What does left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy mean?
Author Ольга Кияница
2019-01-31
The left ventricular hypertrophy (GNLD) is an abnormal expansion and thickening of the walls of the left lower chamber of the heart, which performs the main job of pumping blood over a large circle of blood circulation. LFS in some cases is considered a serious pathology due to the gradual progression of disorders. The clinic becomes especially pronounced, when the left ventricle is overloaded with work. As a result, the body functions inefficiently, which, in turn, can lead to additional cardiovascular complications.
In modern medicine, hypertrophy of the left ventricle is regarded as a specific, that is, the most characteristic, heart failure in hypertension.
It is important to know that with hypertrophy of the left ventricle, the risk of developing heart failure (CH) and sudden death increases. It is also noted the dependence of the frequency of occurrence of HDL on age and sex. In view of this, it is not always possible to answer the question clearly, which means hypertrophy of the left ventricular myocardium.
Video: LVH - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Symptoms
Description of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy
Hypertrophy of the left ventricle should not be taken lightly. The fact that this pathology can develop without the slightest manifestation makes it a rather unfavorable disease, which can cause serious damage to health due to damage to the chamber of the left ventricle. Not to mention that when the wall of the muscle is thickened and enlarged there is a risk of a number of additional complications.
LFH can lead to low blood supply and weakening of the muscle tissue, which in turn contributes to the poor functioning of the heart chamber and the reduction of blood flow or even the complete cessation of the work of the left ventricle.
On the other hand, if LVH is detected in the early stages and the treatment is properly performed, serious complications may not arise. In order to prevent the pathological condition, it is necessary to constantly monitor blood pressure, to adhere to the basic rules of healthy eating and to observe the appropriate way of life.
Mechanism of development of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy
LHF gradually develops as a result of increased heart load. This is often associated with some of the major diseases, such as:
- arterial hypertension;
- aortic stenosis;
- aortic regurgitation;
- mitral regurgitation;
- coarctation of the aorta.
With these and similar pathologies there is a long overload of the left ventricle. Also, LVH can cause coronary artery bypass grafts. In particular, normal tissue of the heart muscle (myocardium) tries to compensate for hemodynamic disorders due to low blood supply (ischemia) or complete cessation of blood supply to the myocardium (infarction).
Because the left ventricle is overloaded due to these factors, its muscle tissue thickens and increases in size. At the same time myocardium loses its elasticity, because of which the heart works inefficiently. As a result, the body does not pump blood with the required force and in the required volume.

Causes of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy
The underlying causes are cardiovascular diseases, such as arterial hypertension and valve malformations.
Additional factors for the development of LNG:
- Age - the older the person becomes, the greater the likelihood of developing left ventricular hypertrophy.
- Weight - in case of overweight or obesity, the risk of developing LHL is significantly higher than in the absence of these pathological conditions.
- Genetic predisposition - the pathology is more likely to be encountered in a burdened family history with cardiovascular diseases, which can lead to hypertrophy of the left ventricle.
- Paul - From the standpoint of various studies, women are more prone to hypertension, one of the main causes of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy compared with men.
According to Framingham's study, left ventricular hypertrophy occurs in 16% of men and 19% of women before the age of 70, while in older people the following percentages are observed: 33% and 49%.
Additional risks of left ventricular hypertrophy
In addition to the dysfunction of the left heart chamber against the background of LV hypertrophy, other complications that are associated with ineffective myocardial work may occur. In particular, an increase in the muscle tissue of the heart means that the wall becomes weaker, while losing its elasticity. In this way, the chamber does not fill in properly, and the pressure in the heart decreases, which creates an additional force load on the myocardium. This also leads to a decrease in blood supply to the heart, since blood vessels supplying the myocardium are compressed.
The left ventricular hypertrophy tends to cause an abnormal heart rhythm known as arrhythmia. An irregular or rapid heartbeat may also develop in the type of atrial fibrillation, which reduces the blood flow efficiency of the body. In the worst case, hypertrophy of the left ventricle leads to a sudden and unexpected stop of the heart, and therefore to death.
Diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy
Symptoms of left ventricular myocardial enlargement at the beginning of the disease may be absent. This is due to the fact that in the early stages of hypertrophy of the left ventricle still retains the normal function of the heart. The cardiac muscle tends to gradually change, but eventually the myocardium becomes denser and rigid, with the background of which the symptoms become noticeable.
Symptoms of left ventricular hypertrophy may include:
- Shocking breath.
- Fast tiredness.
- Chest pain after workout.
- Involvement of heartbeat.
- Dizziness
- Spontaneous loss of consciousness.
If any combination of these signs arises, it is recommended that you contact your doctor immediately. Especially, do not hesitate if you have to experience the following:
- Chest pain that lasts more than a few minutes.
- Heavy breathing.
- Severe, repetitive dizziness or loss of consciousness.
The diagnosis of hypertrophy of the left ventricle is based on a thorough study by the physician of the history of the disease and physical examination of the patient. Then the doctor will appoint several studies. Additional tests for diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy include:
- Electrocardiography (ECG ) - this diagnostic method is based on the measurement of electrical signals that are produced when the heart is contracted.
- Echocardiography (echocardiography) - The test works by using sound waves that produce myocardial images in real time. With the help of the echocardiogram, muscle tissue thickening may be detected, and the amount of blood that passes through the heart is determined at each stroke.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a highly sensitive device for visualizing various organs, including the heart.As a result of the study, detailed images are obtained to detect any anomalies.

Hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart on the ECG
There are many criteria for the diagnosis of HLG. The most commonly used are:
- Sokolov-Lyon criteria (wave depth S in V1 + is the highest wave height R in V5-V6, that is> 35 mm);
- Voltage criteria (to be supplemented by non-inferior signs, which are considered as diagnostics of LHZ).
Voltage criteria
In the diagnosis of hypertrophy of the left ventricle on the ECG, these criteria are still known as the Cornell Voltage Index.
Standard References
- Rib R in I lead + tooth S in III out. more than 25 mm.
- Rib R in aVL shaft. more than 11 mm.
- Rib R in aVF shaft. more than 20 mm.
- Socket S in aVR out. more than 14 mm.
Breast Cancer
- Rib R in V4, V5 or V6 out. more than 26 mm.
- Rib R in V5 or V6 out. plus tooth S in V1 out. more than 35 mm.
- The largest tooth R plus the largest tooth S in the thorax is more than 45 mm.
Indirect signs
- The increase in the peak time of the tooth R is more than 50 ms in a well. V5 or V6.
- The presence of depression (decrease) in the segment ST and inversion (elevation) of the tooth T in the left-hand side, indicating left ventricular overload.
Additional changes in electrocardiograms observed with LDZ
- Increase left atrium.
- The deviation of the electric axis to the left (although it can also be normal or horizontal).
- ST in the "right" chest lead V1-3 (which "does not match" with deep teeth S).
- Definition of waves U (often proportional to increase of amplitude QRS).

LNG according to the voltage criteria for ECG evaluation: S prick in V2 otv. + tooth R in V5 otv. more than 35 mm.
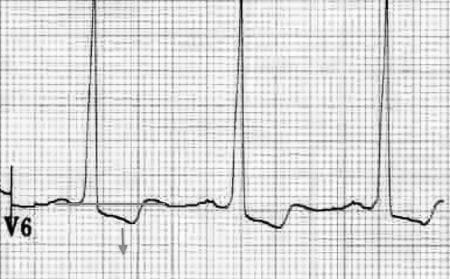
Structural deformation of LV: depression of the segment ST and inversion of the tooth T in the thoracic nodes.
It is important to note that the presence of only voltaic criteria is not an exact indication of the LNG.
An electrocardiogram is an insensitive method of diagnostics. For example, in patients with clinically significant left ventricular hypertrophy observed with echocardiography, a relatively normal electrocardiogram can be determined.
Video: LVH, RVH (left ventricular & right ventricular hypertrophy) EKG criteria
Answers to Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current treatment for left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy?
The treatment of LHH is primarily due to the elimination of the underlying cause. Medical or surgical effects may be involved, which depends on the main disease and condition of the patient.
Key strategies for the treatment of HLZ depending on the cause:
- Hypertension is treated by a change in lifestyle and medications.
- The stenosis of the aortic valve is mainly eliminated surgically.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can be treated with drugs and surgical methods with the implantation of special devices.
- Athletic LV hypertrophy does not require treatment.
Treatment of hypertension, due to which the LSH developed
In this disease, the following principles of therapy are used.
1 Changing lifestyle:
a . Loss of weight - LNG is more likely to occur in people with obesity, regardless of the level of arterial pressure. A study of weight loss in such cases has shown that such a change positively influences the course of the LHZ.Additionally, control over arterial pressure improves.
b . Healthy Nutrition - With LNG , you need to eat more fruits and vegetables, reduce the consumption of refined carbohydrates and foods saturated with fats.
c . Salt restriction - you should reduce the amount of salt used and do not eat food containing a large amount of salt (dried fish, sprats, cheeses, sausages).
d Regular physical activity - it is worth doing exercises lasting at least 30 minutes 3-4 times a week. You can try lively walking for 30 minutes every day. If there is any other heart disease or if you have shortness of breath during physical load, then you should first consult with the attending physician.
e. Smoking cessation.
f Do not drink alcohol , in some cases, it can be harmed to the body, even if you use moderate amounts of alcoholic beverages.
g. Managing stress - Meditation and other relaxation methods may be helpful.

2. Drug treatment:
a. Thiazide diuretics - Medications of this type can promote blood circulation, further reducing blood pressure. Of this pharmacological group, chlorthalidone (Thalitone) and hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide) are often prescribed. They can be used as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs. This is the first version of antihypertensive therapy, but if necessary, the doctor may prescribe other medications.
b. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (iApf) - these drugs expand blood vessels, resulting in lowering blood pressure. When the blood pressure is low, the load on the heart muscle also decreases, and the blood flow through the heart becomes more intense. Examples of drugs from this group include captopril, enalapril (Vasotec), and lysinopril (Zestril). Side effects can be expressed in an irritating dry cough.
c. Angiotensin receptor blockers (BAR) have similar effects with ACE inhibitors, but do not cause the development of a permanent cough. Examples from this group of drugs are: losartan (Cozaar). Usually, ACE inhibitors and BAR are not combined, as this may lead to an increase in potassium in the body (hyperkalaemia).
d Blockers of calcium channels (BKC) - these drugs prevent the penetration of calcium into the cells of the heart and the walls of the blood vessels, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure. Examples from this group are amlodipine (Norvasc) and diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac).
e. Beta-adrenoblockers . Drugs such as atenolol (tenormin), acetobutolol (Sectral) can lower heart rate, reduce arterial pressure and prevent some adverse effects of stress hormones (adrenalin). Beta-blockers are usually not prescribed as an initial treatment for hypertension. The doctor may recommend adding beta-blocker if another type of treatment was ineffective.
Treatment of aortic valve stenosis, which caused left ventricular hypertrophy
When aortic valve stenosis, the aortic opening becomes insufficient for passing blood. The left ventricle should work harder to push blood, which increases the load on the heart. In such cases, a surgical operation is performed to reconstruct the changed valve or replace it with an artificial or fabric valve.
Treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, which can also be the cause of LHH
In hypertrophy of the left ventricle associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, medications, surgery, device implantation, and lifestyle changes can be used.
1. Changing the way of life is the same as with hypertension. However, it is necessary to clarify from his doctor, whether it is possible to train or not, which exercises are appropriate, how long and with what intensity they need to be performed.
2. Drugs for relaxing the heart muscle and slow heart rate:
a. Beta-blockers are metoprolol, propranolol and atenolol
b. The blockers of calcium channels are verapamil, diltiazem.
c . If there are any arrhythmias, then amiodarone or other antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed.
d Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots - warfarin.
3. Surgery:
a. Removal of part of thickened septum between ventricles.
b. Implantation of cardioverter defibrillator . The device is usually embedded if there is a life-threatening arrhythmia or increased risk of sudden death due to cardiac arrest. This small device continuously controls the heartbeat. If there is a life-threatening arrhythmia, then an automatic blocking of electric strokes occurs with subsequent stimulation of normal heart rhythm.
With athletic hypertrophy, hypertrophy of the left ventricle may also occur. It does not require specific treatment, but it is still better to reduce the intensity of the workout for 3-6 months. During this time, ECG and echocardiography can be repeated to reevaluate the thickness of the left ventricle.
Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy by folk remedies practically does not yield results if the disease is already developing in full swing. Such methods of exposure should be used only for the prevention of major diseases such as hypertension and diabetes mellitus.
Video: How to treat Left Ventricular Hypertrophy? - Dr. Durgaprasad Reddy B
What diet should be used for hypertrophy of the left ventricular myocardium?
The best way to prevent hypertrophy of the left ventricle is to follow a healthy lifestyle in the heart, in which dietary nutrition is of great importance.Additionally, as noted above, you must regularly exercise, maintain a healthy body weight, refuse to smoke and drink alcohol, control the level of cholesterol, glucose and arterial pressure. But the special value is the diverse and balanced nutrition with low salt content.
The diet plays a dominant role in the prevention of heart and vascular diseases, including hypertrophy of the left ventricle. Particularly important is the consumption of omega-3 fatty acids, deficient in the current diet. It has been scientifically proven that omega-3 plays an important role in reducing the risk of developing cardiovascular system pathologies.
Omega-3 fatty acids are mainly found in sea fish - salmon, tuna, mackerel or sturgeon, as well as in green leafy vegetables, in nuts and in vegetable oils (for example, flaxseed and canola). It is recommended that you eat fish at least twice a week in order to guarantee the necessary amount of essential fatty acids.
Various clinical trials have shown that omega-3 fatty acid supplements can reduce the incidence of cardiac pathologies, reduce the development of atherosclerosis and prolong the life of patients with left ventricular hypertrophy.
The best recommendations for using a diet with LV hypertrophy are as follows:
- The food should contain a low level of animal fat, with a predominant amount of whole grains, fruits and vegetables.
- It is necessary to introduce into the habit of buying products in supermarkets to read their composition on labels, which pay special attention to the level of saturated fats. In particular, one should look at the words "hydrogenated" or "partially hydrogenated", often indicated on labels. It is not necessary to eat products with these ingredients as they saturate the body with "harmful" fats and trans fats.
- It is important to avoid or reduce the amount of saturated fat in the diet (more than 20% of the total fat is considered high). Consuming saturated fats in too much is one of the key risk factors for heart disease. Products rich in this type of fat: egg yolks, hard cheeses, whole milk, cream, ice cream, butter and fatty meat, as well as large portions of meat.
- It is worthwhile to give a preference to a skimmed protein diet containing soy, fish, non-fat chicken, lean meat and skim or 1% dairy products.
- It is important to limit the amount of processed and fried food that many people today use.
- It is necessary to use less baking products of store cooking (for example, brooches, cookies and crackers), since they can contain a lot of saturated fats or trans fats.
- It is necessary to use healthy ways of cooking fish, chicken and lean meat - it is a grill, boiling and baking.
- A diet is considered healthy if it is rich in fiber. In particular, it is recommended to use oats, cuts, peas and lentils, legumes (such as beans, black beans, ordinary white beans), some cereals and brown rice.
- The best solution is to refrain from visiting restaurants and other fast food establishments where healthy diet options are difficult to find.
DASH diet with left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy
Practicing low-salt diet (DASH-diet) with hypertrophy of the left ventricle helps to reduce arterial pressure, which means to improve the patient's condition. The beneficial effect on arterial pressure with LSH is sometimes observed after several weeks of its application.
The DASH diet is rich in essential nutrients and fiber. It also includes products that are saturated with potassium, calcium and magnesium. Additionally, there is a lower sodium content (salt) than in a typical diet.

What are the best exercises for hypertrophy of the left ventricle?
The left ventricular hypertrophy, if severe, can ultimately worsen the function of the heart due to the reduction of the strength of the contractions. The best measure for prevention of LFL is to prevent and adequately control high blood pressure using low-salt diet, exercise and the administration of appropriate antihypertensive drugs.
Maintaining an active lifestyle with a moderately high level of aerobic exercise can reduce the chances of occurrence of LHZ or diminish the severity of the disease.
Positive changes in well-being are especially noticeable in people who change their habits and start to lead a more active way of life. Regular exercises, such as walking, cycling , about four hours a week, reduce the risk of developing left ventricular hypertrophy. It has also been proved that the physical load in reasonable limits helps to improve the condition of patients with long-lasting hypertrophy of the left ventricle. In particular, programs of rehabilitation , based on complex physical exercises, are chosen, taking into account individual peculiarities of the patient, are used.
The program of exercises is based on the criteria, corresponding to the medical and cardiovascular indications of the patient:
- Modality : Continuity of exercise is important for patients with left ventricular hypertrophy. During the training, various large muscles are used. For this, swimming, cycling, walking, etc., are best suited. Regular exercise is carried out by conditioning the cardiovascular resistance.
- Frequency : The minimum duration of a workout is three weeks, then a week break can be done and appropriate exercises are performed again for three weeks.
- Duration: The workout should consist of periods of warm-up and cooling, stretching exercises and flexibility, as well as cardiovascular exercises lasting from 20 to 40 minutes at a continuous pace or at intervals.
- Intensity: should be moderate and comfortable, usually with a maximum functional capacity of about 40-85%.
- Gradual progression : Each program should develop slowly but with gradual progress regarding the duration and intensity of the exercise. Such dynamics is extremely necessary for patients with hypertrophy of the left ventricle.
During exercise, blood pressure may increase. In this regard, it will be necessary to reduce the impact of the stress factor before beginning the exercise program.
Is there a difference between the physiological and pathological hypertrophy of the left ventricular myocardium?
Hypertrophy of the myocardium can be defined as an adaptive state of the heart, in which one or both ventricles increase due to the growth of muscle mass in response to increased stress. If the proportionality between myocytes, interstitium and vascularization is maintained against the backdrop of an increase in the muscle mass of the ventricles, then they speak of the physiological hypertrophy of the left ventricle . This state can be fully regressed to some extent, especially when physical training is stopped.
In some cases, the connection between the various components of the enlarged myocardium is disturbed, then a diagnosis of the pathological hypertrophy of the LV is established . Most often, it is caused by abnormal stimuli, such as arterial hypertension or heart disease.
The right ventricle adapts to the hypertrophy of the left ventricle, caused by physical training. This happens in a "mutually beneficial way" and without changing the functional properties of the myocardium. On the contrary, in patients with left ventricular hypertrophy due to arterial hypertension, deterioration of the diastolic function is observed.
Conclusion
Even if there is a slight decrease in blood pressure, it may be enough that the hypertrophy of the left ventricle proceeds more favorably. The same applies to weight correction or refusal from bad habits. All these positive changes help the heart to work better: decreases the number of beats per minute, improves contractile function and develops new arteries. Also, exercising and proper nutrition help control blood pressure, cholesterol and glucose in the blood to the proper level.
Video: Can one live a normal life with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy? - Dr. Durgaprasad Reddy B
Similar articles

Irregular heartbeat, with a slow or slow heartbeat. It manifests itself against a background of hypertonic disease. It may develop due to a hypertensive crisis. It is considered a variant of the complication of the underlying disease, therefore it is necessary to carry out timely treatment.
Hypoxia is a pathological process that develops in tissues when their oxygen demand for its quantity in the cells does not match. This leads to a disruption in the formation of energy necessary for the operation of organs. Myocardial hypoxia occurs with an oxygen deficiency of the heart muscle.

Frequent cases when in absolute, at first glance, health a person suddenly dies. In this case, we can talk about physically trained young people, like Jesse Marunda (American athlete) and Miklos Feher (Hungarian football player). In both victims, as in many similar situations, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy was determined, which caused their death.
