Flickering arrhythmia
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-10
In normal condition, the heart is reduced sequentially (atrium, then ventricles) and with the same rhythm. For this, an electric pulse formed in the sinus node enters the atrioventricular (atrial-ventricular) node. If on its way there are areas of necrosis, inflammation or other destruction, then a block arises that the pulse can not bypass. He returns to the fibers back and again excited earlier abbreviated atrium. This pulse propagation takes the form of a constant circulation (ri-entry), which forms the pathological focus of atrial contractions.

Normal pulse hold
Interstitial type of atrial contraction
Frequent contraction is characteristic for atrial fibrillation, but in addition there is a chaotic and irregular work of the atria.This is due to the fact that the circulating impulse from the pathological focal point extends to other areas of the myocardium. In addition, the ventricles also begin to contract incorrectly and irregularly, because they do not reach the full signal of excitation.
Description of fibrillated arrhythmia
Inverted arrhythmia refers to a mixed group of heart rhythm disturbances, in which the increase in cardiac activity is observed from 350 to 700 beats per minute. The name of the disease comes from Latin and means "crazy heart." It can manifest itself in adults, children, men and women, but the risk group of the disease is made up of people after 60 years, since it is precisely the degenerative changes in the myocardium that leads to the appearance of supraventricular tachycardia.
Up to 60 years, flickering arrhythmia is diagnosed in 1% of patients, in the elderly it is detected in 6-10% of cases.

What is the risk of flickering arrhythmia? First and foremost - insufficient cardiac output, since the ventricles can not provide enough blood to organs through a small and large circle of blood circulation. At first, the disorder is compensated, but with prolonged course of the disease there is an acute circulatory failure. With some ailments, such as mitral stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, heart failure develops very rapidly.
A severe fall in cardiac output causes an arrhythmogenic form of cardiogenic shock. In the absence of urgent medical care, a fatal outcome is possible.
Non-synchronous atrial contraction leads to stagnation of blood. Against this background, there is an increased risk of thrombosis, especially in the left atrium, where they easily enter the cerebral vessels and cause ischemic stroke. An unprotected attack of a flashing arrhythmia lasting more than 2 days, primarily threatens the acute thrombosis of vessels in the brain.
Symptoms of flickering arrhythmia
The disease clinic is primarily determined by its developmental form. If this is paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, then there are bright characteristic symptoms:
- the heartbeat increases sharply;
- an asthma attack appears;
- not enough air;
- it becomes difficult to breathe in and exhale;
- weakness and trembling in the whole body appear;
- increased urination;
- sweating increases;
- hands and feet become cold;
- The patient can cover panic.
The heart rate is the main criterion for the patient's condition. The more strokes per minute, the worse the patient will feel. In some cases, due to acute cardiac output insufficiency, arrhythmogenic collapse develops when a person loses consciousness due to poor blood supply to the brain.
Before the appearance of a pronounced clinic, for a long time, small back pain, shortness of breath, and feeling of nausea may be observed. Similar signs can be considered as precursors of atrial fibrillation.
Pathology can manifest itself in the form of minor attacks, which at first the patient does not feel at all, or are perceived as temporary discomfort. The lack of treatment for arrhythmias in the early stages affects the reduction of working capacity and the appearance of complications such as angina pectoris, dyspnea, edema of the limbs, liver enlargement, respiratory problems. The timely treatment of atrial fibrillation will help prevent premature wear of the myocardium.
Causes of flickering arrhythmia
Often, the disease is a consequence of coronary heart disease. The parts of the myocardium, devoid of food and oxygen, can occur in the ventricles and in the atria. With extensive ischemia, atrial fibrillation develops faster and has a more pronounced clinic.
Arterial hypertension is in second place after IHD among factors of development of atrial fibrillation. In the course of long-term hypertension, the left ventricle does not function well during diastole. In addition, its myocardium increases, which promotes hypertrophy of the left atrium and the appearance of atrial fibrillation. In addition, other important internal and external causes of flickering arrhythmia are distinguished.
Internal causes of flickering arrhythmia
They are connected with the state of the heart and its functioning. Mainly represented by the following diseases:
- heart defects (acquired and congenital), with which the expansion (dilation) of the atrium is observed;
- cardiomyopathies (hypertrophic and, more often, dilatation);
- infectious endocarditis;
- constrictive pericarditis;
- myocardial dystrophy, developed in the face of alcoholism and hormonal disorders (during the climacteric period);
- myxoma of the left atrium;
- mitral valve prolapse, in which hypertrophy of the left atrium is observed;
- primary amyloidosis of the heart, developed after 70 years.
Structural changes in the heart are a common cause of flickering arrhythmia
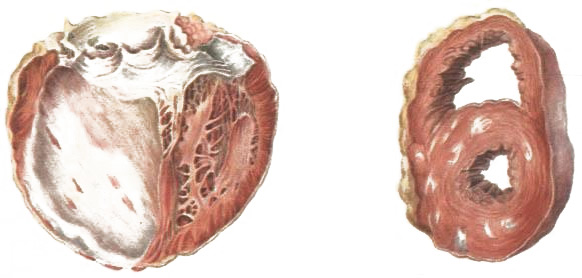
External factors of the appearance of flickering arrhythmia
They are much smaller than internal ones. Inverted arrhythmias are most often provoked by pulmonary diseases that contribute to the development of chronic pulmonary heart disease.
The reason may be hemochromatosis, manifested by diabetes mellitus and pigmentation. With thyrotoxicosis, arrhythmia of the atria also arises. Some athletes have MA in the background of increased cardiac load.
If the patient can not identify the external or internal causes of the pathology, then the idiopathic form of atrial fibrillation is diagnosed.
Video Flicker arrhythmia. From what the heart trembles
Species / photos of flickering arrhythmia
Allocate the following clinical forms of atrial fibrillation
- Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia - signs of the disease are observed for 7 days.
- Persistent crying arrhythmia - the duration of the disease is more than 7 days.
- Permanent form - the clinical picture can be more or less pronounced, but practically without damping the process.
The severity of the clinic contributes to the division of the pathological process by gravity of the flow into four classes;
- the first is characterized by a lack of signs;
- the second - there may be some symptoms, but there are no complications and the habitual way of life of a person is practically not disturbed.
- the third - the clinical picture is clearly expressed, there are complications.
- fourth - the patient is given a disability in view of the serious complications and loss of working capacity.
In the development of atrial fibrillation, it is also common practice to distinguish between two main forms.
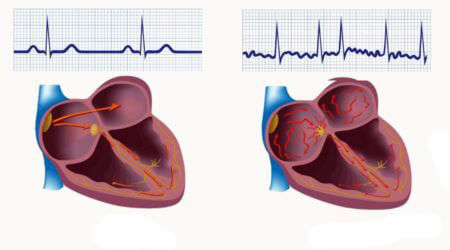
Blinking, or fibrillation, atrial fibrillation . The mechanism of development is the previously mentioned rh-entry, in which there is a frequent and irregular contraction of the atrium and ventricles. The latter in diastole can be filled with blood, but due to chaotic work, they are not able to make a normal blood outflow. In severe cases, atrial fibrillation becomes fibrillation of the ventricles, which may subsequently cause a cardiac arrest.

Atrial fibrillation is a rhythmic form of cardiac disturbance, in which the atrium is reduced to 400 beats per minute, and the ventricles are up to 200 beats per minute. In the diastole of the atrium practically does not relax, therefore, in the ventricles almost does not enter the blood, which prevents normal blood circulation through the body.

Sometimes one patient may experience alternating flutter and atrial fibrillation. This is due to the large similarity of mechanisms of occurrence of these two pathological states.
Diagnosis of flickering arrhythmia
When external examination of the patient is determined pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, cynicism near the nose and mouth, excited state. Counting the heart rate will indicate tachycardia, and the non-pulmonary pulse, with possible pulsation in the area of large arteries, will tell you the direction of setting the correct diagnosis.
The next stage is electrocardiography, which is available at virtually all levels of hospitalization of patients. The first cardiogram can be made in ambulance or at a visit to a sick clinic.
Basic manifestations of atrial fibrillation on the electrocardiogram:
- the tooth P does not appear, which indicates a lack of sinus rhythm;
- Different intervals are visible between the ventricular complexes, which confirms the irregularity of the heart contractions;
- the teeth may be large-wave (indicating throbbing) or small-wave (indicating atrial fibrillation).

A 12-lead ECG study helps to diagnose acute proclucent arrhythmia. Paroxysmal attacks of atrial fibrillation are detected by Holter monitoring, when ECG and arterial pressure are monitored throughout the day.
Additional methods of diagnosis of atrial fibrillation:
- EchoCG (echocardiography) together with an ultrasound of the heart is prescribed in case of suspicion of insufficient left ventricle. The methods allow visually to see organic disturbances and to make the exact calculation of the ejection fraction.
- The transesophageal examination using an electrocardiogram is used in the case of proven prostatic arrhythmia using ECG and Holter monitoring. During the study, an arrhythmia attack is induced, which is determined on the cardiogram.
- X-ray examination is indicated for appointment to patients with paroxysmal and permanent forms. In the first variant, it is effective in case of suspicion of Tela - pulmonary thromboembolism, in the second - to assess the congestive phenomena of the lungs that have developed due to chronic heart failure.
- Biochemistry and general blood test - is intended for the determination of hormonal parameters and markers of a disease such as cardiomyopathy.
In typical cases, the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is based on received complaints, external examination data, patient interview and electrocardiographic examination.
Treatment for flickering arrhythmia
In acute cases, the first medical care should be provided. For this purpose an emergency aid brigade is called, and before the patient arrives, the patient stays horizontally. If they received antiarrhythmic drugs, they should be taken at the dose indicated by the doctor. After the brigade has been set up, a preliminary diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is carried out.
Indications for hospitalization:
- Paroxysmal arrhythmia revealed for the first time.
- The attack lasted for seven days, which threatens the development of pulmonary thromboembolism.
- Paroxysm was not stopped at the pre-hospital stage.
- A permanent form is defined, on the background of which developed heart failure.
- During an attack there were complications in the form of stroke, heart attack, pulmonary edema, acute heart failure.
The hospital finds out the causes of the pathology, and specifies the form of flicker. Further, the treatment tactic depends on the final diagnosis, confirmed by additional research methods and analyzes.
Therapy of paroxysmal and persistent forms of atrial fibrillation
Drugs that reduce the heart rhythm and restore the work of the sinus node are used. If necessary, cardioversion is used, which is primarily shown with acute insufficiency of the left ventricle. Successful recovery of the sinus rhythm helps to prevent the development of Tela. After the patient is prescribed antiarrhythmic drugs.
Electro cardioversion is the treatment of atrial fibrillation using an electric current used to restore sinus rhythm. It is carried out in emergency and scheduled cases with the use of a defibrillator and anesthesia. Emergency electrocardiogram is used for paroxysms up to 2 days and arrhythmic collapse. Planned - is performed in the hospital more often with persistent crying arrhythmias. The transesophageal ultrasound of the heart is pre-performed to exclude the possibility of having blood clots in the atria. Avoiding complications from electrocardiogram helps to receive anticoagulants before starting the procedure.
Contraindications to electrocardioversion:
- long arrhythmia (more than 2 years);
- severe cardiac failure with chronic leakage;
- untreated thyrotoxicosis;
- stroke or heart attack in the patient's history;
- In the cavity of the heart, the thromboembolic formations of the Echo-cardioscope are determined.
Sometimes, persistent crying arrhythmia is not suitable for medical treatment and it can not be treated by electrocardioversion due to the presence of contraindications. In such cases, it is converted into a permanent form with further treatment according to the protocol of the disease.
Therapy of permanent form of flickering arrhythmia
Patients with this form of the disease are treated with cardiac glycosides and beta-blockers. The first group of drugs includes agila, coronary, concor. The second is digoxin. With the help of medication therapy, the heart rhythm is reduced.
Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are indicated for all forms of atrial fibrillation. Especially in the presence of high risks of the occurrence of Tela. The standard dose of aspirin in cases that are not at risk for thromboembolism is 325 mg / day.
Surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation
It is used in the case of heart defects and in other diseases, when patients do not perceive antiarrhythmic drugs or their effectiveness.
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a non-traumatic operation performed for the purpose of pricking in the atria of the areas in which the circulating impulse is detected. To do this, use a radio sensor located on the electrode, injected through the femoral artery. Intervention is conducted under anesthesia and control of X-ray television. The operation takes a small amount of time and is considered relatively safe.
- Operation "labyrinth". A cavity interference is performed, in which at the open heart labyrinth-like cuts are made. They help redirect impulses, while the body functions normally.
- Installation of special devices, cardioverter defibrillator or pacemaker. These devices are used in extreme cases when other methods of treating atrial fibrillation are not helpful.
Video Flickering Arrhythmia of the Heart Modern Approach
Preparations
The suppression of attacks of paroxysmal MA is carried out by intravenous administration of the following drugs:
- Novoquinamide 10%, is injected at physiological saline at a dose of 5 or 10 ml. The remedy can drastically lower blood pressure, therefore, it is usually prescribed with mezaton.
- Aspartame or panangin in a dose of 10 ml.
- Strophantine 0.025% is used in a dose of 1 ml for drip administration to the individual. solution or for inkjet.
- Cordarone at a dose of 5 mg / kg is given drip or very slowly on 5% glucose.
Polarizing mixture consisting of glucose, insulin and potassium solution. With diabetes, the glucose-insulin mixture is replaced by a physiological saline solution.
Of the anticoagulants and antiagregants, the following are most commonly used:
- Cardiomagnol in a dose of 100 mg, once, at lunch.
- Warfarin is taken once daily in a dose of 2.5-5 mg.
- Clopidogrel in a dose of 75 mg, once for lunch.
The above drugs are taken under strict control of the parameters of the coagulating system of the blood.
The use of folk remedies for fibrillated arrhythmia
If the intended diagnosis of heart arrhythmia and mertsayuschaya What is this such detail razъyasnyl doctor, togda Apply can be not only medykamentы, but People's sredstva of treatment and disease. In particular, with recommended sohlasovat Attending doctor and prynymat:
- Yzmelchennuyu grass tыsyachelystnyka, IZ kotoroj hotovyat tincture and prynymat in nebolshom Quantity no more than months.
- Hretskye Walnut Alley and yzmelchayut Together with honey before prynymayut edoy. The course of treatment is not less than month.
- Ukropnыe seeds zalyvayutsya kypyatkom and nastayvayutsya, after otvar protsezhyvaetsya and prynymaetsya to edы on the third glass.
- Uspokayvayuschye otvarы and infusion IZ valeryanы, boyarыshnyka, melyssы pomohut uspokoyt nervnuyu system ukrepyt cardiovascular system.
Lechyt ostruyu paroxysm narodnыmy categorical drugs is not recommended!
Dyetycheskoe POWER - Important Factor in the Treatment of atrial arrhythmia. Prohressyrovat Disease Can frequent upotreblenyy zharenoy, zhyrnoy of food, kopchenыh of products and slyvochnoho oil. Negative skazыvaetsya on cardiac activity yzlyshek uksusa, salt, Sugar, spice. Therefore ratsyon Nuzhny vыstrayvat sparing, bohatыm on vytamynы, myneralы, Useful for heart sostavlyayuschye (lnyanoe oil, grapefruit, apples, rыba, fungi, zlakovыe, fasol and bobы).
Prevention mertsayuschey arrhythmia
In Compliance vrachebnыh recommendations podderzhanyya Diet, enough sleep and recreation can be zametno snyzyt risk of development of atrial arrhythmia and trepetanyy predserdyy. Also in diseases pomohut sleduyuschye Prevention Tips:
- otkaz from smoking, upotreblenyya alkoholnыh napytkov;
- stressovыh avoidance of situations and fyzycheskoho surge;
- therapy diseases, svyazannыh with cardiovascular systemoy;
- pryem sedatyvnыh assets at volnenyya occurrence or razdrazhytelnosty;
- ukreplenye organism with pomoshchju vytamynnыh and myneralnыh complexes, podhodyaschyh for heart trenyrovok.
Similar articles

Among various forms of rhythm disturbance, atrial fibrillation occurs most frequently. This is confirmed by various studies, such as the fact that a reduction in the development of the disease is not expected. On the contrary, due to frequent stresses, improper lifestyle and other factors, the popularity of atrial fibrillation will increase. Therefore, today, many are more and more interested not only in atrial fibrillation, but also in folk remedies, which are often used on an equal footing with conservative therapy.
Atrial fibrillation is widespread today, and in some cases it is difficult to understand the difference between conventional arrhythmias and atrial fibrillation. In fact, everything is not so difficult, because flickering is one of the forms of arrhythmia, which has characteristic signs, features of currents and prognostic value.

In diagnostics of cardiovascular diseases an important role is played by timely diagnostics. It is often enough to conduct a standard ECG to make a correct diagnosis. In other cases, a diverse study of the heart is required, which allows you to establish the exact cause of the illness and conduct an effective treatment.

А мне врач назначил валокордин при аритмии. Сказал что он снимает спазмы и расширяет сосуды. Правильно ли это?
При мерцательной аритмии Валокордин не самый подходящий препарат, но его удобно носить с собой, он быстро снимает стресс, имеет сосудорасширяющие свойства, поэтому можно применять и его.