First aid for stroke: step by step algorithm
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-09-21
Stroke is a brain tissue disorder that is often described as a “brainstorming”. Part of the brain tissue is deprived of oxygen and blood supply, which it needs to perform functions. Pathology occurs because a blood vessel that delivers blood to a specific part of the brain is blocked by a thrombotic clot or other extraneous formation.
The definition of “insult” (Latin insultus “swoop, attack, strike”) comes from the outdated name “apoplexy” (ancient Greek ἀποπληξα “paralysis”).
According to wikipedia.org.
The disease is mostly very acute, and the longer the ischemia of the brain tissue develops, the more pronounced the brain damage and the harder the complications can be. But there is a step-by-step algorithm of actions, according to which first aid is given to the patient for a stroke. Its proper implementation allows a person to get to the hospital in time to receive the necessary treatment.
Video: Stroke || First aid for stroke
3 steps to take in a stroke
It can be anyone who has a stroke. In such cases, it is extremely important to react correctly and to perform certain actions, which are actually first aid.
1. You need to immediately call an ambulance
If you had to be close to a person who had a stroke, you need to act quickly and first of all call an ambulance. The most difficult thing is to correctly identify the symptoms of a stroke, which are listed below.
2. It is important to fix the time when I first had to see signs of “brainstorming”
In some cases, it is extremely important to do this, because to effectively prevent the effects of an impact within 4.5 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, a blood thinning agent, called TAP, or tissue plasminogen activator must be administered. The tool can be provided to anyone who has a stroke. With its help significantly changes the course of the disease, and in some cases, manifestations of stroke are completely eliminated.
Patients may be candidates for more advanced treatments, such as endovascular treatment. This method of surgical treatment consists in removing the clot that occluded the vessel and provoked the development of a stroke.
If necessary, aneurysm fixation is performed, which is a swollen blood vessel that ruptures and causes pressure in the brain. Endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke, the most common type of stroke, should be performed within 24 hours after the onset of the disease. It is important to know that earlier treatment improves the outcome, so time is crucial.
3. If necessary, perform CPR
Most stroke patients do not need cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). But if a person is unconscious, it is important to first check the pulse and breathing. If the physiological parameters are not determined, you must contact the ambulance and begin to make CPR.
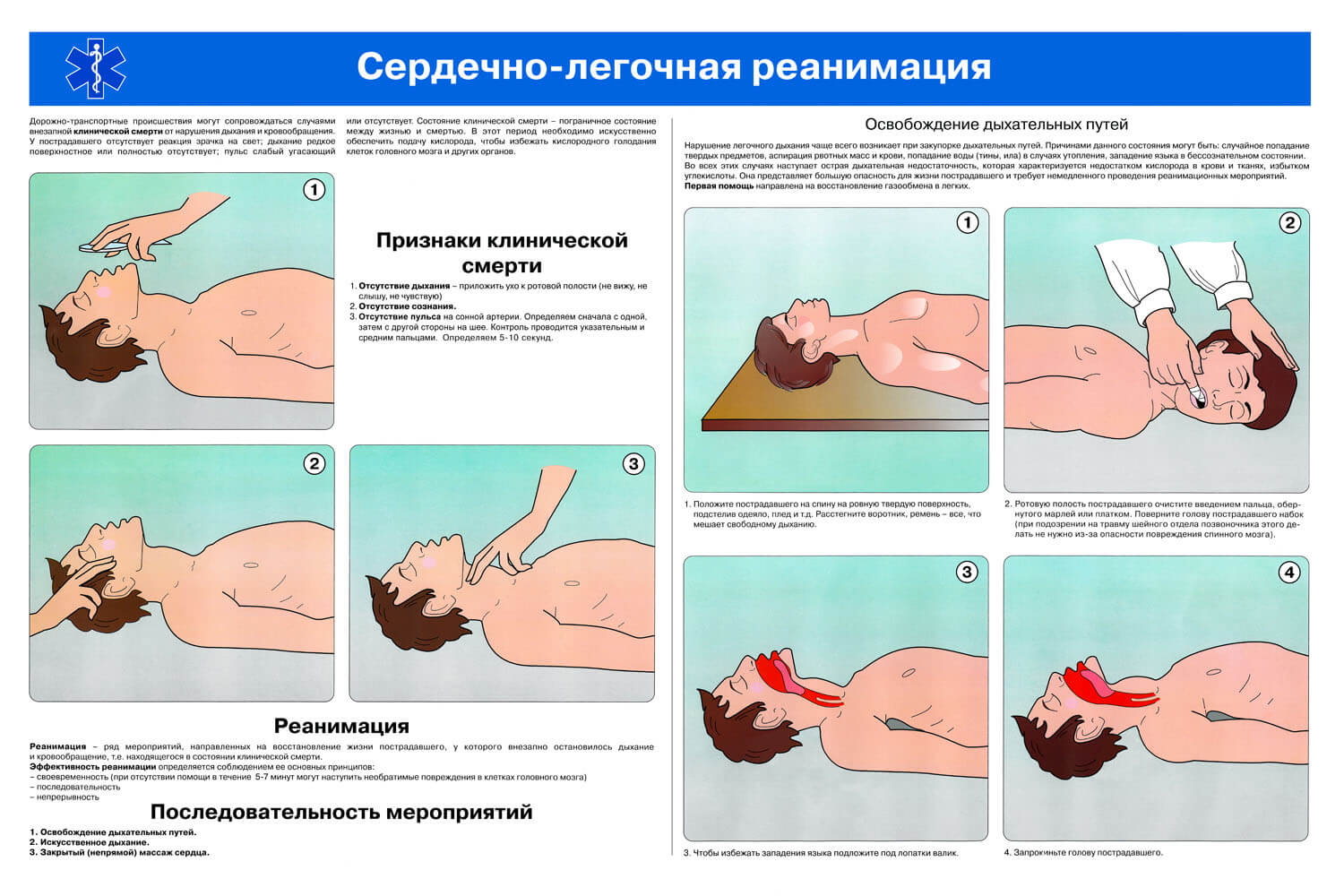
Far from providing first aid to people in performing CPR, a dispatcher who can tell the main sequence of actions can help.
3 things not to do in a stroke
There are certain nuances of the course of the disease, according to which a number of actions should not be performed. This will improve the prognosis for the disease and prevent the development of undesirable consequences.
If a neighbor has a stroke, you should not let him fall asleep.
In such situations, patients often complain of a sudden feeling of drowsiness, especially when a stroke occurs for the first time.
It happens that when the symptoms appear, the patient, instead of going to an ambulance, goes to bed for several hours, because there is great fatigue. Only after such a “rest” come to the hospital. But with a stroke. The road is every minute. The medicine that doctors could give to a survivor after a stroke is strictly time dependent. Therefore, under no circumstances should you go to bed in order to call your primary health care doctor in a day or two. Instead, the patient, either alone or with help, should immediately go to the nearest hospital.
Patients with suspected stroke should not be given medicines, food or drinks.
There are two types of strokes:
- Hemorrhagic stroke due to rupture of a blood vessel.
- Ischemic stroke formed by blockage of a blood vessel with a blood clot.
80% of strokes are ischemic, but if a sick person belongs to the remaining 20%, and the formation of a stroke is associated with a ruptured blood vessel in the head, you should not offer any medications, including aspirin.
Without a survey it is impossible to say exactly what kind of stroke a person had. Therefore, it is necessary that he be taken to the emergency department, where a computer scan of the brain will be carried out.

In order not to bring more time than good, you should not give a person who has a suspicion of a stroke, any medicine.
Also, if the patient is conscious, it is not recommended to offer food or drinks before an ambulance arrives. Such a precaution is due to the fact that sometimes a stroke affects a person's ability to swallow.
Get behind the wheel if you suspect a stroke
In some cases, the ambulance team may not arrive at the call. In such cases, if you have your own car, the victim of a stroke is better not to sit on the steering wheel. It is necessary to find a person who could take to the hospital. It is also desirable that when calling an ambulance a special reanimation car is provided, in which medical workers will be able to provide the victim with all the necessary medical assistance allowed at this stage of exposure.
The main signs of a stroke
Correct and timely response will allow a clear definition of the symptoms of "brainstorming." Today, there is an approved FAST control.
Historical reference
FAST was developed in the UK in 1998 by a group of stroke physicians, ambulance staff and emergency doctors. The development was an integral part of the training project for ambulance staff. FAST was created to accelerate intravenous administration of tissue plasminogen activator to patients within 3 hours after the onset of acute stroke.
FAST is an abbreviation used as a mnemonic that helps to detect and improve the response to the needs of a person with a suspected stroke. Abbreviation means:
- Face - “lowering the face”
- Arm - “hand weakness”
- Speech - “Speech Difficulty”
- Time - “time” to call emergency services.
Lowering a face is when a part of the face, usually only on one side, is lowered and difficult to move. In some cases, this is very similar to a wry smile.

Hand weakness - the patient loses the ability to raise the arm completely.

Problems with speech - is determined by the impossibility or difficulty with understanding speech or pronunciation of words and small sentences.
Time — If any of the above symptoms are more or less pronounced, the time begins. It is necessary as soon as possible to contact the emergency service or to take the patient to the hospital.
Additional symptoms:
- Blurred, blurred or double vision in one or both eyes.
- Difficulty in speaking, speech interruption and confusion.
- Difficulty in walking and balancing.
- Sudden severe headache with vomiting or severe nausea.
However, quite often the blows are painless, which may surprise the average person. If there are risks to the development of the disease, you need to know the principles of first aid in stroke, which were given above.
Risk factors and stroke prevention
Many of the risk factors associated with poor lifestyle. Some of them include:
- Obesity.
- Stress.
- Passive lifestyle.
- Chronic alcoholism.
- Drug use, such as cocaine.
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus and cholesterolemia.
- Smoking, including passive.
- Sleep disturbance by type of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia.
Lifestyle changes can help prevent stroke. Depending on the number and strength of exposure to risk factors, the attending physician or cardiologist may recommend medications for the prevention of stroke, if necessary.
Depending on the area of damage to the brain, the severity and temporary interventions between stroke and emergency care, the disease can lead to temporary or permanent disability. Therefore, for optimal recovery after a stroke, rehabilitation is required. Existing programs in this direction include the participation of specialists and rehabilitation therapists with a focus on:
- Recuperation
- Restoration of functions such as speech, vision, balance, breathing, etc.
- Back to active life.
To learn more about stroke, you can ask questions to experts in the field of stroke.
Video: First aid: stroke

Спасибо большое! Нужно иногда обновлять свои знания в голове, мало ли что понадобится… Мне полагаться не на кого, живу одна. Так что для меня самое главное-это профилактика. Принимаю гинкоум для разжижения крови, слежу за питанием, за активностью… Тромбов нет, а значит инсульт и инфаркт не страшен.