First aid for acute coronary syndrome
Author Ольга Кияница
2019-02-28
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a group of diseases associated with reduced blood supply to the heart muscle.Blocking can be sudden and occur in an instant. Another variant of the course of the disease is the gradual disappearance of the blood supply over a certain period of time.
ACS can occur in different ways, therefore the treatment methods depend on the size of the myocardial damage, but in any case, first aid for acute coronary syndrome should be provided competently and in a timely manner.
During first aid, drugs from the group of nitrates and analgesics are often used. Additionally, the patient is examined by electrocardiography, ultrasound and other diagnostic methods. This allows us to estimate the size and location of the site of injury.
Video: What is Acute Coronary Syndrome?
Description of acute coronary syndrome
The pathogenesis of diseases from the ACS group is associated with fat-like substances deposited on the walls of the coronary arteries. These vessels supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients.
The heart works normally when a constant and full supply of blood rich in oxygen is provided. A blood clot or cholesterol plaque formed in an artery most often leads to blockage of the coronary artery.
Types of acute coronary syndrome
The medical term “acute coronary syndrome” is used to describe three options for the course of coronary heart disease (CHD):
- Unstable Angina
- Myocardial infarction without ST segment elevation (NSTEMI)
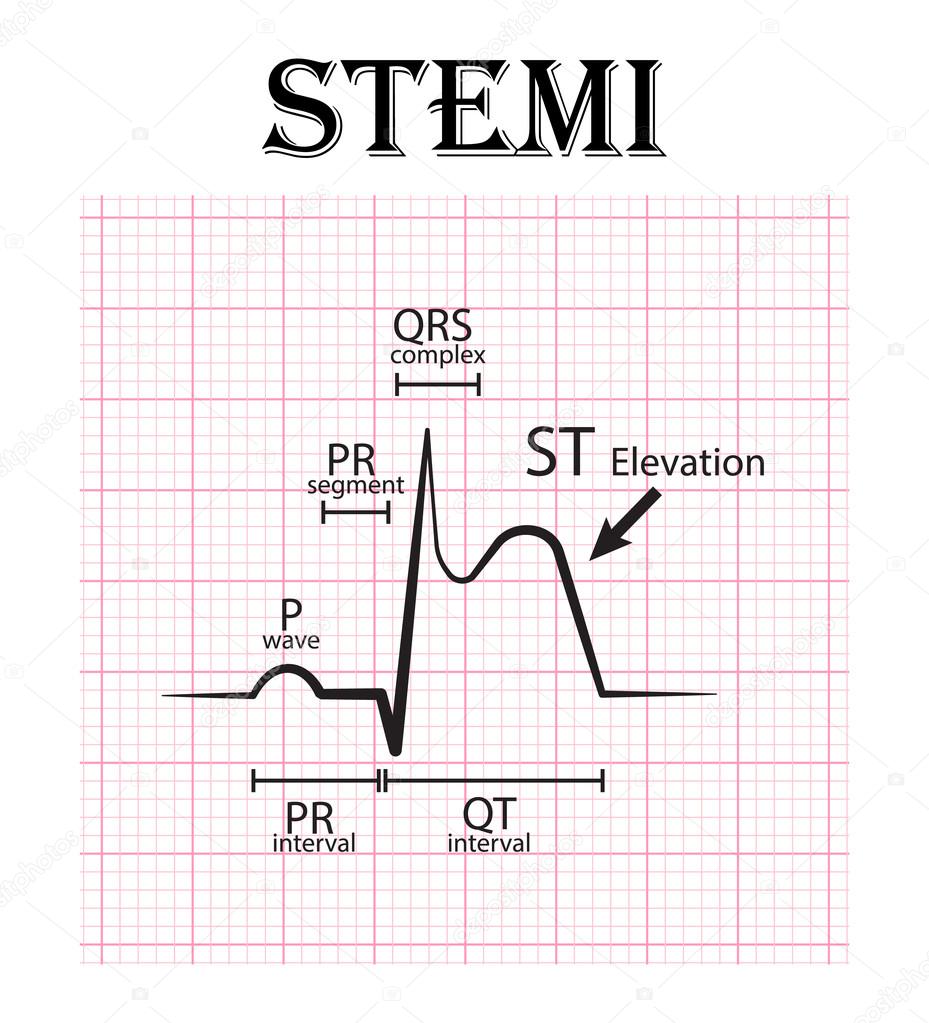
- Myocardial infarction with ST segment elevation (STEMI)
In the case of supplying the heart cells with an insufficient amount of oxygen, the cardiomyocytes may die and then they talk about necrosis of the myocardium. This process is irreversible, therefore, first aid for ACS, which helps keep heart cells viable, is extremely important.
A lack of blood supply to any tissue is referred to as ischemia. With the complete cessation of blood flow occurs necrosis. In case of necrotic damage to the heart muscle, a diagnosis of a heart attack or myocardial infarction is made.
During ischemia, the heart cells do not die, but their damage occurs due to oxygen starvation. This leads to the fact that the myocardium is not functioning properly or effectively. The pathological condition may be temporary or permanent.
To compile the correct treatment, the type of acute coronary syndrome is determined, which depends on the location of the blocked area, the duration of oxygen starvation and the number / size of the area of damage.

Symptoms of acute coronary syndrome
The clinical picture of ACS usually develops quickly, sometimes without any prior manifestations. Nevertheless, there are symptoms that can warn a person that his health is impaired.
Common manifestations of acute coronary syndrome:
- Chest pain or uncomfortable feeling behind the sternum
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms, back, jaw, neck or abdomen
- Confused breathing
- Dizziness or general feeling of weakness
- Dyspepsia
- Nausea or vomiting
- Excessive sweating
These symptoms are very serious, and when they appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
Chest pain that develops on the background of acute coronary syndrome may begin suddenly, without any previous signs. This is especially true for a heart attack.
In other cases, the pain may noticeably increase even after rest. This feature is especially characteristic of unstable angina.
Chest pain or discomfort behind the sternum, as a rule, is most often found in patients with acute coronary syndrome.Nevertheless, clinical signs often depend on the age, sex of the patient and the presence of other cardiovascular diseases.

Risk factors and diagnosis
There are certain circumstances in which the probability of developing acute coronary syndrome increases markedly.About them should know as many people as possible. Risk factors include:
- Elderly age - 45 years and older for men, 55 years and older for women
- High blood pressure
- Elevated cholesterol
- Smoking
- Lack of physical activity
- Unhealthy food
- Obesity or overweight
- Diabetes and other endocrine disorders
- Familial predisposition
Diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome
Identification of coronary syndrome is carried out by a cardiologist, taking into account the following characteristics:
- Determination of troponins in blood secreted by damaged heart tissue
- Identification of clinical signs of the disease
- Obtaining the results of electrocardiography (ECG)
Proper identification of the type of disease is especially important when it comes to choosing a treatment strategy. To clarify the diagnosis is used as an ECG, and other imaging methods:
- Electrocardiography (ECG) . This test allows you to measure the electrical activity of the heart by means of electrodes attached to the skin. Abnormal or irregular impulses may indicate poor heart function due to insufficient oxygen supply to the myocardium. Certain types of electrical signals can also indicate the location of the block.
- Blood tests . Some enzymes can be detected in the blood, especially if the death of the cardiomyocyte has occurred and damage to the cardiac tissue has occurred. The definition of these components indicates a heart attack.
- Ultrasound of the heart . This ultrasound scan can show if the heart is getting enough blood. Also allows you to assess the status of the area of damage after a heart attack.
Doctors may also use other tests to determine whether additional treatment is necessary or the presence of concomitant heart disease.
In particular, sometimes a person with suspected ACS is prescribed to wear a Holter monitor, which records the electrical activity of the heart for a day or two. Holter monitoring helps determine if a person has abnormal heart rhythms or a periodic lack of blood supply to the myocardium. This research method is especially helpful when the patient has no complaints.
Additional diagnostic methods such as CT and MRI can be used to exclude other causes of the disease, as well as better assess the human condition.

Treatment of acute coronary syndrome
In the first place - this is an urgent medical impact. In providing first aid for ACS, every minute is important, since death can start very quickly from the onset of a heart attack.
Short-term treatment strategy includes reducing pain and improving blood flow, which allows the myocardium to be restored as quickly as possible.
Long-term treatment tactics are based on improving overall heart function, managing risk factors and reducing the likelihood of developing a heart attack. Most often, long-term therapy is carried out in a hospital setting and includes a combination of medicines with surgical procedures.
Medications used to eliminate acute coronary syndrome:
- Nitroglycerine
- Antiplatelet drugs
- Beta blockers
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors)
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
- Statins
People who call an ambulance are often advised to take aspirin before her arrival. If medications cannot alleviate problems and restore proper heart function, angioplasty may be necessary in combination with stenting. Also, depending on the evidence, coronary artery bypass surgery may be performed.
Video: Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
Algorithm of first aid to patients with acute coronary syndrome
In case of suspected ACS, first aid and hospitalization of the patient are prerequisites for a successful outcome and the exclusion of further complications. Emergency care, as well as transportation of a patient with an acute heart attack, is carried out in the supine position with the head slightly raised.
The main stages of first aid for ACS:
- Nitroglycerin is placed under the tongue of the patient. This is the first aid in heart failure, as well as in acute coronary syndrome. You can take the medicine if necessary every 5-10 minutes.
- Acetylsalicylic acid (chewable tablet 160-325 mg) is taken in the absence of nitroglycerin.
- Clopidogrel is used in cases where the patient has an increased sensitivity to nitroglycerin.
- Oxygen therapy . Inhalation is performed using hydrated oxygen using a mask or a nasal catheter (feed rate 4-6 L / min). If there are no devices for inhalation, it is necessary to provide access to the patient with a sufficient amount of air. This is especially true when a seizure occurred in a stuffy room.
- Anesthesia with nitroglycerin - is carried out under the control of blood pressure and is administered intramuscularly in combination with dimedrol.
- Morphine hydrochloride is injected intramuscularly with 1% in the form of a folic solution of 1:20, allowing to relieve pain that does not go away for a long time.
- Heparin (5 thousand units).
Further tactics depend on the data of electrocardiography and the general condition of the patient.
NSTEMI and NSTE-OKS treatment
If the ECG does not show typical changes, then it can be an ACS without ST-segment elevation (NSTE-ACS). Also, patients often suffer from "ST-free myocardial infarction" (NSTEMI).
Treatment of unstable angina and NSTE-OKS is carried out initially with aspirin, and secondarily with an inhibitor such as clopidogrel or diacylglycerol. Heparin (low density), such as enoxaparin, is also used. Trinitroglycerin and trinitroglycerol are administered intravenously if the problem is not resolved.
A blood test is used only if you need to check the increase in cardiac troponins within 12 hours. If the result is positive, then a typical coronary angiography is done urgently. It allows you to quickly identify a heart attack and in a fairly short time.
If the troponins are negative, exercise with a test on the treadmill. If there are no signs of a high ST segment on the ECG until the next morning, then angioplasty may be indicated.

Lifestyle changes
In some cases, acute coronary syndrome can be prevented. Another heart disease often leads directly to ACS, but those who do not have cardiovascular diseases can protect themselves by adhering to the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- Follow a heart- healthy diet that includes more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Do not smoke , and if it is difficult to refuse yourself, you can try medications and advice to lose your bad habit.
- Lead an active lifestyle , that is, to engage in regular exercise in order to have good physical fitness. People should strive for moderate exercise at least 2-3 hours a week.
- You need to pay attention to a number of physiological indicators , it is especially important to know your blood pressure and cholesterol level and understand what these numbers mean and how to keep them in the optimal range.
- Maintain a healthy weight , which will remove the extra burden from the heart.
- Drink alcohol in moderation , it is desirable to reduce to one or two alcoholic beverages per day, and it is better to completely give up on them, so that there are no factors that increase blood pressure.
People who have had problems such as a heart attack in the past may also have aspirin recommended in addition to taking other medications on a daily basis. In aspirin, there is acetylsalicylic acid, which helps prevent platelet formation and reduces the likelihood of another heart attack by about 22%.
By correcting lifestyle and using the right medication, you can prevent or cure acute coronary syndrome. This will allow to continue to engage and work in your pleasure.
Video: Acute Coronary Syndrome DETAILED Overview (MI, STEMI, NSTEMI)
