Acquired heart defects
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-03-04
Acquired heart defects (PPP) are still known as valve dysfunctions. They represent a cardiac disorder associated with changes in the morphology and functional capabilities of all or individual elements of the valve apparatus.
The share of acquired heart defects accounted for up to 25% of all organic heart lesions. In this case, the lesions are more susceptible to the valves of the left half of the heart than the right one.
The defects of the heart may be expressed in a stenosis or, on the contrary, insufficiency of the valves. Also isolated are combined lesions, including symptoms of both insufficiency and stenosis of the valve apparatus. In most cases, the development of the pathology is directly related to the presence of an infectious agent in the body. There are other predisposing factors in the development of PPP, which are determined during the examination of the patient.
Video to Live! Death of the heart is mitral stenosis
Classification
Acquired heart malformations are classified according to different characteristics, but they are most commonly shared:
- on the degree of severity of the PPP clinic (without significant manifestations, moderate clinic and pronounced);
- by etiology (atherosclerotic, rheumatic, bacterial, syphilitic, etc.)
- on the degree of disruption of the circulatory system (compensated, subcompensated and decompensated).
According to the location of the affected valve, the following defects are distinguished:
- monovalent (defect of mitral, tricuspid or aortic valve);
- combined, which can be double-valves and three-valve.
There are 8 types of vices that are associated with four valves:
- Aortic valve - may be aortic valve stenosis and insufficient aortic valve.
- Mitral valve - there is mitral valve stenosis and mitral valve deficiency.
- Tricuspid valve - Tricuspid valve stenosis and tricuspid valve insufficiency.
- Valve of the pulmonary trunk - isolate the stenosis and insufficiency of the valve of the pulmonary trunk.
Reasons
In most cases, the acquired heart defects develop on the background of infectious processes, with 50% of patients on PPPs becoming those due to rheumatism. This disease causes, in almost 90% of cases, the formation of stenosis or mitral valve insufficiency; aortic and tricuspid valve may also be affected.
Other causes of PPP infectious genesis include syphilis and bacterial endocarditis, which affects the aortic valve, rarely - tricuspid.
The clinical picture of atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease is often complemented by acquired heart defects. In the context of atherosclerosis, the aortic valve is mainly affected, and in the case of IBD, mitral insufficiency is often formed.
In rare cases, PPPs are formed due to the tumor process, heart injury, or due to the accumulation of parasites.
The education of acquired vices occurs in several ways:
- Formation of stenosis due to scarring of the affected valve valves. Also the cicatricial rigidity of the valves together with the subclavic structures is formed.
- The deficiency of the valve arises as a result of the formation of scars on it, deformation, it can also be destroyed or damaged.
The valve stenosis leads to the formation of anatomical obstacles to the blood flow in the heart cavity, and insufficiency - to the dynamic obstacles that contribute to the return of blood through the damaged valve. Therefore, heart disease is dangerous due to the development of various serious complications.
Kinds / photos
Acquired heart malformations are classified into 8 types that are associated with four heart valves:
- stenosis and failure of the aortic valve;
- stenosis and mitral valve deficiency;
- stenosis and insufficiency of tricuspid valve;
- stenosis and insufficiency of the valve of the pulmonary trunk;
The most common of the listed PPPs will be considered in detail.
Insufficiency of mitral valve
The defect is characterized by the return of some blood from the left ventricle to the left atrium through the poorly closed mitral valve openings. The disorder can be relative, then the folds themselves are not damaged, but the atrial-ventricular hole is expanded for a number of reasons, due to which such a pathology develops.
The organic defect in the type of mitral valve deficiency is mainly associated with rheumatoid endocarditis. At the same time, the valve leaf deflection is deformed, and various ulcers and polyps may form on them. Often this flaw is combined with the stenosis of the mitral opening.

Mitral stenosis
The disorder is still known by the term "left ventricular stenosis". It mainly forms on the background of rheumatism and is a narrowing of the mitral opening. Because of this flow of blood it is difficult to go from one department of heart to another. Prolonged development of the defect leads to dilatation of the right ventricle cavity and, as a consequence, an increase in blood pressure. In severe cases, right ventricular insufficiency is formed.
Video mitral stenosis. Hemodynamics for heart defects. - "Just about the complex"
Insufficient aortic valve
The formation of the presented vice is based on incomplete closure of the aortic valve flaps. A part of the blood ejected in the aorta by the left ventricle returns back, due to which pathology can lead to insufficient left ventricle. The formation of aortic valve deficiency may occur on the background of syphilis, septic endocarditis, arthritis, and rheumatism.
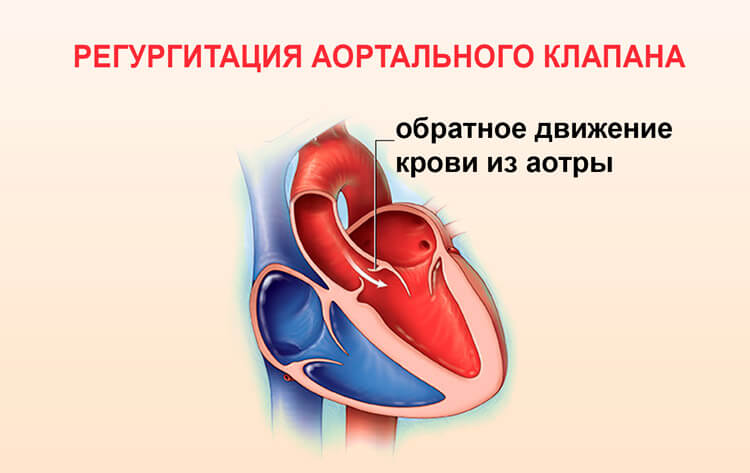
Stenosis of the mouth of the aorta
For various reasons, the aortic hole is narrowing, which makes it difficult to throw blood into the aorta on the left ventricle. Over time, the defect leads to an increase in the left ventricle, which in severe cases is complicated by left ventricular failure and cardiac arrest. The defect is characterized by rheumatic origin.

Insufficient tricuspid valve
With a violation of the development of a three-leaf valve, part of the blood from the right ventricle returns to the right atrium, since this valve is located between the right departments of the heart. The opening between the atrium and the ventricle may not completely close due to sclerosing valve valves. With the expansion of the right ventricle cavity, the atrial-ventricular opening is also often extended, which contributes to the development of relative insufficiency of the tricuspid valve. A similar defect is often combined with changes in aortic and mitral valve.
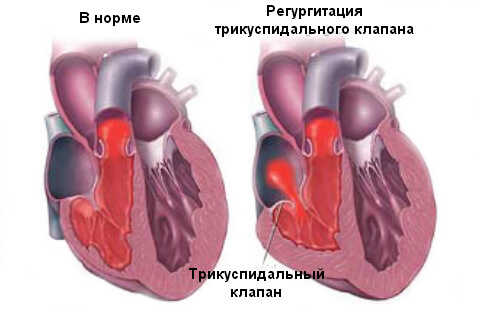
Mitral-aortic defect
At the same time, the pathological changes at the same time affect two valves - mitral and aortic. The narrowing of the mitral opening, which is combined with the disturbance of the functioning of the aortic valve, is most often determined. A combined defect in the form of stenosis of the aortic and mitral valve may also be formed.
Diagnostics
Today, various methods are used to determine the localization, the type and severity of heart disease. First of all, the patient is interviewed, then his objective examination, which in some cases may imply the idea of a type of vice.Palpation, percussion and auscultation are also important, for example, when the mitral stenosis can be heard, the "rhythm of the quail", also known as the three-part rhythm.
Clinic
Much depends on the severity of the defect, often expressed by the degree of hemodynamic disturbances. It is easier to make compensated forms of PPP, harder and harder - decompensated vices, when organic changes in different parts of the heart are observed.
Clinical picture of mitral valve prolapse
Complaints are most often manifested in the phase of decompensation of vice. During physical work, shortness of breath arises, which, in severe condition, begins to manifest itself in a resting state. Often, patients are disturbed by palpitations, dry suprapubic cough, and hypertrophy of the right ventricle is pain in the region of the heart.
When an objective examination of the patient can be noticeably affection nasolabial triangle, swelling of veins on the neck. In children, with the increase and expansion of the right ventricle, a "heart hump" is formed. When listening to cardiac activity, there is often a noise during systole and an accent of a second tone over the pulmonary artery.
Clinical picture of mitral stenosis
Patients may be disturbed by shortness of breath, which at first appears only during exercise or physical work, and when progressing the disease develops into rest. It is also often noted that the hoarseness of the voice is a dry cough that can reach the hemoptysis. In addition, patients may complain of pain in the heart and weakness.
With objective examination, pale skin is determined, the cheeks may be bluish, while the lips and tip of the nose have a bluish tinge. Strong thrills can be felt in the heart area. For this blemish is characterized by a three-part rhythm and noise at the top of the heart. In determining the pulsation on the left hand, it will be weaker than on the right side, with arterial pressure often decreasing due to a lack of cardiac output.
Clinical picture of aortic stenosis
For a long time, it almost never manifests itself, except that there was a narrowing of the aortic hole by ⅔ from the normal state. In such cases, patients complain of back pain, especially during physical work. There may also be a dizziness, and in severe cases, anesthetic conditions arise.
Progression of left ventricular failure is manifested by pronounced dyspnea, severe weakness and fatigue. In the stage of decompensation of the defect, swelling of the lower extremities and heaviness in the region of the liver are observed.
With objective examination, paleness of the skin, edema, acrocyanosis, veins on the neck are noticeable. When feeling in the region of the heart, a strong push is felt, pulsation in the hands is often weakened, systolic pressure can also be reduced.
Clinical picture of aortic valve insufficiency
The compensated form of blemish is almost non-existent. Occasionally, patients report an increased frequency of heart contractions, combined with pulsation behind the sternum. In the period of decompensation, there is a pain in the heart, crippling, of a type of stenocardia, while it is poorly converted to nitrates. The condition is aggravated by the presence of edema, shortness of breath, weakness and dizziness.
At an objective examination, the skin of the patient is pale, the peripheral arteries pulse, due to which there is a symptom of "dancing carotid". Changes in the limits of the heart in the direction of magnification, the impulse on the apex is often strengthened and displaced. At auscultatory listening, the tones are weakened, and organic and functional noise are determined. It also listens to the pathological tone of Traube, the double noise of Vinogradov-Dyrozier.Additionally there is an increase in pulse and systolic pressure, while diastolic is often reduced.
Instrumental survey methods
All patients with suspected heart disease should be advised to undergo echocardiography, which is necessarily supplemented by dopplerography. As a result, it is possible to determine the severity of the disorder and decompensation.
Additional survey methods:
- electrocardiogram;
- X-ray of the heart, which is performed in three positions (lateral, oblique and straight);
- phonocardiogram;
- computer tomography;
- laboratory tests.
Treatment
There are several ways to resolve the issue with acquired heart defects. Medication treatment is considered less effective, whereas complete cure is possible with successful surgical intervention.
Medicinal therapy
Suitable for those patients who have a compensated defect. It is also often performed before surgery. The main groups of drugs used during medication therapy for acquired heart malformations are as follows:
- beta-blockers;
- anticoagulants;
- cardioprotectors;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- cardiac glycosides;
- ACE inhibitors.
If a patient is contraindicated in surgical treatment, then a scheme of medical treatment is also prepared.
Surgical treatment
Conducted in cases where the patient has a sub-compensated or decompensated heart disease. Depending on the testimony, a suitable method is selected from the following:
- plastic surgery;
- valve-retaining;
- angioplastic
In severe cases, replacement of the valve may be required, which implies the installation of a mechanical or biological prosthesis. If necessary, reconstruction of the aortic root, atrioplasty or restoration of normal rhythm may be performed.
All patients who have undergone surgery have undergone a course of rehabilitation. It can consist of medical physical education, respiratory gymnastics, and the reception of medicines. In the period of rehabilitation, analyzes and studies are conducted to control the patient's well-being. This is especially needed when using indirect coagulants in the postoperative period.
Video Acquired heart disease: surgical treatment
Complications
Violation of the operation of the valve apparatus leads to a change in the blood flow in the heart organs, due to which the circulatory system disorder is manifested. Prolonged development of the disease provokes stagnant phenomena in the small and large circle of blood circulation.
Complications associated with PPP:
- enlargement of the right ventricle;
- enlargement of the right atrium;
- enlargement of the left ventricle.
Long-term implications of development of acquired heart defects:
- insufficiency of cardiac activity, first in a compensated form, and then in decompensated;
- heart stop.
Forecast and prevention
The favorable prognostic conclusion relates to asymptomatic acquired heart defects, as well as timely corrected conservative or surgical treatment.
An unfavorable prognosis is posed in the case of severe hemodynamic changes that significantly affect the work of the heart and the body as a whole. In the stage of decompensation, physical activity may also be significantly disrupted, due to which the patient is recognized temporarily or permanently incapacitated.
Prevention of PPS is as follows:
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases should be promptly eliminated by appropriate therapy.
- Immunity needs to be strengthened by suitable medications prescribed by the doctor.
- It is important to stop smoking and use caffeine-containing, alcoholic beverages in an increased amount.
- Body weight should be within normal limits.
- Physical activity should be maintained at an acceptable level.
Acquired heart defects during pregnancy
Among the pregnancies, the incidence of PPP often reaches 6%, with the share of mitral stenosis accounting for 3%.Depending on the degree of load on individual valves, their damage occurs to a greater or lesser extent. Most often, the function disorder is observed on the part of the mitral valve, then the aortic valve, the three-winged and the last one, the valve of the pulmonary trunk, are followed by the frequency of the defeat.
In 1991, Vanina L.V. offered to assess the risk of pregnancy and childbirth in pregnant women with heart malformations according to the following scheme (while other pathologies should be absent):
- The first degree of risk - the pregnancy is favorable, as the rheumatic process is in the stage of remission, and the expressed symptoms of heart failure are absent.
- Second degree of risk - rheumatism is in the active phase of development, in addition the initial signs of heart failure are determined.
- The third degree of risk - heart failure is in the stage of decompensation, with active rheumatic fever, there are signs of right ventricular failure and other disorders such as atrial flutter or hypertension in the pulmonary artery.
- The fourth stage of the risk - heart disease is decompensated, cardiac insufficiency is total, or there is marked left ventricular insufficiency. Rheumatic process is active, pulmonary hypertension, thromboembolism or atrial fibrillation may also be noted.
Pregnancy is tolerated at the first and second degree of risk and is not recommended for the third and fourth.
The drainage of pregnancy against the background of PPS can be complicated for the following reasons:
- In the first three months, the activity of the rheumatic process, in particular rheumatic heart disease, is intensified.
- In the second trimester of pregnancy there is an increase in the volume of circulating blood, also increases the minute volume of the heart, hemoglobin may decrease markedly.
- After 32 weeks an active set of weight is underway, the uterine's bottom is highly located, so blood circulation in the pulmonary artery may be difficult. The diaphragm capabilities are also reduced.
The genetic process leads to an increase in blood pressure, minute and systolic volume of the heart. After delivery, there is a sharp change in the pressure inside the uterus and abdominal cavity, which can lead to collapses.
The above factors, as well as many other causes, can significantly complicate the course of pregnancy against the background of acquired heart defects. Because of this, one should be very careful about your health and the condition of the baby. It is important not to slow down with the setting up of records, the implementation of all medical recommendations.
Pregnant with PPP may file the following complaints:
- weakness in the muscles and in the whole body;
- fast fatigue;
- drowsiness and weakness;
- shortness of breath with rapid heartbeat;
- heaviness in the legs.
Such symptoms can appear only under physical stress, but with the progression of blemish are often observed in a calm condition.
The pregnancy test with PPP is performed in the same way as in the normal state. Depending on the testimony, counseling of adjacent specialists (cardiologist, cardiac surgeon) may be prescribed. If the condition of the patient worsens, an appearance of signs of gestosis, FPN or premature birth occurs, an urgent hospitalization.
Treatment of pregnant women with acquired heart defects
The treatment of pregnant women with PPPs depends on the severity of the vagina and the presence of concomitant diseases. Under favorable conditions non-pharmacological therapy, based on a diet, observance of the mode of work and rest is carried out. In case of a venous return disorder, it is recommended to wear an elastic stocking.
Drug treatment is carried out with the obligatory participation of the cardiologist. Diuretics, cardiac glycosides, thrombolytics are used depending on individual indications. In the inactive form of rheumatic heart disease, an exacerbation prevention is performed, for which gentamicin or ampicillin is used. Additionally, preventive measures are used to reduce the systolic function of the left ventricle, which may be taken nifedipine.
Surgical treatment is used in cases where the condition of the pregnant woman with PPP has deteriorated significantly.The decision to choose a radical method is taken by the cardiostasis. The only thing to understand is that the installation of an artificial valve does not give full caution to the development of heart failure.
Planned hospitalization of pregnant women with PPP:
- Up to 12 weeks - to carry out an assessment of the general condition of the pregnant woman, for which appropriate analyzes and studies are conducted.
- During the period of 28-32 weeks - at this time the body of a woman is experiencing a heavy load, and especially the cardiovascular system, therefore, to support the woman is maintained therapy.
- Within 2-3 weeks before the PDR - antirheumatic and cardial therapy is performed to prepare a woman for childbirth.
Natural delivery is possible only with a favorable course of the underlying disease, and then during the attempts may be used to cut the crotch or overlay obstetric forceps. In other cases, when there are adverse signs of the development of the pathological process, delivery is carried out operatively.
Video Death of the heart is not a verdict. My pregnancy
Similar articles

Among all congenital defects, heart defects are the most common. Perhaps this is due to the most early and intensive development of the cardiovascular system in the first weeks of pregnancy. Whatever it was, but it is for newborns and their parents that it may later be necessary to endure the often vital surgical interventions.

One in 120 babies is born with a heart malformation. Some of them are heavy, but in most cases, they do not represent danger. Defects may include abnormal walls or heart valve shapes, as well as blood vessels that fit or depart from the heart.
During fetal development of the fetus under the influence of predisposing factors, normal formation of the cardiovascular system may be disturbed. As a result of this, congenital malformations are created that can be compatible and incompatible with life. The development of pathology is often associated with the wrong way of life of the mother during pregnancy, although in some cases, heredity plays a big role.
