Atrial fibrillation
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-01-18
Arrhythmia is today determined by many people, since rarely a modern person is not exposed to stressful situations, emotional-psychological stresses. There are forms of rhythm disorder, such as sinus arrhythmia, which are not dangerous to humans, when they are detected, rarely requires specific treatment. But other arrhythmic states are not so harmless.
What is the risk of atrial fibrillation? First and foremost, a possible cardiac arrest, because with the increased contractility of the atrium, ventricular activity also suffers. Therefore, it is important to know in which cases medical assistance may be required due to the pathological condition that has arisen.
Description of atrial fibrillation
Fibrillation should be understood as a frequent contractile activity, when the whole heart or its parts are excited by uncoordinated, chaotic impulses. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a definition of heart rate greater than 150 per minute, with the pathological focus of excitation located in the atria. In such cases, the supraventricular tachycardia is 250-700 beats per minute, and the ventricular mellitus is a bit less - 250-400 beats per minute.
At the heart of the onset of fibrillation of the atrium is the cyclic transmission of the pulse. Due to the influence of various factors (infarction, ischemia, infection)
In the muscular tissue of the heart, areas with a disturbed conducting system are formed. The more they are, the higher the risk of developing fibrillation. If the impulse enters such a site, it can not be transmitted further, therefore it returns and leads to contractility of already passed cardiomyocytes.
Normal pulse transmission

Atrial fibrillation
In some cases pathological foci of heart cells are created, which themselves begin to generate a pulse. If there are many such foci, the work of the heart becomes uncoordinated and chaotic. No matter how the pathological impulses are created in the atria, they do not fully reach the ventricles, so the latter do not contract as quickly as the atrial portion of the fibers.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
Clinical picture is more dependent on the severity of hemodynamic disturbances. In the absence of them, the course of the disease may be asymptomatic. Severe manifestations can cause irreversible consequences leading to heart failure.
The episodes of atrial fibrillation, expressed in paroxysms, may be accompanied by:
- pain in the chest;
- frequent heartbeat;
- rapid urination.
The occurrence of shortness of breath, dizziness, weakness points to the evolving adequacy of cardiac activity. In severe cases, semi-impaired and abnormal states are observed.
Pulse deficiency is one of the features of fibrillation. If a heartbeat is heard at the top of the heart, then when it is compared with the pulse on the wrist, the deficiency of the ripple is determined. This is due to insufficient ventricular ejection of the left ventricle, despite frequent heartbeat.
Thromboembolism , often expressed as a stroke, may be the first sign of atrial fibrillation in those patients who did not complain or perceived rare attacks of paroxysm.
Reasons for the appearance of atrial fibrillation
In most cases, AF develops against the background of cardiovascular diseases. The first place is arterial hypertension, which contributes to the formation of pathological centers that generate extraordinary impulses. A significant influence in the development of arrhythmia is caused by heart failure and acquired heart defects, in which hemodynamics is substantially impaired.
Children may also develop atrial fibrillation. The reason for this are congenital malformations - one ventricle, a defect of the interstitial septum, operations associated with the plastic of the valves.
In diseases such as cardiomyopathy and ischemic heart disease, areas with a disturbed conducting system are formed in the cardiac muscle. As a result, electric impulses are not transmitted fully, but cyclic centers of excitation are formed. A large number of such foci contributes to clinically unfavorable atrial fibrillation.
Among young people in 20% -45% of cases, depending on the type of AF, the pathology develops without cardiovascular disorders.
Of non-cardiac factors that play a role in the development of AF, hyperthyroidism, chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obesity are released. Also, studies confirmed the risk of heredity AF, as 30% of the parents surveyed were ill with this pathology.
Video Fibrillation of the atrium, the main causes
Types / photos of atrial fibrillation
By their characteristics, supraventricular fibrillation is divided into five forms: first detected, paroxysmal, persistent, long-persistent and persistent. EHRA classes are also distinguished from the first to the fourth.
Forms of atrial fibrillation
For the first time, the identified and constant varieties of FP are understood from the names, while others require clarification.
Paroxysmal AF - develops suddenly and lasts no more than 48 hours, but by definition this form of AF can last up to 7 days. In this violation sinus rhythm is restored independently.
Persistent AF - an attack also occurs suddenly and lasts more than 7 days.
Long-lasting persistent form is observed in the patient during the year and for the normalization of the state a decision is made on the choice of the method of treatment (as a rule, cardioversion is used).

Types of atrial fibrillation
They were presented by various European public organizations, as well as by the American Cardiology Association. The basis for the classification of the four types was the number of cardiac contractions:
the first type of normosynthesis (heart rate 60 to 90 in min.);
the second is bradysystolic (heart rate less than 60 in min.);
the third - tachysystolic (heart rate more than 90 in min.);
the fourth is paroxysmal (heart rate 150 per minute and more).

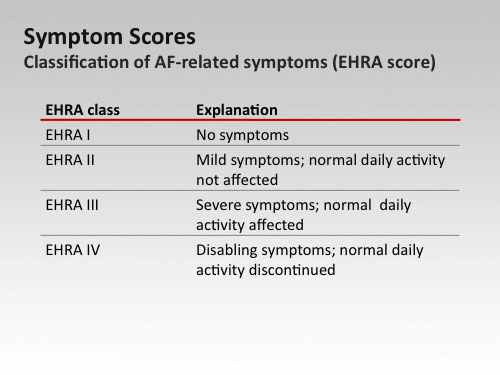
Clinical classification EHRA
It was proposed in 2010 by the European Society of Cardiology. The severity of the signs of the disease formed the basis of the clinical classification, according to which distinguishes four classes of gravity of the process:
I - symptoms are not determined;
II - the patient carries a habitual way of life, although he notes slight signs of illness;
III - the patient's ability to work is impaired due to the pronounced clinic;
IV - severe organic changes have led the patient to a disability.
Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation
Most patients are treated with typical complaints in the clinic to the district doctor. If they are not present, but there are suspicions of AF, other important data about the patient are collected:
- when an attack was observed for the first time;
- how long did he last;
- if treatment was previously performed, the drugs received and their efficacy are clarified.
During the examination of the patient, it can be determined: a pulse deficit, high blood pressure, palpitation at frequent hearing, muffled heart tone. Subsequently, additional research methods are assigned and the first thing is electrocardiography.
ECG signs of atrial fibrillation:
- the tooth R on all leads is absent;
- the waves of fibrillation f are determined;
- There are different distances between RRs.
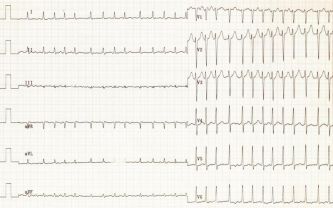
If there are signs of fibrillation, but they could not be fixed on a standard ECG, then Holter monitoring was carried out.
Echocardiography - is done to detect organic disorders. This may be valve malformation or a recent myocardial infarction, "worn on legs". Also, with the help of Echo-KG, the size of the atrium is determined, which in the event of a pathology may be disturbed. This diagnostic method allows you to "see" the thrombotic formation in the atria of the ears, although this pathology provides more information to the transfusional Echo-KG.
Roentgenography of the organs of the chest - helps to determine the expansion of the heart chambers, to assess the condition of the main vessels.
Blood tests, which determine the level of the main hormones released by the thyroid gland (triiodothyronine, thyroxine) and the pituitary gland (thyroid stimulating hormone).
Complications of atrial fibrillation
Acute heart failure - develops in the presence of a patient other than a patient with a cardiovascular pathology. If the patient does not have a concomitant pathology, then no sharp violations are observed.
Ischemic stroke - develops as a result of the entry of blood clots from the left atrium into the vessels of the brain. The complication arises with a frequency of 6% per year, while more concerned with patients with non-rheumatic pathology. Therefore, it is very important to carry out the prevention of thromboembolism by appropriate treatment.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation
The key areas of AF therapy are the following:
- Control of cardiac rhythm - carry out the restoration of sinus rhythm, and then support its prevention of relapses.
- Control of heart rate - fibrillation is preserved, but with the help of medications, the heart rate rises.
To prevent thromboembolism, anticoagulant treatment is used.
Control of heart rhythm
The sinus rhythm is restored in two ways:
- Electric cardioversion is a rather painful procedure, but it is effective. For analgesia, sedative substances are administered, or general anesthesia is performed. Cardioverter defibrillators are two-phase and single-phase. The first ones are more powerful and therefore provide a smaller discharge if the desired result is more quickly achieved. Single-phase devices supply a smaller discharge, so high energy is used to achieve the desired effect.
- Pharmacological cardioversion - based on the use of antiarrhythmic drugs in the form of amiodarone, nibentan, procaineamide, propafenone.
If the patient has a tachysystolic AF, then the heart rate is reduced to 100-90 times per minute. For this purpose, the tablets of metoprolol (beta-blockers) or verapamil (calcium antagonist) are used. In order to prevent thromboembolism, warfarin (an indirect anticoagulant) is prescribed, which is taken both before and after the procedure for three to four weeks.
Heart rate control
It is based on the use of medical products, with which the heart rate drops to 110 per minute in a calm condition. Drugs are taken from different treatment groups and combined in treatment regimens.
- cardiotonics (digoxin);
- calcium antagonists (verapamil, diltiazem);
- blockers of beta-adrenergic receptors (carvedilol, metoprolol).
Amiodarone is prescribed in the event of ineffective treatment with the above drugs. It has a pronounced antiarrhythmic action, however, it should be prescribed with caution to persons under the age of 18 years, the elderly, during pregnancy and the presence of concomitant pathology in the form of bronchial asthma, hepatic and chronic heart failure.
Radiofrequency catheter ablation
It is conducted with the purpose of relieving the patient's condition in the absence of the effect of medication therapy. There are various techniques for conducting surgical intervention:
- The ablation of the lining of the lining of the lungs is effective in 70% of cases, although it is not sufficiently studied for the widespread use.
- "Labyrinth" - effective in 50% of cases, is carried out with the aim of creating the only way to pass the electrical signal. The methodology is in the process of studying.
- The ablation of the pathological focus and AV of the compound - conducting effectively in 50%, with the ablation of the AV node is justified in the case of chronic AF.
- Surgical intervention in the open heart - it is expedient to treat AF in case of operation due to other cardiovascular pathology.
Video Fibrillation of the atrium
Emergency aid for atrial fibrillation
First, intravenous isoptin is administered. If the attack is not stopped, a mezaton with novocainamide is introduced, while the arterial pressure and electrocardiogram are controlled (ventricular broadening is a sign of discontinuation of medication administration).
Emergency care uses beta-blockers (obzidan) and ATP (most often with nodal forms). It is also possible to present in the form of a table the choice of the drug in order to stop the AF attack.
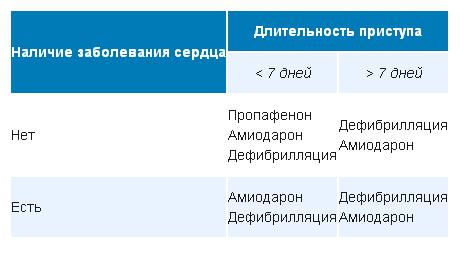
Propafenone should be taken for the first time only under medical supervision, as it is possible a sharp drop in blood pressure.
Lack of results from the use of medications pushes for cardioversion. Other indications for the procedure are:
- the duration of fibrillation is 48 hours or more;
- The patient has hemodynamic disorders in the form of low pressure, decompensated form of heart failure.
An anticoagulant of direct action is obligatory - heparin (low molecular weight or non-fractional).
Secondary prophylaxis of atrial fibrillation
Prevention of the development of relapses of the disease is called secondary prevention of AF. Based on various studies, it was determined that the correct cardiac rhythm persists for one year on average in 40% of patients. The athletes tend to remember arrhythmias, so you need to put a lot of effort to prevent their return. First of all, the following recommendations should be followed:
- It is necessary to carry out therapy of basic diseases complicating the course of fibrillation.
- To take antiarrhythmic drugs and correct them in time when reducing the effectiveness of treatment.
- To refrain from taking alcohol, because every 10 g taken daily increases the risk of myocardial infarction by 3%.

Video Fibrillation of the atrium
Similar articles
First of all, the wrong rhythm is translated into sinus. For this purpose, an electrical or medicinal cardioversion is used with such drugs as propafenone, amiodarone, nibentan, procaineamide. Next, doctors choose one way out of two possible – control of heart rate while maintaining arrhythmia or strategy of rhythm control. In the treatment of atrial fibrillation, anticoagulant therapy is important, which helps to avoid thromboembolism of the arteries of the internal organs and the brain. If medical treatment proved to be ineffective then radiofrequency ablation is used. Cryoablation is also practiced. Antirecurring treatment is based on beta-blockers (metoprolol, bisoprolol, and carvedilol).
