Thrombocytopenia
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-05-10
Thrombocytopenia (TP) - is characterized by a decrease in the number of platelets below 150 × 109 / l. With pronounced degree of illness, there are severe bleeding that can lead to death.
Frequency of occurrence of thrombocytopenia is rather high: approximately 10-130 newly ill patients for 1 million people.
Firstly, laboratory tests are used to determine TP, which in the future can be complemented by instrumental diagnostic methods. The disease is often combined with disorders of the circulatory system, therefore the treatment is mainly used in complex, often complemented by antirecurrent drugs.
Video: Thrombocytopenia: what to do
Description
Platelets, or "blood platelets," are very small, non-nuclear constituents formed in the bone marrow together with other types of blood cells. They pass through the blood vessels to the lesion sites and, under the action of the Brownian motion, are glued together, which allows stopping the bleeding that can occur as a result of the rupture of the blood vessel.
The process of slipping the platelets is also called coagulation. In this case, the formed blood clot - a thrombus. If the platelets are not enough, then there is a thrombocytopenia.
The normal platelet count in adults ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. The number of platelets below 150,000 thrombocytes per microliter below the normal range indicates thrombocytopenia.
The greatest risk of bleeding is observed with a significant decrease in the number of platelets - less than 10,000 or 20,000 cells per microliter. Soft bleeding sometimes occurs when the platelet count is less than 50,000 per microliter.
Mechanisms of thrombocytopenia development can be as follows:
- The bone marrow does not produce platelets in sufficient quantities.
- The bone marrow produces a sufficient amount of platelets, but the body itself destroys them (autoimmune processes) or actively uses them (bleeding).
- The spleen (organ-cemetery of blood cells) in large quantities destroys platelets.
- The above factors are combined, which can also lead to a low platelet count.
Thrombocytopenia may be physiological if there is a slight decrease in platelets in the context of menstruation in women with a disturbed diet and so on.
Basic Thrombocytopenia Facts:
- Women are more likely to be ill than men. At the same time in childhood, the situation is different. From 2 to 8 years of age, TP is more often defined by boys.
- The highest incidence rate is observed at the age of 20 years and after 50 years.
- In ¾ newborns with low weight thrombocytopenia is determined
- In 5% of patients, a severe blood loss or hemorrhage in the brain develops because of which they perish.
- When pregnant, 7% of women in the second half of the period are diagnosed with thrombocytopenia.
Reasons
Many factors can cause thrombocytopenia, therefore, inherited and acquired TP. "Inherited" is when the affected gene was passed on to the offspring through the parents. "Acquired" is when the disease develops throughout life. Sometimes the cause of the disease is unknown, then talk about idiopathic thrombocytopenia.
Thrombocytopenia may develop for the following reasons:
The bone marrow does not make platelets in sufficient quantities
Bone marrow is a spongy tissue that is inside the bones. It contains stem cells that develop into various blood cells: erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. When the stem cells are damaged, the whole process of hemopoiesis is disturbed, resulting in the formation of uncomplicated platelets.
- Cancer
Cancerous conditions like leukemia or lymphoma can damage the bone marrow and destroy stem cells of the blood.Cancer treatment also affects the number of platelets, which is why radiation and chemotherapy are most often diagnosed with thrombocytopenia.
- Aplastic anemia
This rare and serious blood disease promotes the cessation of education in the bone marrow of a sufficient number of new blood cells. It ultimately affects the amount of platelets.
- Toxic chemical compounds
The effects of many toxic chemicals such as pesticides, arsenic and benzene may slow the production of platelets.
- Medicines
Some medications, such as diuretics and chloramphenicol, can slow down the synthesis of thrombocytes.Chloramphenicol (an antibiotic) is rarely used in the United States and other countries of the world. Ordinary prescription drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen may also affect platelets.
- Alcohol
Alcoholic drinks can slow the production of platelets. Temporary reduction in their numbers is fairly common among alcohol users, especially if they eat foods that are low in iron, vitamin B12 or folic acid.
- Viral diseases
Smallpox, epidemic mumps, rubella, Epstein-Barr virus or parvovirus can reduce the amount of platelets for a while.People who have AIDS often also have thrombocytopenia.
- Genetic predisposition
Some genetic conditions can cause a decrease in platelet count in the blood. Examples include Wiskott-Aldrich and May-Hagglin syndromes.
The body destroys its own platelets
A low platelet count can be detected even if the bone marrow produces a sufficient amount of platelets. The body can destroy its platelets because of autoimmune diseases, certain drugs, infections, surgery, pregnancy and some conditions that cause increased coagulation.
- Autoimmune diseases
Arise with the errosion of the body's platelet and other blood cells by the immune system. If an autoimmune disease leads to platelet damage, then thrombocytopenia may develop.
One example of this type of autoimmune disease is immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). In this disorder, there is an unceasing bleeding, that is, blood does not turn off, as it should. It is assumed that the autoimmune response causes most cases of ITP.
Other autoimmune diseases, in which thrombocytes break down, include lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Medicines
The reaction to some medications can be expressed in the destruction of the body of its own platelets. Examples of drugs that may cause this disorder are quinine; antibiotics containing sulfate; and some medicines against seizures, such as dilantin, vancomycin and rifampicin.
In the treatment of heparin, a pathological reaction that leads to thrombocytopenia may also develop. This condition is called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (GITP). Her development is most often associated with hospital treatment.
With GITP, the body's immune system attacks a substance formed by heparin and a protein located on the surface of the platelets. This attack activates the platelets, and they begin to form blood clots. Thrombi can be formed deep in the legs (deep vein thrombosis), or they break up and move to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
- Infectious Disease
Low platelet count may be the result of blood saturation with bacterial infection. Viruses such as mononucleosis or cytomegalovirus can also lead to insufficient platelet count.
- Surgery
Platelets can be destroyed when they pass through artificial heart valves, blood vessel transplants, or apparatus and tubes used for blood transfusion or bypass grafting.
- Pregnancy
Approximately 5% of pregnant women develop mild thrombocytopenia, especially in the prenatal period. The exact cause of this violation is unknown.
Additionally, some rare and serious illnesses can lead to low platelet counts. Examples of this are thrombocytopenic purpura and disseminated intravascular coagulability of the blood.
Video: Why the platelet counts fall?
Clinic
On the background of both moderate bleeding and severe bleeding, the main symptoms of thrombocytopenia develop.Bleeding can occur inside the body (internal bleeding), as well as under the skin or on its surface (external bleeding).
Signs and symptoms may appear suddenly or over time. Mild thrombocytopenia often has no symptoms or symptoms.As a rule, it is detected during normal laboratory blood tests.
In severe thrombocytopenia, bleeding can occur in almost any part of the body. In some cases, bigger blood loss results in emergency medical care, which needs to be addressed in a timely manner.
External bleeding is usually the first sign of low platelet count. On the skin it is often expressed in purpura or petechiae.Purple - violet, brown and red bruises that can occur quite easily and often. Petechia - small red or purple points on the skin.
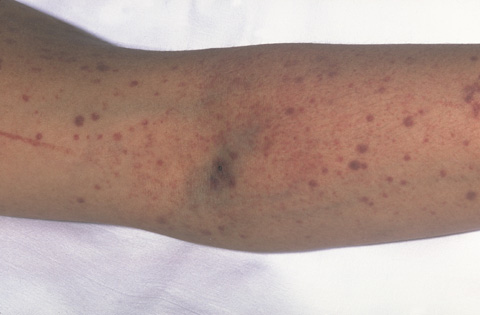
The photo shows purple (bruises) and petechial (red and purple points) of the formation on the skin. Bleeding under the skin causes the appearance of purple, brown and red.
Other signs of external bleeding include:
- Long-term bleeding, even due to minor damage
- Bleeding from the mouth or nose, as well as during brushing your teeth
- Vaginal bleeding (especially in severe menstrual cycles)
- Bleeding after surgery, medical manipulations or dental treatment.
Intestinal bleeding or hemorrhage in the brain is a serious condition and can be fatal. Signs of this pathology include:
- Blood in the urine / stool or bleeding from the rectum. In this case, the chair may be with red streaks of blood or dark color. (The addition of iron may also cause a dark, resinous chair.). Similar symptoms are more common in bleeding from the sections of the digestive tract
- Headaches, dizziness, paresis, blurred vision, and other neurological symptoms. These problems are inherent in hemorrhages in the brain.
Diagnostics
The final diagnosis of thrombocytopenia is based on the history of the disease, the physical examination and the results of the patient's analyzes. If necessary, the patient is hematologist. This is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of blood diseases.
After diagnosis of thrombocytopenia, it is important that the cause of its development is determined. Various research methods are used for this purpose: analysis of the history of the disease, laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostics.
The history of the disease
In the course of studying the history of the disease, the physician will necessarily know the patient's answers to the following questions:
- Which medications are taken, including over-the-counter medications and herbal remedies. It also reveals the content of quinine, which is often found in drinking water and food.
- Whether there are blood diseases from close relatives.
- Has blood transfusion been performed recently, how often do sexual partners change, whether intravenous medications are introduced and whether contact with contaminated blood or harmful fluids occurs at work.
Physical examination
During a physical examination, bleeding symptoms such as bruises or patches on the skin can be detected. It is mandatory to check for signs of infection, such as fever. It also feels (palpated) on the abdomen, which allows you to determine the enlarged spleen or liver.
General blood test
With this analysis, the level of red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets in the blood is measured. To do this, a small amount of blood, usually from the patient's finger, is taken, and then examined under a microscope. At thrombocytopenia, the results of this test will show insufficient platelet count.
Blood smear
The special method verifies the appearance of the platelets, for which a microscope is used. A small amount of blood is also taken for this test, most often from the finger.
Bone marrow examination
To study the functional capabilities of the bone marrow, two tests are performed - aspiration and biopsy.
Bone marrow aspiration can be done to find out why there is not enough blood cells to be formed. For this test, the doctor takes a bone marrow sample with a needle, which is further examined under a microscope. With pathology defective cells are determined.
Bone marrow biopsy is often performed immediately after aspiration. For this test, the doctor takes a sample of the bone marrow through the needle. The fabric is then examined for which the number and types of cells, including platelets, are checked.
Other diagnostic methods
Depending on the readings, an ultrasound examination, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging are performed. In the presence of concomitant diseases, the study of the affected organs is performed.
Treatment
Depending on the severity and causes of thrombocytopenia, appropriate therapies are prescribed. The main purpose of treatment:
- prevent death;
- reduce the risk of developing disability;
- improve the patient's general well-being;
- to improve the quality of life of the patient.
At a mild degree of TP specific treatment is not carried out. In such cases, it is often enough to adhere to the general recommendations given to patients with TP to prevent accidental bleeding. Also, the patient's condition often improves in treating the underlying cause of the disease.
- If the TP is a response to the medication taken, then the doctor may prescribe another medication. Most people recover after such changes have been used.
- For heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, discontinuation of heparin may be inadequate. In such cases, another remedy must be prescribed to prevent blood coagulation.
- If the immune system contributes to lowering the platelet count in the bloodstream, then the doctor may prescribe medications to suppress the immune response of the body.
Treatment of severe thrombocytopenia
Different methods of treatment are used to improve the condition of a patient with severe thrombocytopenia: special medications, blood / platelet transfusion or splenectomy.
- Medicines
The doctor may prescribe corticosteroids, also called steroids. With their help slowing down the platelets. These medicines are administered via a vein or taken as tablets. Most commonly used in modern medicine is prednisone.
Steroids used to treat thrombocytopenia are different from the illegal steroids taken by some athletes to increase efficacy.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe immunoglobulins or drugs, such as rituximab, which help reduce the immune system's response. These drugs are injected through the vein. Other medicines may also be prescribed, such as
eltrombopag or romiplostim, which increase platelet count. The first drug is taken in the form of tablets, and the second - as injections.
- Blood transfusion or platelets
It is used to treat people with severe bleeding or high risk of bleeding. To perform this procedure, intravenous access is made, then donor blood or platelet mass is introduced.
- Splenectomy
During this operation, the spleen is removed. It is most commonly used if medication is ineffective. Mainly shown by adults who have been diagnosed with immune thrombocytopenia. However, even in such cases, medications are often the first type of treatment.
Prevention
The ability to prevent thrombocytopenia depends on the specific cause of its development. There are such risk factors that can not be corrected (age, gender, heredity). However, measures can be taken to prevent health problems associated with thrombocytopenia. For example:
- You must avoid drinking alcohol because it slows down the synthesis of platelets.
- It should not be contacted with toxic chemicals such as pesticides, arsenic and benzene, which can slow the production of platelets.
- It is worth avoiding drugs that in the past have contributed to a decrease in platelet count.
- It is important to remember about medications that can affect coagulation and increase the risk of bleeding. Examples of such drugs are aspirin and ibuprofen.
- If necessary, you should talk to your doctor about vaccination against viruses that may affect the platelet production.In particular, vaccines against epidemic mumps, measles, rubella and chickenpox may be needed.
Life with thrombocytopenia
If thrombocytopenia is diagnosed, then you should monitor any signs of bleeding. If you have any, you should immediately inform your doctor.
The symptoms of bleeding may appear suddenly or over time. Severe thrombocytopenia often causes bleeding in almost any part of the body, which can lead to emergency medical attention.
Measures should be taken to avoid health problems associated with thrombocytopenia. In particular, it is necessary to take prescribed medicines in time, as well as to avoid injuries and injuries. If a fever has developed or there are other signs of an infectious disease, you should immediately inform your doctor about this.
Medicines
You need to tell your doctor about all the medicines that are taken, including over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, supplements and herbal remedies.
To reduce the risk of bleeding, aspirin and ibuprofen should be avoided, as well as all medications that may contain them in their formulation.
Wounds and injuries
All injuries that can cause bruising and bleeding should be avoided. For this reason, it is not necessary to participate in sports, such as boxing, football or karate. These types of sports often lead to injuries that may even be complicated by a brain hemorrhage.
Other sports, such as skiing or riding, also expose the patient to traumatic injury, which can lead to bleeding. To find safe physical activity, you should consult a doctor.
When driving a car, you must take precautions such as using a seat belt. If you are to work with knives and other sharp or cutting tools, then you should wear protective gloves.
If your child has thrombocytopenia, you need to protect him from injuries, especially head injuries, which can cause brain hemorrhage. You can also ask the attending physician whether it is necessary to limit the activity of the child.
Infectious diseases
If the spleen was removed, then the chances of getting sick with certain types of infections increase. It is necessary to monitor the febrile condition or other signs of infection, about which is communicated to the attending physician in a timely manner. Additionally, vaccines may be needed to prevent infection by certain infections.
Forecast
Thrombocytopenia may be fatal, especially if bleeding is severe or if a brain hemorrhage occurs. However, the general prognosis for people with this disease is good, especially if the cause of low platelet count is detected and treated.
Video: How to increase the number of platelets in the blood
Similar articles

Athletes train, eat well, stay active and maintain a healthy weight. It does not seem fair that they may develop varicose veins. In fact, there are such sports activities, when the question of whether you can play sports with varicose veins, is given a definite negative answer.

Arterial pressure can increase not only from smoking, drinking alcohol or excessive stress, but also with malnutrition. Often, it is often enough to buy fast food, in order to significantly damage your health in a short time. Therefore, if there is a high risk of developing hypertension, you need to know those products that lower and increase pressure.

In many cases, the development of severe heart disease can be prevented through exercise. Most of the leading experts in the field of cardiology are confident that heart training should be an integral part of a healthy lifestyle. In this case, doctors prescribe specific exercises even for patients suffering from cardiopathology.
