Systolic arrhythmia
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-10
In the normal state, the heart cycle consists of alternating periods: systoles (contractions) and diastoles (relaxation). During the diastole of the atrium, blood from the vessels comes into them, then their contraction (systole) and the expulsion of blood into the ventricles occur. The latter are also filled with blood in the diastole from the atrium and further it is expelled during the systole into the circle of circulatory circulation.
The contractile capacity of the heart is evaluated precisely by its working capacity during the systole period, that is, by the fraction of the ejection. Normally, it is 55-70%
Systolic function is the ability of the heart, evaluated by measuring the ejection fraction. This indicator is determined by ultrasound diagnostics of the heart. If less than 40% is determined, then talk about systolic insufficiency
functions because the blood supply system receives less than 40% of the blood volume. This pathology is also known as heart failure with systolic dysfunction of the left ventricle. Systolic arrhythmia may also develop, is it dangerous if this state can be understood only by considering the subject presented in detail.
Video Heart Cycle
Description of systolic arrhythmia
Systolic arrhythmia is a change in normal cardiac activity, which is associated with the systole phase, most often the ventricles. In this disorder, there is an increase or decrease in heart rate with the appearance of clinical signs characteristic of arrhythmia.
Systolic arrhythmias are more susceptible to people after 60 years of age who have been diagnosed with ischemic heart disease or have other cardiac pathologies.
At the heart of the development of the disease are the mechanisms characteristic of arrhythmias. The first is a violation of the conduction function. With organic heart lesions, pulse pathways may change, resulting in a change in the ECG during the period of systole in the form of an extraordinary contraction (extrasystoles). Similar causes also contribute to an increase in the automatism of heterotopic foci and the amplitude of trace potentials. In addition, an uneven repolarization of the myocardium may occur, which is rather peculiar to the affected heart muscle in the coronary artery bypass graft.
Symptoms of systolic arrhythmia
For pathology practically all signs of violation of cardiac rhythm are characteristic. Mostly complaints are filed against:
- sensation of jerky blows in the region of the heart;
- increase or decrease in heart rate;
- autonomic disorders in the form of dizziness, sensation of weakness, increased sweating, anxiety.
If other diseases are associated with systolic arrhythmia, then their symptoms are added to the above symptoms. First of all, the violation of the rhythm often develops against the background of other cardiac pathologies. Therefore, the patient may have shortness of breath, heart pain, edema. A similar clinic is more pronounced in heart failure with dysfunction of the left ventricle.
Vegetative disorders can exacerbate the clinic's expressed sense of anxiety, reaching in some cases before a panic attack. Patients may complain of sticky sweat, weakness throughout the body, feeling tides or heat. Externally such manifestations can be expressed in excessive paleening or reddening of the face.
This type of arrhythmia is more characteristic of people of the age, therefore, among children occurs only in combination with congenital malformations or acquired severe cardiac pathology. It is difficult for children to explain that they do not, therefore, they can complain in the form of frequent knocking of the heart, "bad heart beats", etc.
Causes of systolic arrhythmia
The disease is most often associated with another cardiac pathology. The highest percentage of occurrence - with ischemic heart disease a. In this violation there is an organic lesion of the myocardium due to insufficient coronary circulation, which affects the work of individual departments or the heart as a whole.
Among other cardiac causes, it should be noted:
- heart failure;
- acquired and congenital heart defects;
- cardiomyopathy;
- infectious myocardial lesions.
External effects on the heart also play an important role in the development of arrhythmias. It may be incorrectly chosen dosages of drugs that enhance the ejection fraction - adrenergic agents, or vice versa, they weaken it - cardiac glycosides, antiarrhythmic drugs, diuretics.
Electrolyte impairment often causes arrhythmias, since the activity of the heart depends largely on the concentration of such trace elements in the blood as magnesium and potassium. Negatively affects the work of the heart as a lack of potassium and magnesium, and an excess of the first and excess of the amount of calcium in the blood.

With some diseases, the work of the heart increases with the possible development of systolic arrhythmias. First of all it concerns thyrotoxicosis, when the thyroid gland begins to intensively produce thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Systolic arrhythmia may also appear on the background of diabetes mellitus, as carbohydrate metabolism disturbs the functioning of many systems and organs, including the heart.
Types of systolic arrhythmia
The presented form of arrhythmia is not individually classified, but in clinical practice it is customary to distinguish between different types of changes in the frequency of heart rate. These may include tachycardia, bradycardia and extrasystoles.
Tachycardia
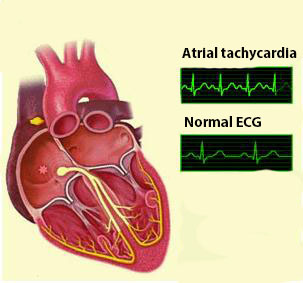
Characterized by an increase in heart rate more than 90 times per minute. Some patients do not feel the change in heart rate, but as a rule, people in the elderly are very sensitive, so for them, each rhythm disorder is a whole unpleasant event. Therefore, tachycardia is often transmitted in combination with head and heart pain, increased fatigue and weakness.
Tachycardia itself is not dangerous, but in combination with other disorders of cardiac genesis can lead to a number of serious complications - myocardial infarction, stroke, heart stops.
Tachycardia often develops after overeating. This is due to increased digestion, which contributes to the rise of heart rate. Also, physical activity can raise the number of cardiac contractions, but unlike the pathological state, the physiological tachycardia is normalized over time. Therefore, the presence of a heartbeat at rest is a terrible sign of severe organic damage to the heart.
Bradycardia
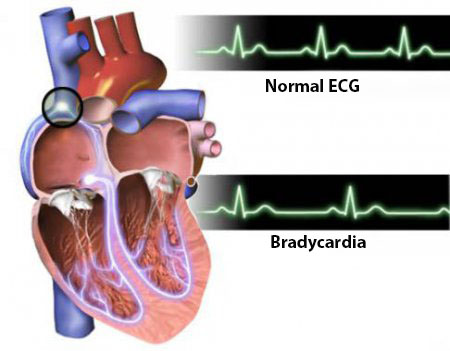
It is a sign of slow heart function and is determined by measuring heart rate, which, when bradycardia is less than 60 times per minute. Some people, most often athletes, are determined by physiological bradycardia. This option is considered a norm, because it does not cause a person's health problems.
Pathological bradycardia is characterized by a number of diseases, first of all - for heart failure. With this pathology, the left ventricle can not do the normal discharge of blood, which leads to the weakening of all vital functions of the heart.Therefore, systolic arrhythmia in the form of bradycardia can be one of the first signs of deterioration of the heart.
Extrasystole
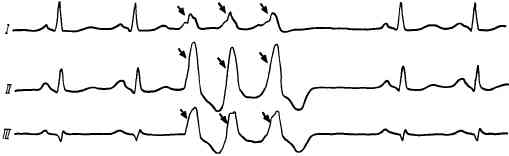
Disturbing heart rhythm is quite common for all age groups. It manifests itself as suddenly occurring interruptions of cardiac activity, sometimes accompanied by cramping pains or pressure in the region of the heart. Most often, especially in the case of young people and children, practically do not feel.
In the case of systolic arrhythmia, manifested in ECG in the form of extrasystoles, it can be noted that its development against a background of heart failure is also an unfavorable symptom. This may indicate the ongoing processes of myocardial lesions, which lead to the development of ectopic foci. Their occurrence often provokes premature contractions.
Diagnosis of systolic arrhythmia
The main diagnostic method for diagnosis of arrhythmias is electrocardiography . With its help can be defined as tachycardia, and bradycardia and extrasystoles.
Common ECG symptoms with sinus tachyardia and bradycardia:
- The teeth P are determined in front of each QRS complex, indicating sinus rhythm;
- the correct rhythm is observed in tachycardia and bradycardia, as indicated by the same RR interval;
- The heart rate with tachycardia is increased, with bradycardia reduced in comparison with the age norm.

Extrasystoles on the ECG show extraordinary contractions, which are divided, depending on the localization of the ectopic focus, on the atrial or ventricular.
Additional information on the condition of the patient is obtained through ultrasound examination of the heart, stress tests, daily monitoring. Laboratory tests are also performed on suspicion of hormonal disorders or electrolyte disturbances.
Treatment and prognosis for systolic arrhythmia
The first occurrence of an attack of systolic arrhythmia should alert the patient and his relatives, as the pathology can end with a number of adverse complications:
- atrial fibrillation;
- ventricular fibrillation;
- aggravating the course of the underlying disease, in particular heart failure.
How to help a patient during an arrhythmia attack?
- Soothe in the possible ways, for which it is worth helping to sit or lie comfortably;
- open the window and try to relax, breathing fresh air;
- drink water at room temperature, non-carbonated;
- take a soothing remedy (a few drops of tincture of honeysuckle, valerian);
- If an attack continues, call an ambulance.
Initially detected arrhythmia with the development of an acute clinical picture, which is not stopped using conventional methods, is treated in a hospital setting. This is necessary in order to prevent the above-mentioned complications.Therapy is organized on the basis of antiarrhythmic drugs, general strengthening agents, possibly using immunocorrectors.
How to treat heart arrhythmia?
Prevention of systolic arrhythmia
It is based on the use of therapy for the underlying disease. In addition, you must follow the general guidelines for the prevention of rhythm disorders:
- To lead a healthy lifestyle, with the abandonment of bad habits and rational balanced nutrition.
- Maintain a schedule of days in which the time for work and rest should be properly planned.
Avoid stressful situations, and in the event of anxiety or anxiety, do not wait for arrhythmia, and carefully take a sedative.
