Tremor of the atrium
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-10
Tremor of the atrium refers to secondary pathologies, that is, diseases that have developed in the background of other disorders. Most often it manifests itself in paroxysmal form, when a person may not feel an attack or make complaints of an uncomfortable condition. There are protracted paroxysms lasting for days and even weeks. Trembling can alternate with flickering atrium, which complicates the clinical course of the disease.
An increase in the number of cardiac contractions affects the severity of symptoms, which is often associated with hemodynamic disorders.
With a mild severity of the disease, the restoration of normal rhythm occurs independently. In severe cases, the accompanying frustration pathology does not allow the heart to cope with its tasks, which becomes the reason for the provision of medical care. It is important to note that if other antiarrhythmic drugs help with rhythm disturbances, cardiopulmonary intervention is often indicated when treating atrial fibrillation.
Video: An overview of Atrial Fibrillation
Description of the atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (TP) refers to supraventricular tachycardia, in which pathological excitation occurs from an outbreak located in the atria. As a result, the rhythm remains correct, but its frequency ranges from 200 to 400 beats per minute.The ventricles do not contract as often as the atrium, as the impulse wave of excitation does not always come to them.

A healthy heart is normally excited regularly and ordered. The signal comes from the sinus node located in the right atrium, first to the left atrium, and then through the atrioventricular node in the ventricle. The conductivity of the AV node is several times lower, compared with sinus, which is necessary for the first reduction of the atrium, and then the ventricles. In this way, the blood first fills the upper parts of the heart (atrium), and then, when relaxed, they pass into the lower (ventricles) and enter the small and large circle of blood circulation.
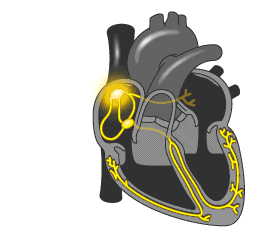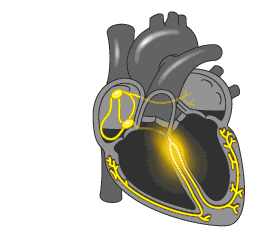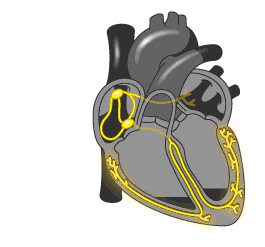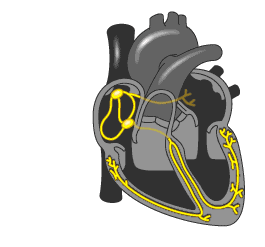
The development of the atrial flutter is associated with a violation of the electrical pulse, which is reflected in the number of contractions of the upper heart. If in norm it makes 60-90 times per minute, then at trepidation - 200-400 times per minute. At the same time, the AV-node is not able to skip so many pulses, so their amount, reaching the ventricle, is two, three and more times less. Correspondingly, the ventricles are reduced 75-150 times per minute.
Patients with WPW syndrome (congenital cardiac pathology) are somewhat more difficult to tolerate TP, which often goes into trembling ventricles due to the presence of Kent's pathological bundle. By it, a pulse is performed faster than the AV node, which threatens the ventricular fibrillation.
Symptoms of atrial flutter
The disease is characterized by common symptoms that arise in many cardiovascular diseases:
- palpitation increased;
- "Interruptions" of cardiac activity, feelings of "fading" and "turning" the heart;
- heart failure is manifested by weakness, shortness of breath, frequent urination.
At the tremor of the atrium, the sinus rhythm is preserved, which is correct and rhythmic, which distinguishes this pathology from atrial fibrillation.
The ripple of the veins is another characteristic symptom of the atrial flutter. When determining it, the difference with the cardiac contractions is evident, which is to exaggerate the pulsation frequency of the veins two to three times.
Clinically unfavorable is the atrial flutter in the case of the ratio of the rate of atrial and ventricular contractions 1: 1. Such an option is very dangerous because of the high risk of developing ventricular fibrillation.
Causes of atrial fibrillation
Mainly associated with organic pathology of the heart, which is expressed in the following diseases:
- infectious processes leading to inflammation of the myocardium (endo- and myocarditis);
- ischemic diseases accompanied by sclerosis of the regions of the myocardium or scar tissue formation (myocardial infarction, cardiosclerosis, cardiomyopathy);
- dystrophic pathologies in which myocardial trophism (myocardial dystrophy) is disturbed,
- hypertonic disease, which affects the work of the left ventricle.
Non-cardiac causes can also be the cause of TP. Pulmonary diseases expressed in an obstructive, chronically leaky form, lead to sclerosis of the pulmonary tissue and an increase in pressure in the small circle of blood circulation.Therefore, TP may be a complication of emphysema, chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma. Also, surgical operations may be complicated by TP in case of coronary artery bypass graft, plastic on the heart valves.
To reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, you should know the risk factors:
- male gender;
- age after 60 years; / li>
- the presence of bad habits;
- lack of potassium in the body;
- idiopathic atrial extrasystole;
- increased production of hormones by the thyroid gland.
If a TP has been observed before, it is necessary to know provocative factors that can cause a new attack:
- taking alcohol or narcotic substances;
- elevated ambient temperature;
- psycho emotional experiences;
- physical stress.
Views of the atrial flutter
According to the classification of H.Wells, 1979, the atrial flutter is divided into two types: typical and atypical. Also, according to the clinical course, TP paroxysmal, constant, persistent and first detected.
Types of atrial flutter
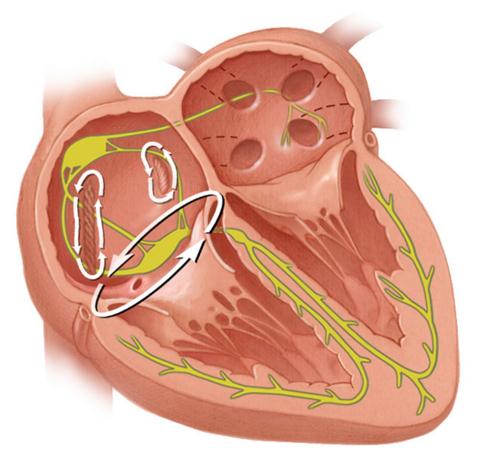
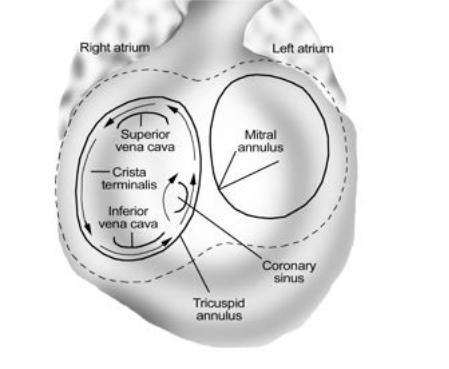
Type I, or typical TP , develops in 90% of cases in the form of an anti-clockwise propagation wave of an excitatory wave. After generating an electrical pulse, the interstitial septum, the posterior wall of the right atrium, alternates the upper hinge of the vein and drops downward along the anterior and lateral walls to the tricuspid ring, alternating in between. Then through the isthmus again passes an interstitial septum. In the remaining 10% of cases, the signal moves clockwise.
For the surgical treatment of TP, this type is more favorable, since in the isthmus area an abnormal pulse circulation is interrupted, for which radiofrequency ablation is used.
Type II, or atypical TP , is created by a return pulse passage in the area of various anatomical structures (pulmonary veins, mitral rings, coronary sinus, scars, and others). This type of TP is mainly due to extensive atrial fibrillation, which has undergone surgical interventions and catheter ablation. Carrying out cardiostimulation for Type II TP is ineffective.
Video: Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms & Treatments
Clinical forms of tremor of the atrium
Depending on the severity of the process and the duration of TP, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- The first occurrence of TP - earlier attacks were not determined by the patient. Clinical form is exposed regardless of the severity and duration of the pathological process.
- Paroxysmal tremor of the atria - has a paroxysmal flow, duration of each attack is not more than 7 days. Maybe his own self-completion.
- Persistent form - is unfavorable in its development, since it does not end there, medical intervention is required to stop the attack .
- Constantly flowing TA - rhythm disturbance has been observed for a year, and improvements in the dynamics of the disease are not visible.
Complications of atrial flutter
Developed mainly in patients with cardiovascular disease:
- development of ventricular or atrial fibrillation, as well as ventricular vomiting;
- long stroke threatens stroke, blockage of the pulmonary artery thrombus, poor functioning of the kidneys;
- in case of arrhythmias in the context of heart disease, TP may be complicated by heart failure and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy, which leads to death.
Diagnosis of atrial flutter
First of all, patients with suspicion of atrial flutter are prescribed electrocardiography.
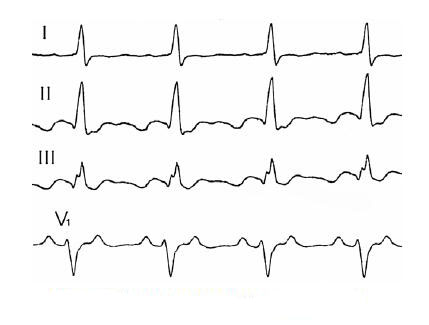
A typical tremor is manifested in the ECG by rhythmic F waves, which appear instead of the characteristic in the norm of the tooth P. The contraction frequency is 240-340 times per min. To determine the passage of the pulse "for" or "against" clockwise, look for the lower and II, III leads. Signs of motion of a signal "against" clockwise: saw-like waves F have a negative phase in II, III leads, and in V1, the teeth F are on the top (positive). When the pulse moves "behind" a clockwise on the ECG, signs can be seen exactly the opposite.
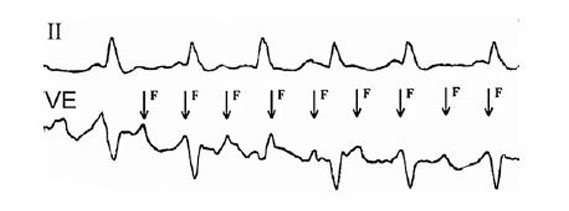
The atypical tremor is characterized by the appearance of a wave of F at a frequency of 340-430 times per minute.Sometimes, the atrial waves can not be seen on the electrocardiogram, then they can be detected using a transesophageal examination (Echo-CG) at the appropriate lead-in VE.
From other methods of diagnosis in the determination of atrial flutter, the following are effective:
Ultrasound - allows you to assess the state of the heart, identify organic and structural changes, specify the size of the heart cavity.
Laboratory diagnosis - conducted in the presence of hormonal disorders associated with the thyroid gland or pancreas, the concentration of electrolytes (especially potassium) is determined by analysis of the rheumatoid factor.
Echo-KG - is appointed to clarify the direction of circulation of the pulse, as well as to see if there are atherosclerosis thrombotic formations.
Treatment of atrial flutter
Atrial flutter attacks with the use of modern treatments are effectively stopped in most cases. Such areas of medicine as medical therapy and surgical treatment are used. Also important is the urgent help in the form of restoring sinus rhythm, used to stop severe attacks.
Recovery of sinus rhythm
It is an emergency treatment that is carried out with atrial fibrillation by medical personnel. There are several ways to restore sinus rhythm: medication and non-drug cardioversion.
Medicinal cardioversion is rarely used in TP, since it is not as effective as atrial fibrillation. Cardioversion is started from intravenous administration of ibutylide, which has the desired effect on average in 60% of cases. In the presence of contraindications to the use of ibutyilda (increased sensitivity to it) enter amiodarone, sotalol. If there is no result of medication cardioversion, then resort to control of heart rate, which uses calcium antagonists and digoxin.
Non-medicated cardioversion is based on electropulse therapy. With a defibrillator, a discharge of 100 J is produced, which is effective in 85% of cases. For comparison, if you make cardioversion with a discharge of 50 J, then the efficiency is achieved in 75%. In some cases, with TT of the first type, it is best to conduct cardiac stimulation using an electrode fed through the esophagus. Sometimes an additional digoxin or antiarrhythmic agent is added, which increases the overall efficacy of the procedure.
In any form of cardioversion, prevention of thromboembolism should be prevented, especially if TP is maintained for 48 hours.
Medicinal therapy
Indications for medical treatment are poor tolerability of patients with an attack, as well as the risk of developing complications.
Based on the use of beta-blockers (metoprolol) under the cover of antiarrhythmics (ibutyil, amiodarone). The introduction of the latter drugs is necessary to prevent the occurrence of ventricular fibrillation.
When developing WPW syndrome, beta-blockers, cardiac glycosides, and other similar drugs can not be used to prevent the complication of the condition. The only thing you can do is use anticoagulants and antiarrhythmics.
Catheter ablation
It is shown when treating the atrium of the first type, when the pulse circulation is carried out counterclockwise. In the area of the isthmus, radiofrequency catheter ablation is carried out, whose effectiveness manifests itself in 95% of cases.
Another type of catheter ablation, cytothermal, has also proven its effectiveness, with the procedure not as painful as radiofrequency ablation. The only thing that any such interference is accompanied by a subsequent recurrence of tachycardia. In addition, after the procedure, the risk of developing atrial fibrillation increases. This is due to structural changes in the heart chambers. Therefore, surgical treatment should be carried out only in extreme cases, when other methods, in particular, medical treatment, do not help.
Secondary prophylaxis of atrial flutter
It is associated with the prevention of the development of complications in the form of heart failure, thromboembolism, tachycardia, especially in the presence of a patient in the risk group. You should also pay attention to the following recommendations:
- In time, take antiarrhythmic drugs and monitor the regimen of the day, the correct alternation of work and rest.
- In order to avoid the development of tachycardia and arrhythmias, it is necessary to drink calming remedies, which also help in stressful and emotionally tense situations.
- The level of potassium should be normal (3.5-5.5 mmol / l in the blood) in order not to disturb the work of the heart, for this you can take the appropriate medications or eat foods rich in potassium (raisins, bananas, kiwi, beets, carrots, beef , non-fat fish).

вап