Recurrent tachycardia
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-14
Recurrent tachycardia (RT) is also referred to as non-paroxysmal or continuous-recurring. In its development may affect various departments of the heart (atrium, ventricles).Diagnosed at different ages, including infants.
The occurrence of recurrent tachycardia is detected much less frequently than it occurs with paroxysmal tachycardia. For example, among infants, the incidence of pathology is 1 RT in 333,300 live children, according to studies in the UK.
Very often the disease is asymptomatic, but it can quite rapidly lead to the development of heart failure. Therefore, it is important, at the slightest suspicion of cardiac pathology, to perform diagnostics, followed by, in most cases, catheter ablation.
Video Tachycardia. What is that What to do Tips for parents
Description of recurrent tachycardia
Until the end, the pathological physiology of RT has not been studied to date. According to some assumptions, recurrent tachycardia is formed as a result of the action of microscopic tumors that may resemble myocardial hamartomas. In the clinic, a similar pathology is known as histiocytic cardiomyopathy.

Other researchers point out that the basis of the pathology is the disruption of the formation of electrical impulses, which can be presented in two versions. The first is connected with trigger activity, which is created on the background of the effect of late depolarization. In the second case, pathological automatism is observed, which triggers the process of formation of a rapid heartbeat.
Symptoms of recurrent tachycardia
For a disease characterized by prolonged attacks of the heartbeat. Patients can complain about the feeling of "leaping heart", "jumping off heart from the chest", it becomes difficult to make a full breath.
In a recurrent tachycardia, 10% of the time goes through attacks during the day.
In some cases, the pathology proceeds asymptomatic or the symptoms of the disease are poorly expressed. Then the symptoms of rhythm disturbance are determined by instrumental research methods or during auscultation of a heartbeat by a doctor.
Causes of recurrent tachycardia
To date, they have not been fully explored. The development of the disease in infancy, often after 3 to 30 months, indicates that there is a hereditary factor. Sometimes paroxysms depend on physical activity. Some cases of development of RT in professional athletes are described. Yet to reliably name the causes of the appearance of recurrent tachycardia is still not possible.
Types / photos of recurrent tachycardia
The pathological process is capable of affecting such parts of the heart as the atrium and the ventricles.Correspondingly, recurrent ventricular tachycardia and recurrent atrial (supraventricular) tachycardia are distinguished.
Recurrent ventricular tachycardia
The second common denominator of the pathology is the non-paroxysmal continuously recurrent ventricular tachycardia (NSCLC). In this form of the disease, pathological rhythms often follow from the right ventricle, namely from the outgoing tract. Therefore, ventricular tachycardia is still known as ventricular tachycardia from the outgoing tract (right ventricle).
The course of the disease is characterized by short but frequent "salvos" of the heartbeat, when the heart rate rises to 150 beats / min. In children, the heart rate can be from 170 to 440 beats / min. Sometimes, instead of attacks, there are isolated extrasystoles that are combined with a long sinus rhythm. Nevertheless, according to studies, such manifestations of the disease still remind RT.
Recurrent atrial tachycardia
During an attack, CT heart rate may rise to 140-180 beats / min. With daily observation of a patient, it is often noted that a higher rate of development is observed - from 105 to 170 beats / min. Patients often do not make special complaints, all the illness has a clear clinical significance. First of all, this is due to the fact that the long course of pathology can lead to a decrease in the ejection fraction, the development of arrhythmogenic dysfunction of the ventricles, in some cases dilatation of the right and left atrium develops.
Diagnosis of recurrent tachycardia
First of all, standard electrocardiography is performed. With its help, the following attributes of RT are determined:
- With ventricular recurrent tachycardia, widespread ventricular complexes and high-amplitude teeth R. are often determined which, depending on lead, can have positive or negative deviations.
- At atrial recurrent tachycardia, changes in sinus rhythm, deformation of the tooth P, and an increase in the frequency of heart contractions can be observed.
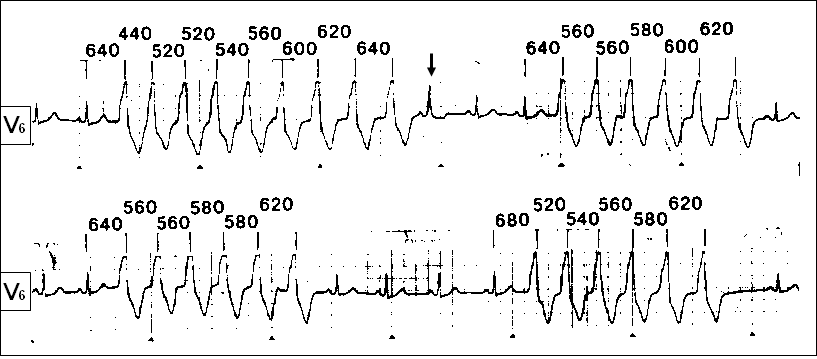
Holter monitoring is also used to help determine the duration and frequency of seizures within a day or three. An electrophysiological study is also carried out, which is especially relevant in the case of targeting a radiofrequency catheter ablation.
Dosage-assisted samples are assisted in the diagnosis of ventricular RT. With their help, tachycardia depends on sinus rhythm. Some patients have an increase in sinus activity when performing physical loads, and with the background of this decrease the appearance of ventricular ectopic activity. If the physical load is reduced, then the RT begins to appear.
ECHO KG is another study that is shown to all patients in the RT. It is performed to evaluate the activity of the valves of the heart, the thickness of the heart muscle, confirmation or elimination of myocardial hypertrophy.
Treatment and prevention of recurrent tachycardia
Emergency assistance is available to eliminate seizures. In particular, lidocaine is used, which is administered at a dose of 1-2 mg / kg. With this medication, heart rhythm slows down. If it is not possible to use lidocaine, or after its introduction there is no effect, then amiodarone is administered.
During a recurrent tachycardia, using cardioversion is inappropriate because it does not produce a proper result.
Prevention of relapsing tachycardia is to prevent the development of arrhythmia after cessation of an attack. To do this, use the same amiodarone or flekainide. If necessary, the therapy is supplemented with beta-blockers. RFA is an extreme method of treatment and can be performed after an assessment of the patient's condition.
If the patient is a professional athlete and he has a question about participation in the competition, then radical treatment using the RFA and further surveillance should be conducted. The lack of attacks for 4 weeks after treatment allows you to return to training under medical supervision.
Prognostic value for recurrent tachycardia is relatively favorable. Pathology does not provoke the development of ventricular fibrillation, but with prolonged flow can complicate the condition of the patient, contributing to the emergence of heart failure.
