Thrombosis
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-05-10
hrombosis is a condition caused by the formation of a blood clot that interferes with the normal circulation of blood throughout the body. Depending on the place and size of the blood clot, thrombosis can be extremely serious and even life-threatening.
Thrombosis is often combined with thromboembolism and then there are such terrible complications as a heart attack and a stroke.
Different methods of investigation are used to determine the location of the thrombus and the determination of the condition of the blood coagulation system is significant. When confirming the diagnosis, anticoagulation therapy is performed, and further preventive measures are taken.
Video: Than Thrombosis Is Dangerous?
Description
Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block the blood vessels. There are 2 major types of thrombosis:
- Venous is when a blood clot overlap partially or completely blood flow to the vein. By venous blood vessels flow from the body towards the heart.
- The arterial is when the blood clot blocks the artery. By arterial blood vessels carry oxygen from the heart to all parts of the body.

The main mechanisms of thrombosis development
- Hypercoagulation - in the context of certain autoimmune processes or genetic disorders, increased blood coagulability develops. According to the latest data, in the deep vein thrombosis, neutrophils are directly involved. In particular, they act as mediators during pro-thrombotic actions. Also, hypercoagulation is often associated with the administration of certain drugs and the passage of therapy, including antitumour.
- Damage to endothelial cells - there are many different factors contributing to damage to the inner layer of the vessels (endothelium). Under the influence of the tissue factor on the endothelium, platelets settle down, which results in thrombosis.
- Disturbance of blood circulation - the same is most often noted in violation of the activity of the heart, when blood begins to stop in venous blood vessels, due to which thrombosis and embolism develop. Also malignant formations can push the vessels, including large ones, which inevitably leads to thickening of the blood and thrombosis.
Reasons
Venous thrombosis can be caused by:
- Diseases or injuries of the venous leg vessels
- Complete or partial loss of mobility for any reason
- Bone fracture
- Some medicines
- Hereditary disorders
- Autoimmune disorders that lead to hypercoagulability
Arterial thrombosis is most often caused by atherosclerotic vascular lesions. This occurs when fat or calcium compounds are deposited on the walls of the arteries. The plaques thus formed may partially or completely block the vessel. In some cases, the educated thrombus is torn off and falls with the blood flow to other organs and systems, disturbing circulation in them.
Arterial thrombosis may develop in the coronary arteries, and then the heart muscle is affected, with all the consequences, including angina and myocardial infarction. When arterial thrombosis is formed in the blood vessel of the brain, then favorable conditions for the development of stroke are created.
Risk factors
Most of the risk factors for venous and arterial thrombosis are the same.
Risk factors for venous thrombosis may include:
- Family predisposition to deep vein thrombosis
- Hormonal therapy or birth control pills
- Pregnancy
- Injury of the venous vessel due to operation, fracture or other.
- Hypodynamia, for example, after surgery or during a long trip
- An inherited disorder of the blood coagulation system
- Installation of a venous catheter
- Old age
- Overweight or obesity
- Some pathological conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, pulmonary disease, or Crohn's disease
Risk factors for arterial thrombosis may include:
- Diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Lack of activity and obesity
- Bad nutrition
- Family predisposition to arterial thrombosis
- Old age
Video: Why do people form blood clots?
Species
Arterial thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in the artery. As a rule, arterial thrombosis can affect any organ of the body. Most often diagnosed:
- Stroke (hypoxia of the brain due to a disturbance in nutrition and oxygen intake)
- Heart attack (coronary artery bypass graft, known as "myocardial infarction")
- Disruption of arterial blood circulation in the limbs.
Coronary artery disease is the most common cause of mortality in Europe, which accounts for 1.8 million deaths per year. Today, every fifth death is from coronary disease. It is determined in 22% of women and 20% of men. About one in every twelve men (8%) and one in every ten women (11%) die of this disease. [1 - European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics? 2012 edition]
When arterial thrombosis occurs, anticoagulant (or antithrombotic) medications are used to prevent further clot growth and dissolution of existing clots that block coronary arteries. In most cases, anticoagulants are given in combination with other medicines, and if necessary, medical manipulations.
Venous thrombosis is the formation of a thrombotic clot inside the veins. For today, the following types of venous thrombosis are defined:
- gate vein;
- renal veins;
- jugular vein;
- vessels of the venous sinus of the brain;
- Badda-Chiari syndrome;
- Paget's syndrome - Schrötter;
The presented forms of vein thrombosis are collectively known as venous thromboembolic formations (WCO).
The exact number of people who suffer from the WTO each year is difficult to determine, but recent epidemiological studies show that the annual incidence of the WTO is about 1 per 1000 population. [2 - Glynn RJ et al. Ann Intern Med 2007; 147: 525-33; Amin A, Stemkowski S et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2007; 5: 1610-6]
According to statistics, the WTO is the third most common cardiovascular disease (after ischemic heart disease and stroke). In the European Union alone, more than 540,000 patients die every year from the WTO, twice the number of Europeans who have died from breast cancer, prostate cancer, HIV / AIDS and road accidents. [3 - Cohen AT et al.Thromb Haemost. 2007; 98: 756-64]
Thrombosis of superficial veins ( SLE ) is a blockage by a thrombotic bunch of superficial veins of the upper or lower extremities. Typically, TPV is estimated as benign pathology, which often causes significant inconvenience. Some studies have shown that 5-10% of patients may develop a serious progression of the disease in the first three months if they are not adequately treated. [4 - Bauersachs RM, Hämostazologie 2013; 33: 2]
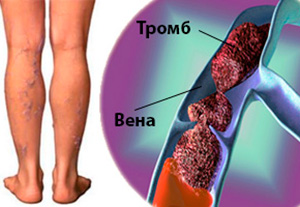
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a definition of blood clot in the deep vein of the limb or pelvis. Most commonly occurs in the lower extremities, such as deep vein thighs. With the development of DVT, the amount of returned oxygen-free blood to the heart is limited.
Though MSW and TBV bring a lot of inconveniences, their main danger is associated with the development of severe complications that increase the risk of pulmonary embolism.
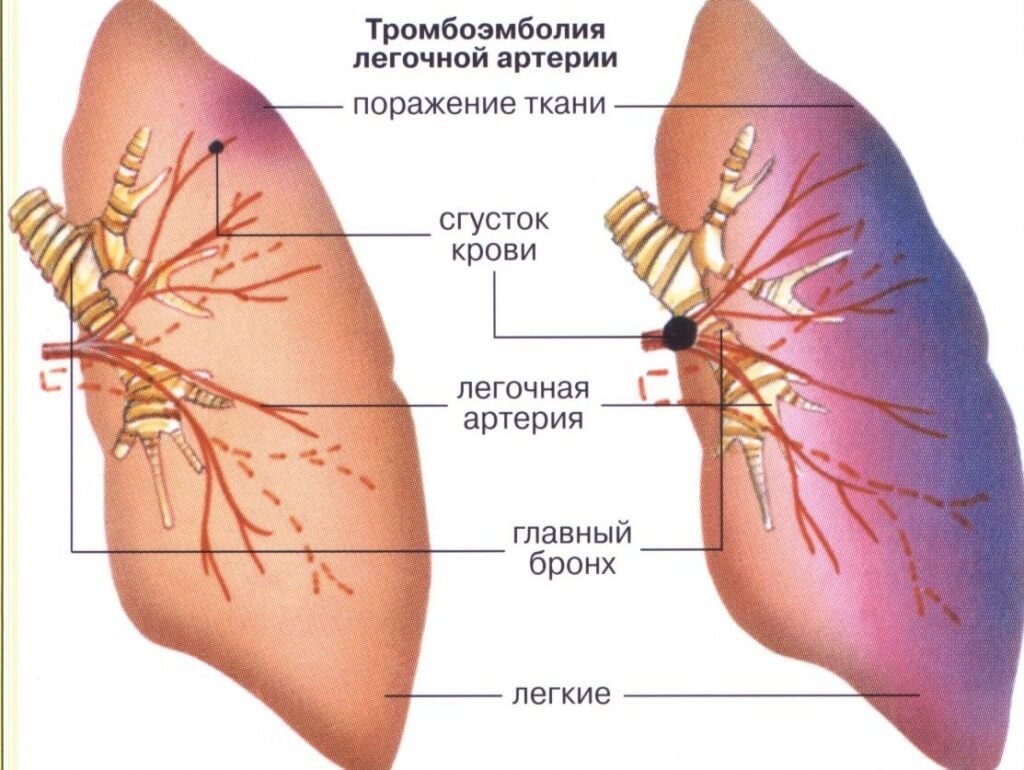
Pulmonary embolism (LE) occurs when the thrombus is separated from the vessel and through the venous system moves with blood through the right side of the heart and then gets into the pulmonary artery.
The clots settle down in the pulmonary artery, which can cause partial or complete blockage of the vessel. The effects of LE vary depending on the size and location of the thrombus. However, LE is an extremely dangerous pathology that can lead to fatal outcome.
Clinic
A more acute and pronounced clinical picture is characteristic for arterial thrombosis, whereas the blockage of venous vessels is less noticeable, but this does not reduce the degree of danger of their development.
Common symptoms of thrombosis are as follows:
- Fast fatigue
- Ungrounded fatigue
- Sudden change in mental condition
Symptoms of thrombosis may be similar to other diseases, especially if there is a heart attack or stroke on its background, then the characteristics characteristic of these pathologies are determined.
Depending on the location of the thrombus, the following symptoms can be detected:
- The heart is a pain in the cardiac region, sweating, shortness of breath and discomfort in the upper body
- Lightweight - acute chest pain, tachycardia, sweating, cough with blood and shortness of breath
- The legs are excessive pain, edema, redness, a feeling of warmth in the area of lesion and cramp
- The abdomen is abdominal pain, diarrhea and vomiting
- The brain is a change in vision, difficulty in conversation, severe headache, numbness or weakness on one side of the body and dizziness
When should I immediately contact a doctor?
- Painful feelings are sharply expressed or marked by their increase
- Breathing became discontinuous or breathless
- There was a fear of death or expressed anxiety
Diagnostics
Physiological examination of the patient and especially the affected leg or arm is necessarily supplemented by instrumental research methods. In particular, it is conducted:
- Ultrasound diagnosis. With the aid of sound waves, the degree of blood flow disturbances in the arteries and veins is estimated.
- Laboratory tests that allow you to determine the severity of blood coagulation. In particular, a prothrombin test, a TV test (thrombin time), an activated partial thromboplastic time is performed.
- Venography . At the beginning of the study, the X-ray contrast agent is injected into the vein. Then an X-ray image is made, on which vessels are visible, including narrowed and clogged ones.
- MRI or CT . Such a visual diagnosis is selected taking into account the type of thrombus and the presumed location of its location.
Treatment
During the design of the appointment letter, doctors often take the following points into account
- Age of the patient, his general health and the history of the disease
- Duration of the disease
- Relaxation in the use of patients with drugs or therapies
- The presence of relapses
- The wishes of the patient
Treatment of thrombosis is primarily due to the use of anticoagulants or, as they are commonly referred to as "blood diluents." Although these medicines do not actually "dilute" the blood, but only slow down the ability of the body to form new blood clots.
Anticoagulants usually begin to be administered in a hospital, especially in the first 5-10 days after diagnosis. This period is considered to be the most serious or severe during the development of the disease. If necessary, anticoagulants are prescribed for home use, especially those who are at risk.
Home treatment with anticoagulants can last for weeks, months or even years, which prevents the appearance of new blood clots. A similar phenomenon is especially indicated for atrial fibrillation and other forms of arrhythmias, in which a progressive reduction of atrium develops.
When treating with anticoagulants it is important to follow the following guidelines:
- You must necessarily take the medicine according to the prescriptions.
- With your doctor you need to continue to maintain close cooperation.
- When determining any symptom of thrombosis and / or the appearance of side effects from the administration of prescribed drugs, you must inform your doctor about this.
- If necessary, repeated tests are given, which will allow controlling the level of blood coagulation.
- When visiting a doctor, do not hesitate to ask questions of interest.
Anticoagulants used in the treatment of thrombosis:
- Nefractionated heparin
- Low molecular weight heparin
- Warfarin
- Direct oral anticoagulants
Treatment of thrombosis by folk remedies
According to nutritionists and macrobiotic consultants, it is necessary to avoid products that promote the development of inflammation in the body. These include white bread, cakes, pastries, cookies, refined butter. All these products, as a rule, contribute to the formation of blood clots. At the same time, it is worthwhile to include in the diet of the substance that can improve the blood condition.
1. Turmeric
The active compound present in turmeric, known as curcumin, is involved in thrombolysis, which prevents vascular thrombosis. Its healing properties can also help in the treatment of pain caused by already formed blood clots.
2. Garlic
According to some nutritionists, garlic contains sulfur compounds which are known to contribute to the dissolution of blood clots. One should consume one raw garlic clove in the morning to get effective results.
3. Hot pepper
Many peppers, including acrid, are natural blood diluents and have an effective effect on its rheological properties. All this thanks to the presence of salicylates in them.
4. Arjuna Terminal
According to nutritionist Simran Saieni from Fortis Hospital, Arjun ki chhaal or Arjuna Termination - it is very effective in brightening blood. For reception it is necessary to take a crust of evergreen tree and insist it in warm water. Take such an infusion every morning.
5. Flax seeds
These tiny seeds are filled with very useful omega-3 fatty acids that help prevent blood clots and improve blood circulation. Omega-3 is also found in red fish, which is also desirable to be included in the diet.
Video: 5 products forbidden with thrombosis - a diet
Complications
Thrombosis can block blood in any veins and arteries. Complications depend on where the defeat is located. The most serious health problems are:
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Serious breathing problems.
With a small thrombosis, its lysis (dissolution) is possible, which allows the blood flow to completely or partially recover.In the unfavorable course, connective tissue grows, which leads to the appearance of a seal.
Prevention
Reduce the risk of developing thrombosis in the following ways:
- Maintain sufficient level of activity
- After surgery, start physical activity as soon as possible
- During long trips, legs must perform acceptable exercises
- Should wear special stockings that have a compressive effect
- Stop using alcoholic beverages, which often lead to dehydration and congestion
- Quit smoking
- Lower weight
The treatment of concomitant diseases, especially those such as diabetes, high blood pressure and high cholesterol, also helps to prevent thrombosis.
Video: Prevention of heart and blood vessel thrombosis

Часто сейчас у всех такая проблема встречается… Поэтому лучше своевременно думать о профилактике, конечно. Я принимаю лекарство гинкоум для разжижения крови. Правильное питание, банька, спорт-это все само собой. С анализами все в порядке, тромбозом и не пахнет))