What is acute vascular failure?
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-10-31
Acute vascular insufficiency (BCH) refers to critical conditions. May be leaky in the form of fainting, shock, collapse. In the occurrence of a pathological condition, various predisposing factors take part, but the disease has the same clinical picture.
In case of acute vascular insufficiency, a disproportion between the volume of the vascular bed and the volume of blood circulating in it is determined.
The standard treatment methods are used to cure acute vascular insufficiency, but then it is necessary to correctly determine the cause of the illness so that the serious consequences can be eliminated.Different research methods are used for this purpose.
Video Heart Failure. From what the heart is weakening
Pathogenesis of the disease
There are several mechanisms for the development of acute vascular insufficiency. Some of them are associated with organic lesions of the heart, others - with pathological conditions that could have arisen as a result of injury, burn, etc.
Causes of vascular insufficiency:
- Hypovolemia or circulatory vascular insufficiency is a reduced amount of circulating blood. Such is found in bleeding, severe dehydration, burning states.
- Vascular vascular insufficiency - the amount of circulating blood is increased. The vascular wall tone is not supported due to endocrine, neurohumoral, neurogenic effects. In case of incorrect administration of barbiturates, ganglion blockers may also develop vascular BPH. Sometimes there is a toxic effect on the vascular walls, the expansion of vessels due to excessive concentration in the body of biologically active substances in the form of bradykinin, histamine pr.
- Combined vascular insufficiency - the above factors are combined and have a negative effect on the functioning of the vascular bed. As a result, an increased volume of the vascular bed and an insufficient amount of circulating blood are diagnosed. Such a pathology is often found in severe infectious-toxic processes.
Thus, it turns out that the OSN occurs for a variety of reasons, and all of them, as a rule, relate to critical states or severe pathologies.
Types of acute vascular insufficiency
It was noted above that there are three main types of OSN - faint states, shock and collapse. The most commonly encountered group of vascular failure are fainting. They can occur at any age and are often associated not only with cardiovascular pathology, but also with the disregulation of other organs and body systems.
Fainting
They represent an extensive group of cardiovascular disorders. They can be defined as a mild degree, and more pronounced, even dangerous for a person.
Main types of syncope:
- Syncope or fainting - often associated with cerebral ischemia, when the patient suddenly fails. Syncope can also provoke finding in a stuffy room, emotional excitement, fear of blood and other similar factors.
- Neurocardiac fainting - often associated with severe coughing, strain, pressure on the epigastric area, as well as urination. The patient may feel weakness, headache, difficulty in making a full breath even before the fainting. A similar condition is called pre-morbid.
- Cardiac fainting - may be obstructive and arrhythmic. The second variety is often associated with increased or delayed heart rhythm. The fainting develops suddenly and after cyanosis is revealed, the weakness is expressed after the return of consciousness in the patient. Obstructive malformations are often associated with heart defects in the form of stenoses, when the blood flow collides with an obstacle when pushed out of the cavities of the heart.
- Vascular fainting - often presented as cerebral and orthostatic disorders. The latter form is characterized by a short-term manifestation, and after the faint there are no vegetative disorders. Cerebral syncope is more prolonged, the patient in the aftermambous period feels poorly, in severe cases, paresis and speech and vision impairment are determined.
When squeezing, the vertebral arteries may also experience fainting. Such a pathology is often associated with a sharp withdrawal of the head. If there is a poor blood flow through the carotid artery, then vision is lost on the side of the lesion and motor ability - on the opposite.
Collapse
With collapse, a decrease in the volume of circulating blood with a simultaneous vascular tone disorder is observed.Such a condition is often considered as a pre-anxiety state, but the mechanisms of development of these pathologies are different.
There are several types of collapse:
- Sympathetic tonic - often associated with strong blood loss, an exciskosis. In particular, compensatory mechanisms are launched that activate the chain of activation of the sympatho-adrenal system, spasm of the arteries of the middle order and centralization of the blood circulation system. Symptoms of exocytosis are sharply expressed (body weight drops sharply, the skin becomes dry, pale, brush and stool chill).
- Vagotonicheskaya collapse - is characteristic for the edema of the brain, which often occurs in infectious-toxic diseases. Pathology is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure, blood vessels expand and blood volume increases. Objectively, the skin becomes marble, grayish-cyanotic, also determined by spattered dermographism and acrocyanosis
- Paralytic collapse - is based on the development of metabolic acidosis, when the amount of biogenic amines and bacterial toxic substances increases in the blood. Consciousness is sharply depressed, crimson spots appear on the skin.
In all forms of collapse, there is a rare change in the parameters of cardiac activity: arterial pressure decreases, pulse increases, breathing becomes difficult, noisy.
Shock
The presented pathological process is acutely developing and in most cases threatens human life. Severe condition occurs on the background of respiratory distress, blood circulation, metabolic processes. The work of the central nervous system also shows serious disturbances. Due to the involvement of many micro- and macrocirculatory structures in the pathology of the body, there is a general deficiency of perfusion of tissues, as a result of which homeostasis is disrupted and irreversible destruction of cells.
The shock state of the pathogenesis of development is divided into several types:
- cardiogenic - arises due to a sudden decrease in the activity of the heart muscle;
- distributive - the cause of the disease is a change in the vascular tone due to neurohumoral and neurogenic disorders;
- hypovolemic - develops due to the sudden and severe decrease in the volume of circulating blood;
- septicemia is the hardest form of shock, since it includes the characteristics of all the previous types of shock, often associated with the development of sepsis.
The shock state during its development takes several stages: compensated, decompensated and irreversible. The terminal stage is considered to be the last stage, when even the provision of medical care does not have the result of action. Therefore, it is extremely important not to slow down when the first signs of shock occur: sharply elevated pulse, shortness of breath, low blood pressure, and lack of urination.
Video What you need to know about cardiovascular failure
Clinical picture
Shock and collapse are almost identical. In the objective examination, loss of consciousness (if there is a swelling) or its preservation is determined, but there is a hindrance. The skin is pale, the nasolabial triangle is thickened, and the release of cold sticky sweat. Breathing is frequent, often superficial.
In severe cases, the pulse becomes so frequent that it is not determined by palpation. The blood pressure is 80 mm Hg and below. An indication of the onset of the terminal state is the appearance of convulsions, unconsciousness.
The faults are characterized by the presence of pre-anxious state, when the patient feels:
- ringing in the ears;
- nausea;
- pronounced weakness;
- frequent yawning;
- rapid heartbeat.
If a person still loses consciousness, then he can rarely be defined heartbeat, superficial infrequent breathing, low blood pressure, narrowed pupils.
Emergency help
When faulty, the following actions must be performed:
- The patient is placed on a flat surface and slightly raised the legs.
- There should be access to fresh air, it is also important to unbutton the collar, remove the tie, loosen the belt.
- The face is wetted with cold water.
- Under a nose for a few seconds a fleece with a shampoo is put.
- In case of prolonged fainting, an ambulance is called.
Guilty hypoglycaemic conjunctivitis can be stopped using sweet, but similar is possible only when the patient returns to consciousness. Otherwise, the arrived medical brigade will have a drug effect.
When collapse, first aid is as follows:
- The patient should be placed on an even surface and raise his legs.
- When you are in the room, windows or doors are opened.
- The chest and neck should be freed from tight clothing.
- The patient is covered with a blanket, if possible, heats up with warmths.
- In the presence of consciousness give you a drink hot tea.
When collapse, it is important not to delay the emergency call. On arrival, the brigade of medical workers begins to carry out transfusion-infusion therapy, with the presence of bleeding, plasma substitutes, colloidal solutions, whole blood are introduced. If hypotonia preserves the background of the treatment, then dopamine is introduced. Other measures of prevention of serious complications are carried out in the conditions of the hospital, where the patient is delivered obligatory.
Emergency care with shock is to immediately call an ambulance, because only with the availability of special medications, and sometimes the equipment, can bring the patient to normal.
Video Heart Failure - Symptoms and Treatment
Similar articles
In cardiology, there is such a term as heart failure. What threatens this pathology is important to know all patients with severe cardiovascular disease. The timely provision of medical care helps to alleviate the patient's condition with this pathology, and in some cases prevent a sudden cardiac arrest.

Vegeto-vascular dystonia (or neurocirculatory dystonia) is a complex of emotional disorders that are combined with a set of various disorders in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. This syndrome can be accompanied by extremely variable symptoms: violations of the motility of the digestive tract, heart rhythm, blood pressure, pain in the heart, dizziness, fainting, sensations of a lump in the throat, etc.
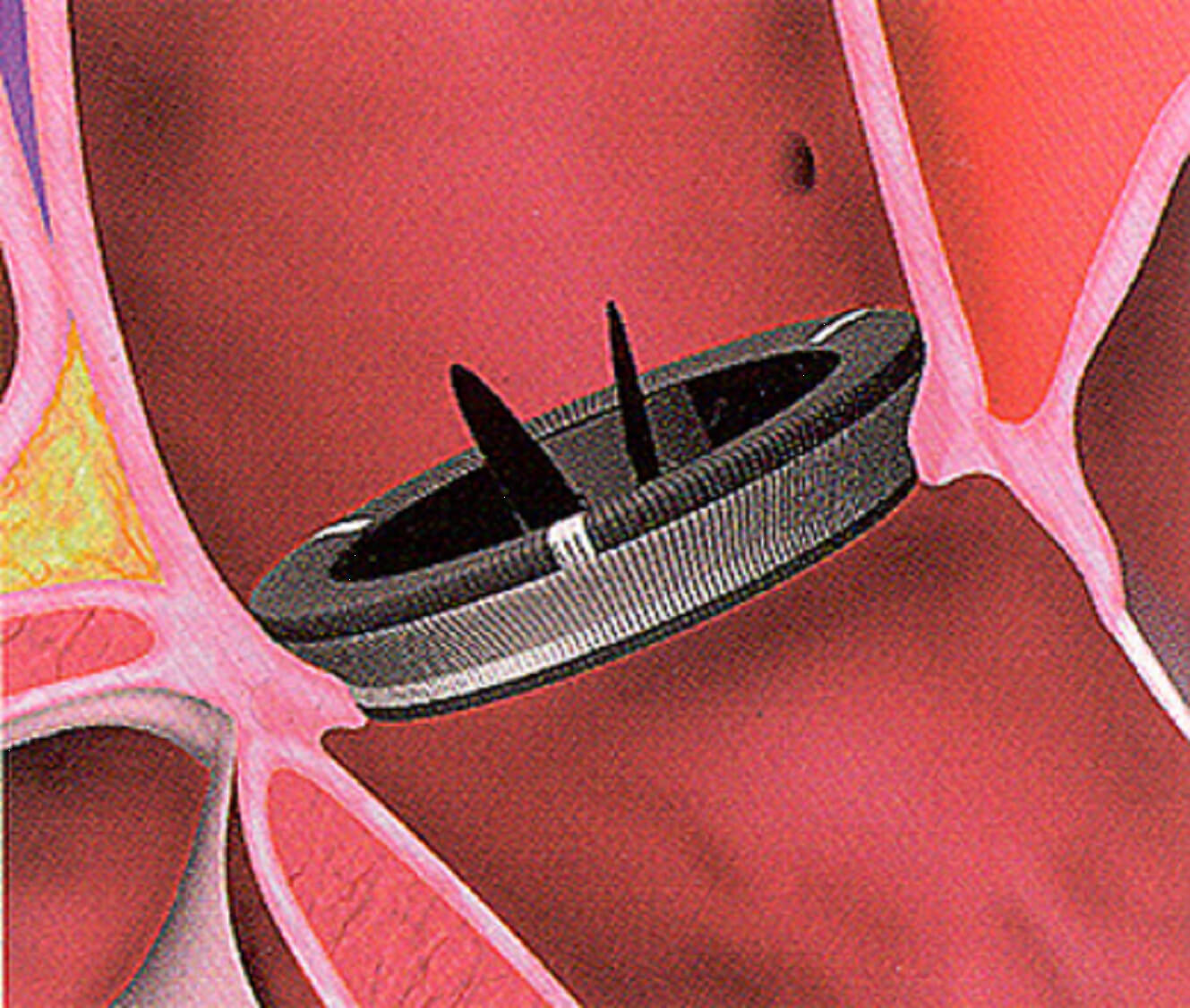
With certain lesions of the aortic valve, aortic insufficiency arises, which, in the absence of treatment, can lead to serious complications and even death. In the provision of medical care, in most cases a favorable prognosis is given.
