Medicinal arrhythmia
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-10
The heart is sensitive to many factors that affect it from within the body and from the outside. Some of them can cause a rhythm disorder, which can be expressed by an intensified or weakened heartbeat. In some cases it is difficult to control the root cause that can cause arrhythmia: high temperature rise against the background of an infectious disease, insect bites or hormonal disorders. But sometimes banal overdose of drugs can cause serious medication arrhythmia, which has to be stopped by special methods of treatment.
Medication arrhythmia is not included in the classification of ICD-10, but in medical practice it is often considered as a deviation from the norm of cardiac rhythm of unspecified pathogenesis.
In its development, medication arrhythmia is manifested by various types of cardiac impairment. Both tachycardia and bradycardia are observed, as well as crying arrhythmia may occur in the presence of an organic lesion of the myocardium. It all depends on the drug, which dose has been exceeded.
Description of medication arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is a disturbance of the rhythm of cardiac activity, which is expressed in the change in the frequency of heart contractions in the direction of increase (tachycardia) or decrease (bradycardia). It is also possible to develop a paroxysmal arrhythmia such as extrasystole or paroxysmal tachycardia.
Medicamentous arrhythmia occurs most often on the background of the lack of perception by the body of certain drugs or excessive use of them. This is precisely why many manufacturers on the packaging of medicines indicate the possible influence of its components on those or other organs.
For adults, the normal state is characterized by heart rate 60-90 times per minute, rhythmic and uninterrupted activity of the heart.
The work of the heart can be stimulated by the action of various substances. There is a heartbeat or heart failure that has a different degree of severity. Asymptomatic arrhythmias practically do not violate the habitual way of life of a person and he is considered clinically healthy. But with excessive exposure to toxic or medicinal products, the activity of the cardiovascular system is often severely disrupted, which can lead to severe consequences.
What is the risk of medication arrhythmia ? First and foremost, a sharp violation of hemodynamics. In a short time from the onset of the drug, rapid heart failure and, as a consequence, clinical death may develop rapidly.
Symptoms of medication arrhythmias
The insignificant effect of drugs is often expressed in palpitations, dizziness, and weakness. Throbbing shocks may be felt in the heart area.
During the overdose of medications, the appearance of nausea is characteristic, which in some cases ends with vomiting.
A significant overdose of drugs causes the development of a serious clinic. Severe pain may appear in the area of the heart, there is a lack of air, and in some cases, arterial pressure rises. The heartbeat may increase in the form of atrial fibrillation, that is, reaching 500-700 counts per minute. Such a sharp deterioration of the general condition may result in cardiac arrest.
Causes of medication arrhythmias
Many modern drugs are capable of acting in one way or another on cardiovascular activity. Some become the cause of a heartbeat, others are bradycardia. Some medications can cause acute heart failure and, as a result, heart failure.
What drugs can cause medication arrhythmias?
- beta-blockers;
- clonidine and reserpine;
- cardiac glycosides;
- adrenomimetics and psychostimulants;
- some antiarrhythmic drugs.
Beta-blockers - Metoprolol and atenolol are most commonly used in this group. They mainly help reduce heart rate and are therefore often used in antiarrhythmic therapy. Also prescribed for the prevention of relapses of repeated infarction and the treatment of arterial hypertension. With their overdose, they can cause bradycardia.
Clonidine and reserpine - refer to antihypertensive drugs. Affects cardiac activity by reducing emissions.
Cardiac glycosides - this includes corglicon, digoxin, strophanthin. They have a glycosidic structure, so they can work as selective cardiotonics. With their overdose accumulate in the body, which subsequently is expressed in bradycardia, that is, the decrease in heart rate.
Adrenomimetics and psychostimulants , as well as substances similar to them acting on the principle of action of the substance (caffeine and atropine), stimulate the work of the heart, which is expressed in tachycardia.
The combination of some drugs adversely affects cardiac activity, so medical treatment should be prescribed by a doctor.
What drugs can cause heart failure?
- Miorelaksants - relax muscle fibers by blocking specific receptors. As a result, not only the body immobilises, but also reduces cardiac output. Overdose in 90% of cases occurs in the death of a person.
- Preparations for heartburn, such as Domperidon, have a very negative effect on the work of the heart, can cause seizures, nervous disorders and cause a clinical death.
- Antibiotics are quite dangerous for people who are prone to allergic reactions, diabetes and diseases of the respiratory system. The macrolide medication arrhythmia is especially common. Among them, clarithromycin, erythromycin, azithromycin were negatively identified.
- Vitamins - very useful in small doses in case of excessive use become a reason for cardiac arrest. First of all it concerns vitamin K, which is known as vikasol, widely prescribed before delivery or surgery. Overdose of calcium leads to thrombosis, including in the vessels of the heart, which in turn can cause its stop.
- Psychotropic substances - may be of chemical or vegetable origin. In case of overdose, tachycardia, interruptions in the rhythm of the heart, discomfort and chest pain are caused. In addition, the consciousness is broken, the muscles on the limbs and the face begin to decrease involuntarily. In addition, blood pressure may rise sharply, which will lead to clinical death.
Arrhythmias that arise from overdose of drugs
During the overdose of medical preparations, various forms of arrhythmias are associated with the disruption of conduction of an electrical pulse through the heart. Most commonly, sinus and paroxysmal tachycardia arise. Heavier complications include cardiac blockages and atrial fibrillation.
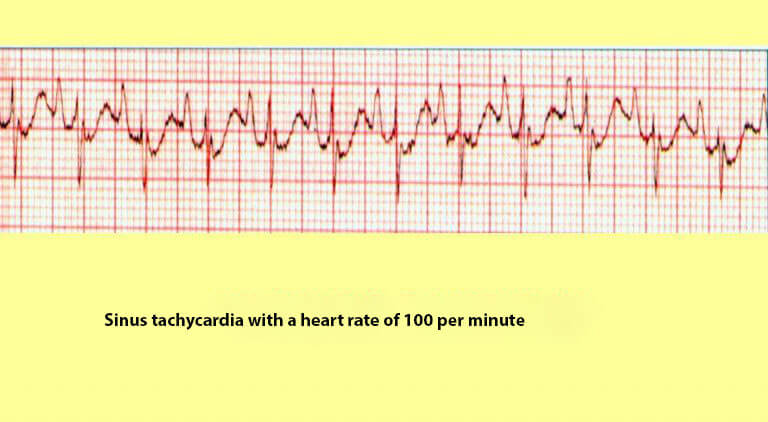
Sinus tachycardia
It develops when overdose of adrenomimetics, psychostimulants, or non-perception of these drugs by the patient. It manifests itself as a pronounced heartbeat with the preservation of sinus rhythm. With this arrhythmia, heart rate can reach 150 times per minute.
Against the background of a rapid heartbeat, anxiety and fear for life may appear. If the overdose was insignificant, then after a while the heart rhythm will come to the normal. Otherwise, you should seek medical assistance.
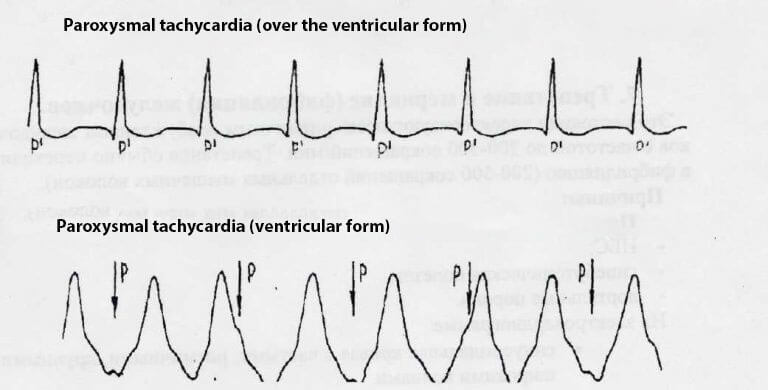
Paroxysmal tachycardia
It manifests itself in the form of attacks of the heartbeat that arise suddenly. In the area of the heart there are jerky blows. As a rule, the patient is able to accurately indicate when he has started and ended an attack. After the overdose of drugs, there may be several. The stronger the dose was chosen, the more pronounced the clinic. In complicated cases, paroxysmal tachycardia is rapidly converted to fibrillation, which should be rendered immediately to medical workers.
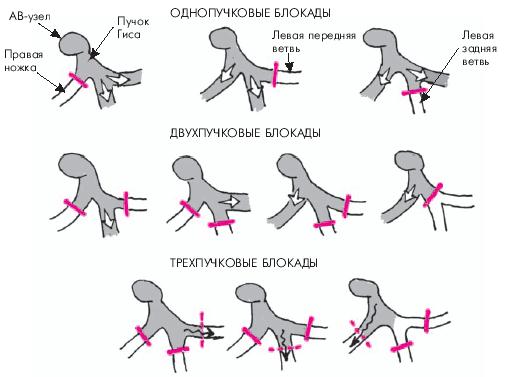
Heart blockades
A special form of arrhythmias, characterized by impaired pulmonary conduction disturbance in cardiac departments.Quite often there are elderly people taking heart glycosides during the treatment of hypertension. Characterized by slowdowns and interruptions of cardiac activity. Most commonly occurs bradycardia, which, in particularly dangerous cases, ends with a heart failure. Therefore, it is very important cardiac glycosides, and drugs similar to them, to take in precisely prescribed dosages by the doctor.
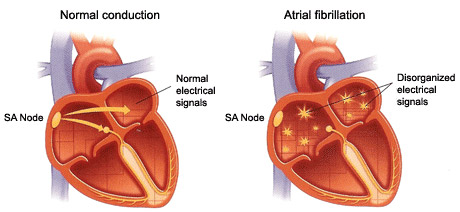
Inverted arrhythmia
The most dangerous of all forms of medical arrhythmia, since during its development there are serious disorders of hemodynamics. Pathology is more common in women than in men. The flicker is accompanied by a rapid and chaotic reduction of atrium - from 400 to 600 times per minute. At the same time in the ventricles do not receive all the pulses, therefore their frequency of contraction is less - about 300-450 times per minute.
Diagnosis of medication arrhythmia
At first, the patient is examined, they find out complaints from him or his relatives, and after listening to the heart, the lungs for a more precise diagnosis are given directions to additional research methods.
Electrocardiography is the basic method of diagnosis, which helps to detect up to 90% of all types of arrhythmias, including medicated ones. The main thing is that the rhythm disturbance was available at the time of the study. It is not always possible to achieve such a similarity with single extrasystoles, paroxysmal tachycardia.
Holter-Electrocardiography - Used to diagnose unstable, single-type violations of rhythms. For medical arrhythmias, this is not so characteristic, except that when there is a chronic intoxication with medicinal substances
A tilt test is conducted to determine drugs that can cause arrhythmias or loss of consciousness. To do this, the patient is locked up on a table, which tilts in different directions. Drugs suspected of developing arrhythmia are also administered intravenously. During the study, the cardiogram is recorded, the blood pressure is determined, and conclusions are drawn based on the data obtained.

Treatment and prognosis for medication arrhythmias
In the event of medication arrhythmias, first of all, stop taking medications that provoke cardiac arrhythmias. The ambulance brigade is then called and care should be provided to the patient before her arrival.
Principles of first aid in case of overdose of medicines:
- The patient should be put in bed, give a drink of pure non-carbonated water.
- If possible, open the windows for fresh air inflow or use another possible method.
- It is not necessary to cause vomiting in the patient or to rinse the stomach , since such actions only complicate the course of medication arrhythmias.
- It is possible to give activated charcoal that will help to remove products of intoxication from the body.
Any medication poisoning is treated in a hospital setting. In severe cases, the patient may be in intensive care for several days. As a rule, lidocaine is administered to eliminate arrhythmia. The only thing he should normally tolerate is the patient. At bradycardia, atropine is administered intravenously. Beta-adrenergic blockers and potassium supplements may also be used if they, again, did not cause arrhythmias.
After discharge, you must carefully monitor the condition of the patient for at least six months. Cardiac examinations should be performed regularly. In the future, medicines should be more carefully selected in the treatment of major illnesses.
With the timely conduct of detoxification therapy, the prognosis for medication arrhythmias is favorable. Although about 8-15% of the victims die from overdose of the same heart glycosides.
Video Poisoning - Emergency care
Prevention of medication arrhythmia
The main thing is to receive only those medications prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication with the use of cardiac glycosides, beta-blockers, adrenergic drugs, psychotropic drugs and banal anti-inflammatory medicines can be fraught with life-threatening consequences.
It is important not to overdo the reception of already prescribed medications. Sometimes it may seem that the dose is wrong, because the desired result is not visible. It is absolutely impossible to decide such issues alone, but only to express their opinion to the treating doctor, who will make the final decision on increasing the dosage or canceling the drug.
Video for Phenazepam: Efficiency, Duration of Admission, Side Effects, Overdose

Как правило, многие люди страдают разными болезнями и, поэтому, обращаются к разным специалистам, которые выписывают лекарства, не согласуя их с другими назначениями..Купив разные лекарства от разных врачей, пациент начинает их принимать одновременно. А как они действуют на организм при совместном приеме? Не может ли навредить такое действие сердцу,почкам или печени?