Right ventricular heart failure
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-03-17
Right ventricular heart failure (PZHCH) is a heart disease, in which there is a violation of the right ventricle (PZ). Today, left ventricular insufficiency is more often diagnosed, although it is considered that the isolated PZHSH has a more unfavorable prognosis.
In the course of right ventricular heart failure is divided into acute and chronic, and in each case there are characteristic features in the part of the clinic, diagnosis and treatment.
PZHSN is also known as a "pulmonary heart", since the right ventricle puts blood through a small circle of blood flow passing through the lungs. The greater the disturbance of the activity of the childbirth, the more pronounced the clinic of the disease and the higher the risk of edema of the lungs, which may eventually result in the death of the patient. Therefore, it is extremely important to begin the treatment of the disease in a timely manner and carefully to prevent the recurrence of PFS insufficiency.
Video Right Sided Heart Failure - Explained in 2 Minutes (Right Ventricle Failure)
Reasons
There are two broad groups of factors contributing to the development of right ventricular heart failure.
- Primary failure of the right ventricle in the absence of pulmonary hypertension.
- Myocardial infarction
- Secondary renal failure with increased loading or volume of pumped blood.
- Pulmonary embolism
- Disease of the mitral valve with pulmonary hypertension
- Congenital heart defects
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Extensive lung resection
- Violation of the left ventricle
- Defect of interatrial septum
- Defect of interventricular septum
More recently, high mortality was observed among patients with isolated myocardial infarction, which led to overestimate the significance of the disease's risk.
Various congenital heart defects are often associated with a reflux, usually due to increased load, volume overload, or both. Defects in the septum are usually associated with PZHSN; as a rule, due to the fact that the blood is dumped from the left side of the heart to the right. Tetrada Fallo is another congenital malformation, in which hypertrophy of PC and, ultimately, failure of CVA occurs due to obstruction of the pulmonary artery, into which blood flows from the cord blood. In an adult with a recovered Fallot tetrad, a CVD can still occur due to pulmonary regurgitation, especially when the tricuspid valve is used to restore the structure of the affected vessel.
Risk factors
Factors of right ventricular heart failure may include:
- Age: Men 50 to 70 years of age often experience right-sided heart failure, especially if they have previously had a heart attack.
- Chronic diseases: Pulmonary diseases such as COPD or pulmonary fibrosis, diabetes, HIV, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or iron / protein accumulation can lead to right-sided heart failure.
- Irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias): abnormal heart rhythms, especially if they are very frequent and fast, can weaken the heart muscle.
- Pulmonary pathology : Blood clots or high blood pressure in the lungs can increase the risk of right-sided heart failure.
- Inflammation of the pericardium: the disease provokes a decrease in the size of the pericardial bag that compresses and tightens the cardiac muscle.
- Racial predisposition: African American men are at greater risk than others, developing right-side cardiac insufficiency.
- Some chemotherapeutic and diabetic drugs: Certain medications have been found to increase the risk of PBS.
- Valvular heart disease: Damage or defect in one of the four heart valves can interfere with effective hemodynamics.
- Viral infection: some viral diseases can damage the heart muscle, including the right ventricle.
Pathogenesis
The main stages of the formation of the PRSN:
- Expansion of the chamber of the PC leads to an increase in the tricuspid ring, which causes regurgitation through the tricuspid valve, which further aggravate the dilatation of the ventricle.
- Over time, hypertrophy of PW occurs as a natural response to increased stress.
- As the CV increases, the crescent cavity of the ventricle is broken.
- Interventricular septum extends into the cavity of LV. This is due to the fact that the pericardium restricts the space available for the expansion of the heart, and consequently, an increase in the size of the psoriasis should be accompanied by a decrease in the amount of LV.
- The displacement of the septum worsens the filling of the LV and, consequently, disturbs its function. This phenomenon is called ventricular dependence.
- As LV's dysfunction develops, systemic blood pressure and blood supply to the coronary arteries are reduced, which further exacerbates the labor.
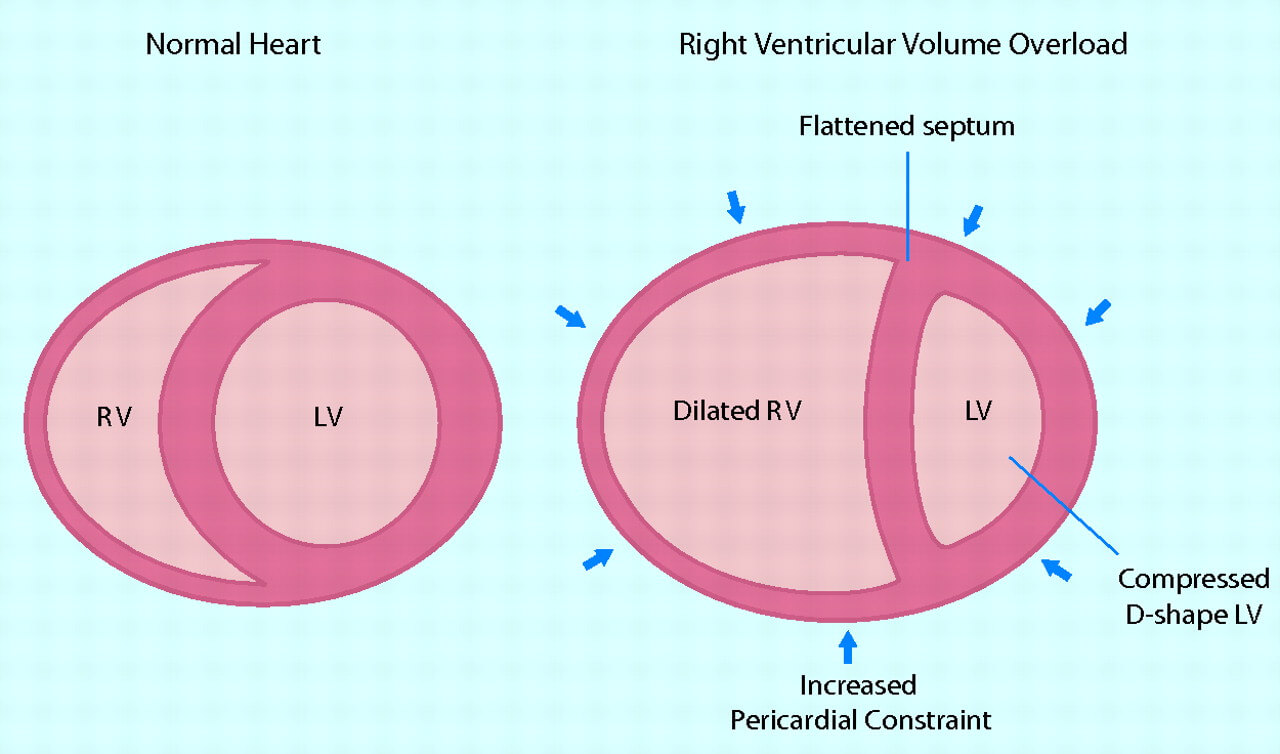
In the unfavorable development of PZHOS, high venous pressure is determined in combination with a decrease in systemic arterial pressure, which impairs the perfusion of the main organs. Such violations can lead to persistent circulatory failure, which ultimately causes failure of all organs and death.
Clinic
In the early development of right ventricular heart failure, the symptoms are weakly manifested. When attaching LV dysfunction, the clinical picture becomes more pronounced.
Signs and symptoms of heart failure are:
- The appearance of shortness of breath, first with physical activity, and then in a state of rest
- Orthopnea (semi-sentimental position)
- Chest pain
- Decreased arterial pressure
- Frequent heartbeat
- Tachycardia
- Fatigue and weakness
- Lack of urination or urine excretion in insignificant quantities
- Anorexia, weight loss, nausea
- Exophthalmos and / or visible eye pulsation
- Chills in the chest, often remotely audible
- Central or peripheral cyanosis, pallor
In severe cases, there is an ascites, an increase in the size of the liver or even anasarca.
Video Heart Failure - Symptoms and Treatment
Diagnostics
At the reception of the cardiologist, a physical examination of the patient is mandatory, during which it can be determined:
- peripheral edema;
- pulsation of jugular veins;
- hepatomegaly;
- systolic murmur of tricuspid regurgitation;
- second tone accent.

After an analysis of the general condition of the patient, instrumental methods of investigation are prescribed. Because of the unusual anatomy of the baby, evaluation of its function is a problem. However, technical advances, especially in the field of echocardiography and MRI of the heart, help to determine the function and volume of the right ventricle, as well as measurement of pressure in the pulmonary artery.
Instrumental research methods at PZHSN:
- Echocardiography
- Electrocardiography
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Roentgenography of the chest
- Invasive diagnostic methods
- Maximum stress testing
- Pulse Oximetry (Determining the amount of oxygen in arterial blood)
Electrocardiography
In most cases, the ECG is estimated within the normal range. When determining the deviation of the axis to the right, suspected pulmonary embolism.
Roentgenography of the chest
This method of research has limited possibilities and does not give a specific identification of right ventricular heart failure. Nevertheless, the expansion of the basement of LA and the veins that are suitable for the heart, as well as the oligomy of the chambers of the heart (the sign of Westermarck) - all this points to pulmonary embolism and PZHSN.
Invasive monitoring
The catheterization of the pulmonary artery is most often performed, which allows you to measure the pressure in the pancreas, the LA, to determine the LA occlusion and the magnitude of cardiac output. When each of these indicators is obtained, a difference in the primary PZHSH from the secondary, combined with increased cardiac load may be performed. Of particular importance is the transpulmonary gradient - the mean arterial pressure in the LA. Also, during the study, pulmonary vascular resistance, calculated by dividing the transpulmonary gradient into cardiac output, is determined. Important constraints that are taken into account when using an AA catheter are an unreliable measurement of cardiac output thermodilution with severe tricupidal regurgitation and the risk of blasting a flotation balloon in patients with severe pulmonary hypertension.
Echocardiography
Today, transesophageal echocardiography (TE echocardiography) prefers to evaluate PZHSN. In experienced hands, this method allows the immediate discovery of enlarged, hypertrophic or poorly contracted PK and associated disorders, such as tricuspid regurgitation and displacement of the interventricular septum.
The following tests may be useful in the initial assessment of supposed right ventricular heart failure:
- Complete blood test (PAK)
- Determination of the amount of iron
- Urine analysis
- The level of electrolytes
- Investigations of kidney and liver function
- Blood glucose level on fasting
- Lipid profile
- Thyroid Hormone Level (TTG)
- The level of the natriuretic peptide B-type and pro-B-type
Treatment
When determining right ventricular heart failure, different treatment strategies are used. First and foremost, the main, and then the additional ones.
The main therapy of PZHSN includes:
- Prevention of repeated attack development.
- Normalization of blood volume.
- Reducing the load on the heart.
- Prevention of hypercapnia and hypoxia.
Blood volume correction
Increased blood volume is normalized by reducing the amount of fluid and salt consumed. If this is not enough, diuretics and substitution renal therapy are used.
Artificial ventilation of the lungs
Helps to reduce the pressure in the capillary network in the lungs, which contributes to improving the general condition of the patient.
Inotropes and vasopressors
- Most often beta-agonists, calcium sensitizers and phosphodiesterase inhibitors are used. With their help reduce the load on the heart, increasing contractility and consumption of oxygen by myocardium.
- Levosimendan is indicated in those cases where it is necessary to reduce the pressure in the airway and improve the function of the breast.
- Norepinephrine, phenylephrine and vasopressin improve ventricular contractility and thus have a positive effect on perfusion of coronary arteries, but if they are not used properly, they increase the consumption of oxygen by myocardium.
- Milrinon and amrinone increase heart contractility through the non-beta-adrenergic mechanism.
Lowering the load
- Sildenafil is an oral drug, an enzyme called phosphodiesterase.
- Milrinon (PDE-III inhibitor): Reduces the pressure in the LA, can be introduced through a nebulizer.
- Systemic vasodilators - hydralazine and others, helping to normalize coronary perfusion.
- Recombinant MNP (cerebral sodium reticulum peptide) is a non-rheidide that reduces pre and post cardiac stress, thereby improving the function of the myocardium without inotropic effect.
Surgical treatment to support breast cancer
If medications are not effective in the treatment of right ventricular heart failure or the symptoms are very serious, implantation of the device for ventricular stimulation or cardiac transplantation may be required.
- Vaginal delivery supplementation (VAD) implant surgery: A special device after implantation helps to reduce weak cardiac muscle more effectively.
- Heart transplantation: an operation is performed when all other methods of therapy for PZHSN have not worked. The damaged heart is surgically removed and replaced by a healthy body from the deceased donor.
Forecast
Overall, despite a significant improvement in medical and hardware therapy, mortality among patients with heart failure after admission is 10.4% in the first 30 days, 22% in 1 year and 42.3% in 5 years.
Cardiac insufficiency associated with acute myocardial infarction has a steady mortality of 20-40%; the same figure reaches 80% in patients who suffer from hypotension (for example, with cardiogenic shock).
Cardiac insufficiency associated with systolic dysfunction is characterized by mortality of up to 50% in 5 years.
The following risk factors are additionally influenced by the prognostic conclusion of hospitalized patients:
- age (elderly and older);
- presence of concomitant pathology;
- the length of the hospital day.
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, the risk of death from pulmonary edema or cardiac output is very high.
Prevention
Far not all risk factors can be adjusted, which is why it is important to take steps that would reduce the likelihood of the development of PRH.
- In the presence of diabetes, it is necessary to observe that it is necessary to eat, how much nutrition is regularly and what level of glucose in the blood.
- Moderate exercises help improve blood circulation and reduce stress on the heart muscle.
- If you experience new symptoms or if you experience side effects from your medication, you should contact your doctor.
- It is important to maintain a healthy weight: Loss of extra pounds and maintaining weight within the normal range reduces the load on the heart.
- When determining sleep apnea, you should use the CPAP / BIPAP device every night.
- Lowering stress can help prevent a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- It is worth remembering the prescribed medications that should be taken in accordance with the prescriptions:
Additionally, it is important to reduce alcohol consumption, in some cases it may be necessary to stop drinking completely. You should also quit smoking because smoking has a very negative effect on the cardiovascular system.
Video Heart Failure. From what the heart is weakening

А из препаратов в аптеке,при сопутствующей фибрилляции предсердий и хронической почечной недостаточностью( категорически отказывается от госпитализации) какие варианты.Гемодиализ отказ- креатинин 675, клубочковой фильтрация 7.62, фибрилляция нормоформа( 60-80),АД 150/90(его стабильное),Принимает валсакор,кетостерил,Панангин.Есть какие то реально препараты в аптеке которые помогут- подскажите если можно.