VSD during pregnancy: diagnosis and possible complications
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-07-24
Vegeto-vascular dystonia (VSD) is not a life-threatening disease, but it can reduce the quality of life a little. Often occurs during pregnancy, although even more cases of development of IRR are observed in women before conception. It is many girls, expectant mothers, often have symptoms of VSD of varying severity. In the future they may also show illness during pregnancy.
The initial occurrence of IRR during fetal gestation is not an indication for abortion, but it is necessary to follow the doctor's recommendations to avoid complications.
In the course of diagnosis, the symptoms are evaluated first, although there are no specific and very pronounced symptoms in the VSD. Sometimes the disease is combined with the pathologies of other organs and body systems, then there are difficulties with diagnosing and setting the right conclusion. In any case, you need to contact the doctor in time to reduce the risks of adverse effects on the fetus.
Video: VSD and panic attacks during pregnancy, what to do?
Description of the IRR
Vegeto-vascular dystonia (vegetative neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy or disautonomy according to Western concepts) is characterized by many conditions that cause the autonomic nervous system (the autonomic nervous system, VNS) to not function properly. VSD can be a complication of many diseases and conditions or may be a side effect after taking certain medications. The treatment or management of any underlying cause is the key to improving the condition of a pregnant woman.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
The vegetative nervous system controls the unconscious functions of the body: breathing, regulation of blood pressure, digestion, maintaining body temperature and much more.
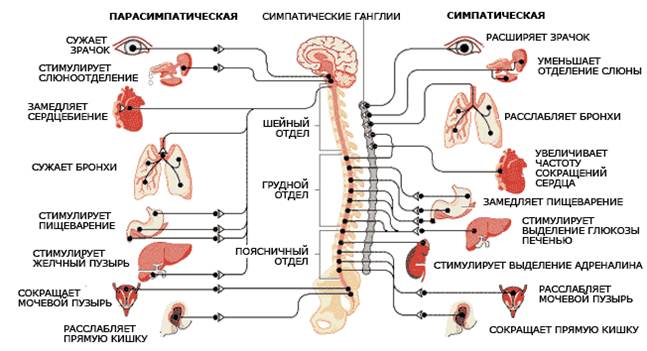
Causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia
There are many major diseases and conditions that can lead to VSD. Drug side effects can also cause disruption of the VNS.
The main reasons for the IRR are:
- Family disavtonomia (Reilly-Day syndrome)
- Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension (progressive autonomic failure)
- Multiple atrophy of many body systems with autonomic failure (Shay-Drager syndrome)
- Parkinson's syndrome with autonomic failure
Secondary causes of IRR include:
- Amyloidosis (abnormal growth of protein).
- Autoimmune neuropathies (Guillain-Barre syndrome, myasthenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus).
- Carcinomatous autonomic neuropathy (often associated with small cell lung cancer).
- Decontamination (decrease in function due to inactivity or illness).
- Diabetes and pre-diabetic condition.
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
- Lyme disease (a disease transmitted by mites and causing symptoms of influenza).
- Lack of nutrition (that is, deficiency of vitamins B1, B3, B6 and B12).
- Paraneoplastic syndromes (disorders caused by immune response to cancer).
- Physical trauma, surgery.
- Pregnancy.
- Viral disease.
- Porphyria (an enzymatic disorder that mainly causes problems with the skin and / or nerves).
- The toxic effect of certain substances (that is, alcoholism, chemotherapy drugs and heavy metal poisoning).
- Treatment with medications, including chemotherapy and anticholinergics.
If a woman has heart disease during pregnancy, it is likely that it will affect the baby.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Common symptoms include:
- Postural hypotension: weakness, dizziness, fainting, dullness of vision, unstable gait.
- Urinary dysfunction: frequent, excessive urination at night, urgency, urinary incontinence, false urges.
- Sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction, vaginal dryness, decreased libido.
- Cardiovascular changes: a feeling of palpitations, heaviness in the heart, a feeling of heart popping out of the chest, irregular and irregular rhythm, an increase or decrease in blood pressure.
- Gastrointestinal dysfunction: intermittent diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, fullness after eating, loss of appetite, slowing of stomach contents, bloating, heartburn.
- Violation of sweating: excessive or decreased sweating.
- Intolerance to exercise and physical activity.
- Paresthesia: Numbness or tingling in the legs, hands, or other parts of the body.

In addition, there may be a headache, "marbling of the skin," inexplicable temperature fluctuations, heat inflow to the head or neck.
Diagnosis of AVR in pregnancy
The attending physician, on the basis of available complaints, obstetric-gynecological examination, can recommend various studies and tests to evaluate the functions of the vegetative-nervous system, including:
- Respiratory tests . Allow to determine the main characteristics of heart rate and blood pressure, especially their reaction to the performance of various exercises, such as a strong exhalation (reception Valsalva).
- Tilt angle test . Helps evaluate the response of blood pressure and heart rate to changes in body position. In particular, an imitation of how a person gets up after lying down is carried out. For this, the patient is put on a table that is slightly tilted in different directions. Most often, they lift the upper part of the body. Usually, when performing such movements, the blood vessels contract in the body and the heart rate decreases. This is necessary to compensate for low blood pressure. Such a response may be delayed or abnormal, and then they speak of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Load test is very simple and affordable. To perform it, a person should stand for a minute, and then poprisedat for one minute, after which you must stand up again. Further, blood pressure and heart rate are measured and the results evaluated.
- Gastrointestinal tests . The study on gastric emptying is the most common method for diagnosing digestive disorders. In particular, slow digestion and delayed emptying of the stomach (gastroparesis) can be detected. These tests are usually conducted by a doctor who specializes in digestive disorders (gastroenterologist).
- The shipmotor test . Allows you to evaluate the function of nerves that regulate the work of sweat glands. In particular, their reaction to stimulation is tested. To conduct it, a small electric current is generated, which passes through special devices located on the forearms and legs, while the computer analyzes the reaction of nerves and sweat glands. During the test, you can feel warmth or tingling.
- A thermoregulatory sweat test . The patient is covered with a powder that changes color during sweat allocation.When a person is placed in a camera with a slowly growing temperature, digital photographs record the results of sweating. A sweat pattern can help confirm a diagnosis of autonomic dysfunction or provide other reasons for reducing or increasing sweating.
- Urinalysis and bladder function (urodynamic test). If there are symptoms of a bladder or other urinary system, a series of urinalysis and bladder tests are done, which allows you to evaluate the function of the system as a whole.
- Ultrasound examination . In the presence of signs of diseases of the cardiovascular, genitourinary, endocrine systems, the doctor prescribes diagnostics by ultrasound. Its implementation is based on high-frequency sound waves, which create an image of the required organs and body systems.
- Electrocardiography . It allows to evaluate the electrical conductivity of the heart, determines the heart rate and the localization of lesions, if any.
Since during pregnancy the condition of not only the woman but also the fetus is evaluated, the VSD carries out careful monitoring of its condition. To do this, it is important to visit the women's consultation on a regular basis and take all the examinations, such as obstetric-abdominal examination, and instrumental examinations.
It is important to know that with the development of pregnancy against the background of the VSD may need to visit your obstetrician and gynecologist more often and this should be done, since the timeliness of patronage depends on the health of the woman and the baby. In addition to the standard set of studies, it may be necessary to carry out other refinement diagnostic methods. In particular, it is assigned:
- Ultrasound of the fetus , which allows you to assess the condition of a developing child, placenta and other indicators.
- Fetal monitoring - is performed during labor to determine the condition of the fetus during labor.
Complications of IRR in pregnancy
Complications - a pathological condition that can occur against a background of vegetative-vascular dystonia during pregnancy and lead to undesirable consequences from both the woman herself and the fetus.
The main danger of VSD is the sudden development of seizures, which are called vegetative-vascular crises. Even worse, when the disease occurs with frequent attacks. There are three types of development of VSD crises.
- Sympathoadrenal crisis . Against the backdrop of a sharp release of a large amount of adrenaline into the circulatory system begin to show signs of the disease without any precursors. In particular, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure and low-grade fever can be noted. The skin becomes pale, there may be a feeling of chills and intense fear. At the end of the attack, involuntary urination occurs with the release of a large amount of light urine. In addition, sudden weakness, low blood pressure can be determined.
- A vagal crisis. Occurs because of the sudden release of large amounts of insulin into the blood. It starts with "harbingers" like a sharp growing weakness, noise in the ears, fogging in the eyes, panic, a sense of lack of reality and hopeless melancholy. There may also be pain in the abdomen and an intense desire for defecation. Finally, blood pressure drops and the patient loses consciousness. Possible involuntary urination and defecation.
- Mixed type of crisis . Occurs in rare cases and can combine various signs of the above conditions. In most cases, there is a sudden onset of shortness of breath, severe dizziness, pain in the occipital part, tachycardia, unsteady gait, a sense of lack of reality, intense fear of death or madness.
In fact, it does not matter when vegetative-vascular dystonia begins - before pregnancy or during its development. In any case, unpleasant complications can occur for both the mother and the child. Since IRR can occur in various forms, there may be some adverse effects.
Complications with IRR
In hypotonic type VSD , that is, the disease is combined with low blood pressure, anemia, placental insufficiency can be determined. Both types of complications threaten oxygen starvation and inadequate fetal development. Newborns, whose mothers were sick during pregnancy VSD, may have insufficient weight delay in psychophysiological development and weak immunity, because of which the child is more likely to have respiratory infections.
In the hypertensive type of VSD , when there is an increased blood pressure, a state of pre-eclampsia may occur. This complication is still known as late gestosis and its development also brings a lot of trouble both to the mother and the baby. In severe cases, there is a risk of intrauterine bleeding and placental abruption. All this ultimately threatens the life of the mother and child.
VSD, pregnancy and children
If a pregnant woman suffers from vegetative-vascular dystonia, toxicosis or frequent psychoemotional stress is noted, this immediately affects the health of the nervous system of the unborn child. As a rule, these factors are not critical and do not cause damage to the brain, but often this is the basis for the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia in a baby after birth.
Do not forget about the environment in which a child grows. Children should live in a positive, peaceful atmosphere. If the family often have quarrels and scandals, then there is an additional burden on the child, and later on his nervous system, which often leads to emotional breakdown. These factors largely affect the autonomic and vascular system of the baby, which also underlies vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Statistics show that most often children suffer from vegetative-vascular dystonia, if they are grown up by single mothers.
It's no secret that there must be a man in the family, but if a woman brings up children alone, she feels unprotected. This condition is often transmitted to her children. Therefore, if it happened that you have to educate your child yourself, you need to make efforts not to think about the bad and not to shift your problems and cares to your baby.
Another critical period is puberty. It is known that active hormonal changes in a growing organism are often accompanied by disorders of the endocrine system. This is actually stress for the body, when the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, gonads do not have time to produce hormones because of the rapid growth and development of the adolescent.As a result, there are bursts of manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia. If in time to understand that the child is prone to illness and take all the necessary measures to limit the stress on the child, then there are all chances to stop the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Video: Pregnancy. How to cope with stress during pregnancy
