Sinoatrial tachycardia
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-14
Sinoatrial tachycardia (CT) is a type of reciprocal rhythm disturbance that occurs in the area of the atrium, that is, over the ventricles. Together with the intraperitoneal reciprocal tachycardia, it occurs much less frequently than the atrioventricular nodal reciprocal tachycardia.
Among supraventricular tachycardia, the synaarthrial reciprocal tachycardia has a frequency of not more than 10%.
Clinically difficult to determine, as there is often an asymptomatic course. The diagnostics uses the same methods as with other forms of tachycardia. A properly established diagnosis helps to avoid complications of a patient's condition, to improve the quality of his life. It can manifest itself at different ages, and is especially often diagnosed in adolescents on preventive examinations.
Video Cases: Tachycardia at a young age
Description of sinatrial tachycardia
The formation of pathology occurs in the type of reentry, with the location of the contour of re-entry in the region of the sinus node. Further, the pulse should be as usual: in the atrioventricular node, in the bundle of Guillaume, and in the Purkinje fibers. At the expense of a similar mechanism of conducting a pulse with a normal rhythm, with sinatoilar tachycardia, the electrocardiogram has practically no changes in the sinusitis P.
Frequent pulse generation contributes to blockade formation at the atrioventricular node level, with no change in the frequency of atrial contractions. In some patients, besides tachycardia, there is an atrioventricular blockage of the Mobitz I type characterized by Wenckebach's periodicity. Similar changes in cardiac rhythm practically do not affect the interval PQ and heart rate.
Symptoms of sinatricular tachycardia
The disease is typical of sinus tachycardia symptoms. Patients feel palpitations, discomfort in the region of the heart, vegetative disorders can be expressed in the form of anxiety, irritability, and weakness.
An important difference in sinoarthritic tachycardia from sinus tachycardia is the sudden onset of seizures, which in the same way end. Another difference between the two tachycardias is the presence of atrial extrasystoles before the occurrence of spontaneous paroxysms.
During an attack, the frequency of heart rate in rare cases increases significantly. Usually heart rate rises to 150 bpm, in young people it can be determined in the region of 200 bpm, while in elderly patients with heart rate is low - about 120 bpm.
The clinical picture largely depends on the concomitant pathology of the heart. In the presence of heart failure, ischemia or heart disease, symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and feeling of "jumping off the heart from the chest" can be detected.
Causes of Sinoatrial Tachycardia
The appearance of the pathology is associated with structural-functional inhomogeneities observed in conducting a wave of excitation in the sinus node and surrounding the heart muscle of the right atrium.
The disease is often diagnosed with lower myocardial infarction, as well as the development of the pathology is observed in coronary artery disease and valve malformations. The incidence of cardiological pathology in CT is higher than in other supraventricular tachycardia.
Diagnosis of sinatricular tachycardia
For diagnosis, an ECG study is conducted, in standard 12 leads. If the signs on the electronogram are identical to sinus tachycardia, but the clinic shows that the course of the disease is characterized by paroxysmal attacks, then the pathology is defined as a sinatricular tachycardia.
To detect the dependence of the onset of CT from the prior atrial extrasystole, transesophageal electrical stimulation of the atria is used.
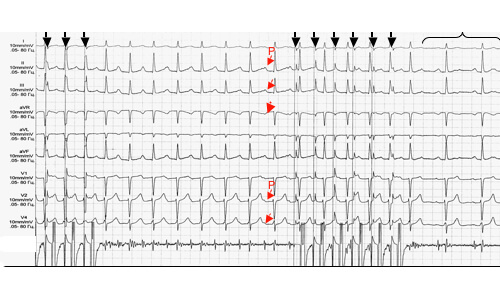 The photo shows the stimulation and cure of a ST attack, which developed at a heart rate of 140 beats / min. For induction, frequent atrial stimulation is used. The red arrows point to the teeth P during CT, which do not differ in shape from those recorded at normal sinus rhythm
The photo shows the stimulation and cure of a ST attack, which developed at a heart rate of 140 beats / min. For induction, frequent atrial stimulation is used. The red arrows point to the teeth P during CT, which do not differ in shape from those recorded at normal sinus rhythm
Treatment and prevention of sinatricular tachycardia
Patients with sinatricular tachycardia should be aware that this pathology is not simple, it can manifest itself at the most inappropriate time, therefore it is worth taking a responsible approach to the treatment process. For example, during paroxysm, it can be stopped by vagotonic tests. In the event of their ineffectiveness, adenosine is administered.
The use of electrocardiogram during synodial tachycardia is ambiguous. With its help it is possible to stop paroxysms, but in some cases the EKS provokes an attack.
If sinus tachycardia often uses radiofrequency ablation, then in the case of sinatralial tachycardia, this method does not provide the expected results. This is due to the fact that the pathway through which the wave of excitation diverges is not the only one; there may be several channels, therefore, it is not always possible to conduct an exact destruction of pathological sites.
Prophylaxis of sinatricular tachycardia is to prevent attacks, for which beta-blockers are used. Sometimes the patient is additionally prescribed digoxin and calcium antagonists.
