Myocardial dystrophy
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-03-06
Myocardial Dystrophy (MIC) is known in medical practice as a secondary pathology affecting the heart muscle. Another common definition is secondary cardiomyopathy, myocardial dystrophy. The disease is not associated with the inflammatory process, but is accompanied by a disorder of myocardial nutrition. Often myocardial dystrophy acts as a complication of another cardiovascular disease.
In 1936 G. F. Lang identified myocardial dystrophy as a violation of the physico-chemical and biochemical structure of the heart muscle and associated metabolic syndromes.
In the process of progression of the disease, the tone of the myocardium decreases, which in the future, under adverse conditions, leads to the development of heart failure. Often, other heart disease develops due to a decrease in blood circulation in the myocardium, as a result of which cardiomyocytes do not receive enough oxygen in the amount necessary for the normal functioning of the organ. The long course of this condition leads to atrophic and even necrotic changes in the heart tissue.
Video Myocardial Dystrophy
Description
The formation of myocardial dystrophy is most often associated with a violation of the process of exchange of various substances that participate in the formation of energy in the heart muscle with its subsequent transformation into the mechanical work of the organ. In severe cases, the course of MKD is complicated by cardiac insufficiency of the myocardial type.
In typical cases, the pathologic MCD is characterized by the absence of an inflammatory process and necrotic changes in the cardiac muscle.
Regardless of etiology, the development of myocardial dystrophy is based on the following mechanisms:
- Stimulation of the sympathoadrenal system, which leads to an increase in the need for heart muscle in oxygen
- Violation of the process of relaxation of muscular myocardial fibers - leads to a change in the oxidative processes and a decrease in the use of oxygen with the activation of proteases
- Accumulation of free radicals, which activates the destructive lysosomal mechanism
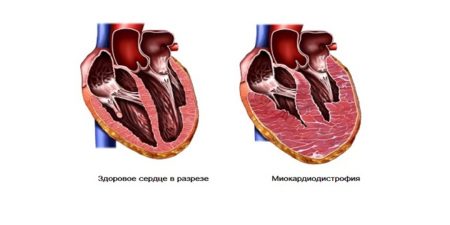
The course of myocardial dystrophy is accompanied by the following pathological changes:
- cardiac muscle innervation
- slow down the process of assimilating oxygen by heart;
- increase in the number of cardiomyocytes calcium ions;
- the appearance of fat cells that gradually destroy myocardium;
- increased activity of enzymes destroying the structure of cardiac cells;
- a decrease in the number of working cardiomyocytes.
Progression of myocardial dystrophy is divided into three stages (Vasilenko V.H., 1989):
- Neurofunctional stage, when the signs of a vegetative nervous system disorder are most often determined.
- The stage of limited changes, in which there are changes in the exchange-structural elements.
- Stage of heart failure of metabolic flow.
It is important to know that heart disorders in myocardial dystrophy are reversible. An urgent visit to doctors and the fulfillment of the conditions of prescribed treatment can completely save a person from heart disease. This disease mainly affects people over the age of forty. But recently doctors have noted the tendency for this pathological condition to appear in the younger group of the population.
Reasons
Myocardial dystrophy develops under the influence of external factors - frequent physical exercises or stresses, stresses, and malnutrition.
The appearance of myocardial dystrophy may be related not only to external but also to the internal predisposing factors:
- acute intoxication of the body (narcotic substances, alcohol, etc.),
- diseases by type of inflammation or infectious process;
- endocrine diseases (toxic goiter, hypothyroidism, acromegaly, diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- disorder of the exchange process;
- congenital neuromuscular disorders such as myasthenia, myodistrophy;
- neurogenic dysfunctions, neurovascular dystonia;
- disturbance of balance of electrolytes of different origin.
Myocardial dystrophy occurs in small children and newborns with those diseases that are characteristic only for this age group
Species
There are several types of myocardial dystrophy associated with causative factors:
- Dishormonal myocardial dystrophy. It manifests itself at a hormonal imbalance in the body, as well as metabolic disorders. Most often, this type of MCD is determined in women suffering from menopause. The disease is accompanied by edema, an increase in the size of the internal organs, discomfort and pain in the region of the heart.
- Tonzilogennaya MKD. Develops against a background of chronically leaking tonsillitis or prolonged and frequent sore throat pain.
- Anemic MKD. Against the background of a massive loss of blood (hemorrhage), myocardial dystrophy is formed. The heart is suffering from lack of oxygen. This pathology is manifested by shortness of breath, pallor and tachycardia.
- Toxic form. It manifests itself in alcohol-dependent patients. Toxins in the form of ethyl alcohol destroy heart cells, affect the nervous system, resulting in fingers always shaking in patients, sweating increases and there is always a lack of air.
- Dismetabolic myocardial dystrophy. Caused by a violation of the protein-carbohydrate ratio in the human diet.
- Myocardial dystrophy after physical stress. This form of illness is susceptible to people who are actively engaged in sports or who experience frequent physical overload. Most often it manifests itself by a sensation of pain, pressure, tingling in the heart region.
- Myocardial dystrophy of complex genesis.Often caused not by pathological processes from the heart, but by external influences of outgoing factors.
Clinic
There are various stages of development of myocardial dystrophy, according to which the disease is divided into three clinical stages:
- The first one is characterized by uncomfortable sensations and pain in the heart, shortness of breath and rapid fatigue without any preconditions. At this stage, an increase in the size of the heart (cardiomegaly) occurs.
- The second - the heart rhythm is broken, the limbs may slightly swell. Cardiac output decreases, which in turn negatively affects the blood supply of organs. With timely treatment, initiated at this stage of MCD, it is still possible to restore cardiac activity.
- The third one is characterized by strong breathlessness, even during rest. Stagnation of blood in blood vessels is detected, which is manifested by severe edema. The patient significantly reduces the working capacity. The heart stops providing a normal circulation process. At this stage there are irreversible changes.
In young people, if there is enough energy and health in the body, myocardial dystrophy can occur without symptoms.At the same time, they are still manifested with age. It is worth noting that the severity of the signs and their variation depends on the characteristics of a particular person.
The main symptoms of myocardial dystrophy are pain and other unpleasant sensations localized in the heart. In addition, there are several additional features:
- Intermittent breathing. It can occur not only against the background of a significant load on the body, but also for no apparent reason
- Arrhythmia In some cases, the heart beats very quickly, with pulsating recoil in the temple area. In others, there is a very slow heartbeat.
- Expressed drowsiness without any particular reason.
- Decrease in working capacity.
The above symptoms may occur in both adults and children, as well as in the adolescence.
Complications
Patients of middle and older age have the most unfavorable complications of myocardial dystrophy. They often consist of almost complete incurability of the disease and the complexity of eliminating clinical signs.
In childhood myocardial dystrophy threatens severe complications. Similar is connected with the fact that the body of the child is not finally formed, and dystrophic disorders can have unhealthy effects on other organs and systems of the body. Insufficient flow of blood to the tissues of the heart and violation of the contractile function of the myocardium negatively affect the physical development of the child. If parents seek help promptly, then you can avoid any violations or complications. But in the absence of adequate therapy, myocardial dystrophy in children may be complicated:
- IBS
- atherosclerosis;
- disturbance of heart rhythm;
- insufficiency of cardiac activity.

Diagnostics
As noted above, myocardial dystrophy occurs in some cases without symptoms. This contributes to the fact that it is clinically difficult to suspect MCD, therefore, at an early stage only a thorough diagnosis will help to determine the dystrophic lesion of the myocardium. Not all instrumental studies are capable of detecting initial abnormalities in the work of the heart, but advanced technologies allow this to be done.
Diagnosis of myocardial dystrophy is carried out with the help of
- Electrocardiography. This method of diagnostics makes it possible to detect even minor changes in the work of the heart.
- Bicycle ergometry Allows physical stress to provoke hidden forms of arrhythmia and fix them with ECG.
- Radiography An X-ray image of the lungs is made, on which pathological processes are visible, as well as the contours of the heart, by which the approximate sizes of the organ are determined.
- Phonocardiography. Allows you to detect the noise in the heart of varying intensity and direction.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the heart. The study allows to determine pathological formations by type of tumor, hypertrophy and others.
- Clinical analysis of blood.
Sometimes a clinical urine test is done. This study has nothing to do with the work of the heart, but heart failure can be detected by analyzing kidney problems.
Treatment
With myocardial dystrophy, the direction of therapy is based on the elimination of the cause of its occurrence. Given the factors of external influence and individual characteristics of the patient, doctors prescribe the complex use of medications for the normalization of cardiac activity, as well as the consumption of hormonal drugs and a wide range of vitamins. Cardiotonics contribute to the normalization of heart rhythm. Due to the fact that the causes of the pathology are individual, a number of drugs are also prescribed by doctors on an individual basis.
Self-medication of myocardial dystrophy is unacceptable. It only exacerbates the course of the disease, which manifests itself as a complication. As a result, the development of the pathology can change in such a way that an irreversible stage of myocardial dystrophy occurs.
Video Dystrophy. Treatment of dystrophy of muscles, myocardium, eyes, liver by folk remedies
Vitamin preparations used in myocardial dystrophy:
- Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
- Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)
- Calcium Pangamat (Vitamin B15)
- Coenzyme Q10
- Cytochrome C.
- Magnesium and potassium salts
Cardiometabolic therapy (improves cardiomyocyte metabolism):
- Levocarnitine (Agvantar) is the main drug used in the treatment of myocardial dystrophy. Helps to improve the functioning of the heart and helps eliminate many clinical signs of the disease.
yocardial dystrophy is not usually treated by surgical intervention, because drugs, as a rule, can completely eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Heart transplants are performed only if the manifestations of severe heart failure are detected:
- heart rhythm disorders;
- severe shortness of breath in a calm condition;
- constant edema of the extremities.
In such cases, basically an open heart operation is performed.
Prevention
To prevent or reduce the risk of developing myocardial dystrophy, it is worth taking the following preventive measures:
- to lead a healthy lifestyle, for which it is important to refuse smoking and drinking alcohol;
- to accustom yourself to daily stressful physical activity, which allows you to keep your heart in the right tone;
- avoid overheating or hypothermia;
- regularly practice contrast contamination;
- annually undergo treatment with massage;
- minimize stress situations;
- take enough vitamins;
- drink at least a liter of fluid per day;
- reduce calorie intake with food.
Video Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases: Contemporary Trends

Я после 40 лет тоже начала принимать витамины для сердца. Периодически пропиваю комплекс витаминов группы В, а недавно еще и коэнзим Q 10 начала принимать, его тоже очень хвалят. К тому же с возрастом он почти не вырабатывается в организме.