greatest role is given to heart disease. But in some cases, the presence of cardialgia is not confirmed, and doctors start talking about intercostal neuralgia. Are there any differences between these two conditions, which are quite similar in their clinical signs?
Relatively rare is a disease such as intercostal neuralgia. If, however, it has arisen, you need to think about the proper treatment that will help improve the condition and, first of all, eliminate the painful sensations. Otherwise, the patient significantly deteriorates the quality of life and possibly the development of other complications, including arrhythmias.
