Heart disease
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-03-17
Heart failure (PS) is an abnormal formation of the heart and adjacent vessels, which, in the absence of treatment, can lead to heart failure. All heart defects are divided into two large groups - congenital and acquired. When they determine medical treatment is ineffective, so for the complete elimination of the defect surgical intervention is used.
The first symptoms of heart failure can be determined after the birth of a baby, and in some cases the diagnosis of heart disease is exhibited during the period of intrauterine development with the help of an ultrasound scan.
Heartburn treatment involves open heart surgery to eliminate serious defects. A catheter with a special cylinder at its tip may also be used to open or expand valves / blood vessels. In some cases, devices are used as an embedded catheter to close pathologies or additional blood vessels.
Video to Live! Heart disease
Normal fetal blood circulation
Blood circulation in the fetus is different in comparison with children and adults.
In the usual case, all the blood going to the heart from the body (venous blood with low oxygen content) passes through the right atrium, and then through the right ventricle and enters the pulmonary artery, and from there into the lungs. Here, blood is saturated with oxygen from pulmonary alveoli, through which carbon dioxide is released. This blood, which is rich in oxygen and now called arterial, returns from the lungs to the left atrium and the left ventricle, and from there comes from the heart into the body through a large artery, called the aorta. Then it spreads through smaller arteries across all tissues and organs.
The fruit is in the uterus, where there is no access to the air necessary for breathing. Instead, he gets oxygen-filled blood from the placenta of the mother through the umbilical cord, while the lungs are filled with fluid in the meantime. Because the fetus does not breathe, only a small amount of blood needs to go through the lungs for their livelihood. The path through which the blood circulates through the heart and lungs is different from the fetus and the newborn.
Before birth, most of the venous blood entering the right side of the heart passes through the lungs filled with fluid and passes through two different short paths, which are:
- Oval openings located between the two upper chambers of the heart, right atrium and left atrium
- Arterial duct (botulla), which is a blood vessel that connects two large arteries, aorta and pulmonary artery.

Similar message paths change immediately after birth. During the passage through the birth canal fluid is squeezed out of the lungs of the newborn. With the first breath of the newborn, the lungs are filled with air, which is saturated with oxygen. The umbilical cord is then cut off and the newborn begins to receive oxygen through the lungs.
Thus, the oval hole and bottle ducts are no longer needed, and they normally shut down during the first few days - several weeks of life. As a result, the blood circulation of a newborn becomes the same as an adult person. Sometimes an oval hole does not close, but in most cases, this condition does not cause any health problems.
Types of heart defects
In the presence of heart defects hemodynamics changes as follows:
- Blood Flow Blood
- Regurgitation of blood flow
- Blockage of blood flow as it happens when a heart valve or blood vessel is damaged
Blood Flow Blood
Typically, the following types of shunting are distinguished:
- From right to left
- From left to right
Right-to-left bypass grafting involves the transfer of oxygen-rich blood from the right side of the heart to the left, where oxygen-deprived blood flows, resulting in arterial and venous blood mixed. The more venous blood is mixed with the arterial one, the more visual signs appear (hybridization of individual parts of the body, especially the lips, tongue, skin and fingers).
Many defects in the heart are characterized by a bluish tint of the skin (cyanosis). This sign indicates that there is not enough blood rich in oxygen. Congenital heart defect, which is often accompanied by cyanosis, is a Fallot tetrad.
The left-to-right bypass is based on the flow of oxygen-containing blood, which is pumped under high pressure from the left side of the heart, to the right side of the heart, where it is mixed with oxygen-deprived blood, sent through the pulmonary artery to the lungs. Left-side bypass makes blood circulation ineffective and increases the amount of blood flowing into the lungs, which sometimes also causes high pressure in the pulmonary artery. With time, the blood vessels of the lungs can be damaged and the right parts of the heart can be overloaded. Heart failure develops. Examples of violations in which left-to-right shunting occurs are defects of the interventricular septum, the interstitial septum, and the open arterial duct.
Repetitive flow of blood flow
When transposing large arteries, the normal position of the aorta and the pulmonary artery relative to the heart changes to the opposite. The aorta, which is the blood supply to the body, is connected to the right ventricle, and the pulmonary artery, the blood supplying lungs, is connected to the left ventricle. As a result, oxygen free blood circulates through organs and tissues, and blood-rich oxygen flows between the lungs and the heart. The body does not get enough oxygen, and severe cyanosis occurs within hours after birth.
Blood flow current
Obstacles may develop in the area of the valves of the heart or in the blood vessels that depart from the heart. Hemodynamic impairment is observed in the following cases:
- When narrowing the pulmonary valve (stenosis of the LC) or narrowing in the pulmonary artery itself (stenosis of the airway). At the same time the blood does not enter normal quantity in the lungs.
- Due to the narrowing of the aortic valve (stenosis of the AK) or blockage within the aorta itself (coarctation of the aorta), blood does not reach the entire body.
- The contraction of the three-leaf valve (on the right side of the heart) or the mitral valve (on the left side of the heart) also leads to a violation of hemodynamics.
Blood circulation can lead to heart failure.< With this condition, the heart can not normally pump blood. As a result, stagnant phenomena in the lungs are observed. Such is fraught with cardiac asthma and other serious complications.
Clinical picture
Sometimes cardiac defects are not clinically apparent or very weak. Symptoms may not be detected even during physical examination of the patient. Some moderate defects promote the development of the clinic in the adult period.
- Since oxygen-saturated blood circulation is essential for normal growth, development, and activity, infants and children with heart defects may develop poorly or lag behind in the body of weight.
- Sick children may have difficulty feeding or get tired quickly during physical activity.
- In more severe cases, respiration becomes difficult or cyanosis develops.
- Older children with heart defects often fall short of their peers during physical exercise or experience shortness of breath, faintness, chest pain, especially during exercise.
An abnormal blood flow through the heart usually causes an abnormal sound (cardiac noise) that can be heard with a stethoscope. Pathological heart beats are often loud or sharp.
The overwhelming majority of cardiac changes that occur in childhood are not caused by heart disease and do not indicate any problems.
In the event of a complication such as heart failure, the heart starts to beat fast and often, which leads to accumulation of fluid in the lungs or liver. The deterioration of this condition leads to frequent breathing, wheezing during inspiration, the appearance of crackling sounds in the lungs and an increase in the liver.
Some heart defects (such as a hole in the interstitial septum) increase the risk of thrombus formation, which can block bleeding in the brain. This leads to a stroke. But this is more typical for adults than for children.
Video The first symptoms of heart problems that should not be ignored
Diagnostics
Many heart flaws can be diagnosed before birth using ultrasonography. If the PS is diagnosed or suspected by an obstetrician, then a pregnant woman is referred to a specialized ultrasound examination called echocardiography. This procedure allows you to study the heart of the fetus in detail. When a serious heart defect is confirmed, optimal care for the newborn can be planned right after birth. Cardiac defects that are not detected before birth are suspected in newborns or young children when symptoms appear.
Diagnosis of heart defects in children is associated with the same methods that are used to identify heart disease in adults.The doctor can diagnose an abnormality by asking questions about the family.A physical examination is required.
If necessary, the following research methods are used:
- Electrocardiography
- Roentgenography of the chest
- Ultrasound echocardiography
- Catheterization of the heart
The ultrasonography of the heart (echocardiography) is used to diagnose almost all specific vices.
Catheterization of the heart can provide detailed information on the anomaly. It is also used to treat some heart defects.
Treatment
There are five main tactics for treating heart failure patients, which can be combined if necessary (combined therapy):
- Open heart surgery
- Catheterization of the heart
- Use of medication
- Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) and ventricular auxiliary devices (VAD)
- Heart transplantation (in rare cases)
Immediate help
Cardiac insufficiency or cyanosis that occurs in the first week of life after the birth of a child is an indication for urgent medical care. Doctors for medical treatment often insert a thin tube (catheter) into a newborn's vein in place of the umbilical cord. Tableted drugs such as prostaglandin are given to reduce heart load. The newborn may also need artificial ventilation of the lungs so that the child can breathe better. In the presence of certain defects, the patient is sometimes fed with oxygen.
Open heart surgery
Many severe heart defects are effectively restored in the open heart operation. The operation time depends on the specific defect, its symptoms and severity. When possible, it is best to postpone the operation until the child becomes a little older. Nevertheless, babies with severe symptoms caused by heart disease should undergo surgical treatment during the first days or weeks of life.
Catheterization of the heart
Valvular and arterial stenosis can sometimes be extended by passing the catheter through the blood vessel in the groin, neck, arm, or even a navel with further flow to the narrowed portion of the heart. A similar procedure is called cardiac catheterization. A special balloon attached to the catheter pumps and expands the site of narrowing, usually in the valve (balloon valvuloplasty) or blood vessel (balloon angioplasty). These exposure methods may be performed instead of an open heart surgery or a postponement of the main open heart operation.
Cardiac catheterization can also be used to close the arterial duct or some holes in the heart (defects in the inter perciptor septum and some ventricles of the interventricular septum). To do this, put a special patch on the defect. Catheterization of the heart does not leave a large scar on the skin, and the patient's rehabilitation time is often shorter than recovery after an open heart operation.
Tablet preparations
When blood flow to the body or in the lungs is very difficult, a drug called prostaglandin can be prescribed to maintain the arterial duct open, which can save the patient's life.
If necessary, other drugs for the treatment of patients with heart disease are used:
- A diuretic, such as furosemide, which helps remove excess fluid from the body and the lungs
- Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE inhibitors) such as captopril, enalapril or lysinopril (relaxes blood vessels and helps the heart to pump blood more easily)
- Cardiac glycosides, among which digoxin is the most well-known, helping the heart to work more actively
- Cardiotonic drugs, including milrinone, are a powerful drug administered intravenously to stimulate the heart to fight more and relax narrowed blood vessels.
Devices for maintaining the function of the heart
In recent years, complex mechanical devices have been used to support the heart in children with severe heart failure that do not respond to drugs. These devices are equipped with a pump that helps to pump enough blood into the lungs and throughout the body when the heart can not work efficiently. They can be used for several days, weeks or even months, which allows the heart to recover from a viral infection or a large open heart surgery. Also, the instruments help stabilize the child's condition until a heart transplant is performed.
When extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), the blood from the newborn is fed into the device, which adds oxygen and removes carbon dioxide, and then returns the blood to the newborn.
ECMO is used in severe conditions caused by serious heart and lung injuries, as well as during long operations, including open heart.
Some devices called ventricular aids (VADs) can be integrated into the body. The device transfers blood from the heart to all parts of the body.
Heart transplantation
In rare cases, when no other treatment is helpful, a heart transplant is performed, but the lack of donor hearts limits the availability of this procedure.
Prevention of complications
Tactics for the prevention of complications in adolescents and children include drugs and changes in their diet (restriction of salt and the use of high-calorie products with a relatively small amount of fluid). These measures reduce the stress on the heart.
Patients who have severe heart defects or have had operations to restore heart anomalies should follow the following recommendations:
- Take antibiotics before visiting a dentist and before certain operations (such as intestine or bladder). These antibiotics are used to prevent serious heart disease called endocarditis.
- It is good to take care of your teeth and gums to reduce the risk of spreading an infection in the body that can affect the heart.
Video Death of the Heart. Operation
Similar articles

Congenital heart defects are cardiac defects that occur during fetal development and are then determined after birth. There are various classifications of congenital heart defects, but the most commonly used correlate with clinical manifestations, defect localization, etc.
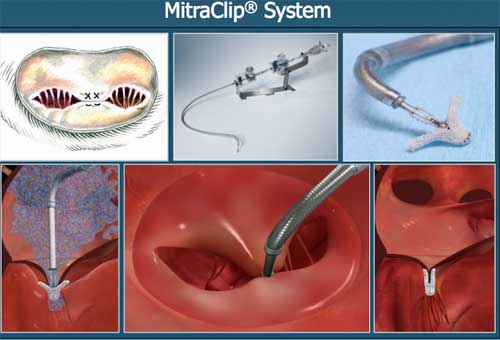
Among all diseases of the heart a special place is occupied by valvular defects, still known as valve stenosis, valve failure, valve prolapse. A large number of people around the world and at different ages are determined by heart defects. In some cases, they are not worrisome, and in others, urgent surgical intervention is required.

There are cardiovascular diseases that can lead to permanent loss of disability. In order to prevent such complications, timely treatment should be performed. Therefore, in identifying the acquired heart defects, it is not necessary to delay with the implementation of medical recommendations.
