Cardiomyopathy
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-03-06
Cardiomyopathy (KMP) is a group of diseases that are associated with similar mechanisms of action on the heart muscle At first, there may be several symptoms or there is no clinic at all. Some patients complain of shortness of breath, fatigue or swelling of the legs due to heart failure. May disturb irregular heart rhythm, as well as pre-anxious and abnormal conditions. Patients are at increased risk of sudden cardiac death.
In 2015, cardiomyopathy and myocarditis were diagnosed in 2.5 million people [1 - GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators]. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy affects about 1 in 500 people, and dilated cardiomyopathy is 1 out of 2500. [2 - "Types of Cardiomyopathy." NHLBI 22 June 2016. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016. Retrieved from August 31, 2016.].Since 1990, KMP has caused 354,000 deaths.Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia is more common in young people.
Some people with cardiomyopathy have no symptoms or symptoms and do not need treatment. In other patients, the disease develops rapidly, the clinical picture is severe, and in the future there are serious complications. In such cases, it is necessary to prescribe a treatment that involves changing lifestyle, taking medications. Surgery can be activated, implantation of the device for correction of arrhythmias is carried out. If necessary, non-surgical procedures are prescribed.
Video cardiomyopathy is a general characteristic
Description
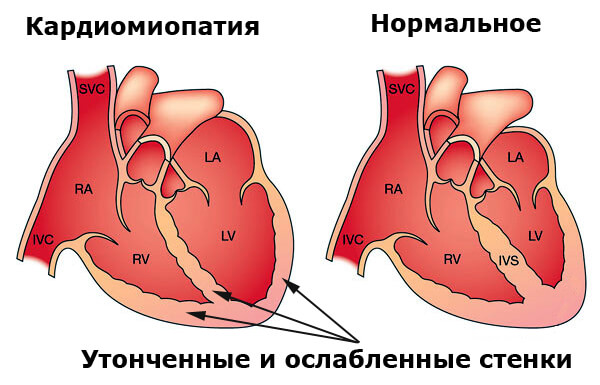
With cardiomyopathy, the heart muscle changes. It may increase, thicken or become more rigid and incapable of contraction. In rare cases, the muscle tissue in the heart is replaced by scar tissue.
In the International Classification of Diseases of the Tenth Revision (ICD-10), the cardiomyopathy group is under code I42.
As cardiomyopathy progresses, the heart becomes weaker. It is less intensely pervading blood throughout the body and is not able to maintain normal heart rhythm.
In severe cases, KMP leads to heart failure or irregular heart contractions, which are called arrhythmias. In turn, heart failure can cause stagnation of blood in the lungs, legs or stomach. The weakening of the heart may also cause other complications, such as problems with heart valves.
Depending on changes in the myocardium, cardiomyopathy is classified into the following types:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (including asymmetric obstructive type hypertrophy with muscular subarateral stenosis)
- Dilatational cardiomyopathy (congestive, congestive)
- Obstructive cardiomyopathy (constrictive, restrictive)
Depending on the cause of the development, cardiomyopathy is divided into the following forms:
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
- Pericardial cardiomyopathy
- Cocaine cardiomyopathy
- Medicinal cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmogenic dysplasia of the right ventricle
- Cardiomyopathy Takozubo
Separate examination of unqualified cardiomyopathy. Cardiomyopathy in children is of great importance, since in such cases there are certain features of the course of the disease, its diagnosis and treatment.
Reasons
There is an acquired and hereditary cardiomyopathy. "Acquired" means that a person is not born with this disease, but it develops already during life on the background of another disease, condition or factor.
"Hereditary" means that the parents passed on to their child the gene responsible for the development of cardiomyopathy. Researchers continue to seek genetic linkages with cardiomyopathy, and they are also investigating how these links cause or contribute to the emergence of various types of disease.
In many cases, the cause of cardiomyopathy is unknown.Often this happens when the disease develops in children.
Causes of development of individual forms of cardiomyopathy:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is most often inherited . This is due to the mutation or alteration of some genes in the heart muscle fibers. Also, the pathology may develop over time with high blood pressure, aging or other diseases such as diabetes or thyroid disease. Sometimes the cause of the disease is unknown.
- Dilatational cardiomyopathy. The reason for an extended KMP is often unknown. About a third of people who are ill with this disease inherit it from their parents.
- Obstructive cardiomyopathy. The most common cause of this form of KMP is amyloidosis (a disease in which abnormal proteins accumulate in organs including the heart), connective tissue growth, hemochromatosis: (an illness in which too much iron is accumulated in the body), sarcoidosis (a disease that causes inflammation and can affect various organs), some types of cancer treatments such as radiation and chemotherapy.
Some diseases, circumstances and substances can also contribute to cardiomyopathy:
- Alcohol, especially when combined with poor nutrition
- Some toxins, such as poisons and heavy metal salts
- Complications during the last months of pregnancy
- A range of diseases: coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, high blood pressure, diabetes, thyroid disease, viral hepatitis and HIV
- Drug use, such as cocaine and amphetamine, and some medications used to treat cancer
- Infections, especially viral, which have a tropism to the heart muscle.
span id="i-3"Risk factors
People of all ages and races may be affected by cardiomyopathy. However, some types of disease are more common in certain groups.
Dilatational cardiomyopathy is more common in African Americans than in white. This type of illness is also more common among men than among women.
Adolescents and young people are more likely to have arrhythmogenic dysplasia of the right ventricle than older people, although for both age groups this form of cardiomyopathy is rare.
The main risk factors
- Family predisposition to cardiomyopathy, heart failure or sudden cardiac arrest
- The presence of a disease that can be complicated by cardiomyopathy (coronary heart disease, heart attack, or a viral infection that affects the heart muscle)
- Diabetes or other metabolic diseases, including severe obesity
- Diseases that can damage the heart, such as hemochromatosis, sarcoidosis or amyloidosis
- Frequent increase in blood pressure
- Asymptomatic course of cardiomyopathy
- Chronic alcoholism.
Identifying people who may be at high risk is very important. This can help to prevent serious problems in the future, which may include the development of severe arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats) or sudden cardiac arrest.
Video Cardiomyopathy - Symptoms, Causes and Risk Group
Species
The main types of cardiomyopathy, such as hypertrophic, dilatational, obstructive, unqualified, as well as arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia will be considered.
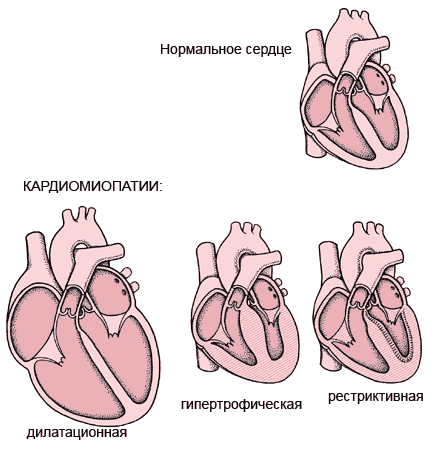
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Very common and can develop in people of all ages. The disease is equally common in both men and women. It is determined in about 1 out of every 500 people.
About hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is said when the heart muscle increases and thickens without an obvious reason. Usually the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart) and the septum (the wall that separates the left and right half of the heart) thickens. The affected areas contribute to the formation of narrowing and occlusion of the ventricles, which creates even greater difficulties for blood transfusion in the heart. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can also increase the stiffness of the ventricular myocardium, alter the structure of the mitral valve, and provoke cellular impairment in the heart tissue.
Dilatational cardiomyopathy
This form of cardiomyopathy is characterized by dilation and weakening of the ventricles. In most cases, the left ventricle is first and foremost a pathologic process can pass to the right ventricle. Weakened heart chambers do not work so effectively to ensure normal circulation throughout the body. As a result, over time, the heart loses the ability to effectively blow blood. Dilatational cardiomyopathy may be complicated by heart failure, heart valve disease, irregular heart rhythm, and blood clots formation in the cells of the heart.
Obstructive cardiomyopathy
The disease develops in cases where the stiffness of the ventricle myocardium increases, although the walls of the heart do not thicken. As a result, the ventricles do not fully relax, and therefore do not fill up with normal blood volume. As the disease progresses, the level of cardiac output drops and the heart muscle weakens. Over time, restrictive cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure and problems with heart valves.
Arrhythmogenic dysplasia of the right ventricle
Pathology is a rare type of cardiomyopathy, which most often occurs when the right ventricular myocardium is replaced by fatty or connective tissue. This often leads to violations of electrical heart signals, which leads to arrhythmias. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia is usually defined in adolescents or young people. In severe cases, it can cause sudden cardiac arrest in young athletes.
Unclassified cardiomyopathy
Other types of diseases are included in this category of cardiomyopathy:
- Hypertrabellarity of the left ventricle (is a congenital cardiomyopathy, in which the normal and second "spongy" layer of the myocardium is detected within the left ventricle).
Takozubo Cardiomyopathy or broken heart syndrome - develops against the background of extreme stress that leads to heart failure. Although this phenomenon is rarely encountered, this disease is more commonly found in postmenopausal women.
Clinic
Some people who have cardiomyopathy have no signs or symptoms. The other clinical picture in the early stages of the disease is poorly expressed.
With the progression of cardiomyopathy, the general condition of the patient worsens, and the work of the heart becomes weakened. This is usually manifested by symptoms and symptoms of heart failure, which include:
- Shortness of breath or shortness of breath, especially during exercise
- Fatigue or severe weakness
- Swelling on the ankles, legs, stomach and veins in the neck area
Other symptoms in cardiomyopathy may be dizziness; delirious; syncope during physical activity; arrhythmia (irregular cardiac contractions); chest pain, especially after exercise or heavy food. Also, heartbeat sounds are often defined - these are additional or unusual sounds that are heard during a heartbeat.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of cardiomyopathy is based on the medical and family history of the patient, as well as the physical examination and the results of laboratory tests / instrumental procedures.
Consultation of specialists
Cardiomyopathy is mainly done by a cardiologist or a pediatric cardiologist who carries out the examination and treatment of the patient. The cardiologist specializes in the diagnosis and therapy of cardiovascular diseases. Pediatric cardiologist - a doctor who cares for children.
Medical and family history
The patient is interviewed, during which complaints and symptoms are presented to the patient. also turns out how long the signs of illness disturb the patient.
The doctor may inquire whether anyone in the family is suffering from cardiomyopathy, heart failure or sudden cardiac arrest.
Physical examination
During a physical examination, the physician must use a stethoscope to listen to the heart and lungs, with the help of which sounds are determined, often indicative of cardiomyopathy. Similar auscultative signs may even allow for a presumptive conclusion on the type of disease.
For example, with obstructive and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, loud heart beats are determined. Also, the "crispy" sound in the lungs is often heard, which can also be a sign of heart failure, which develops most often in later stages of cardiomyopathy.
In addition, swelling of the ankles, feet, stomach or veins on the neck can be determined, which indicates the accumulation of fluid (a sign of heart failure).
Diagnostic tests
The doctor may recommend one or more of the following tests for diagnosing cardiomyopathy.
- Blood test During the study, a small amount of blood is taken. Most often they are taken from the vein with a special needle. The procedure usually takes place quickly and easily, although there is often some short-term discomfort. Blood analysis helps determine the general condition of the patient.
- X-ray of the chest fixes on the film a picture of the organs and structures in the chest (heart, lung and blood vessels). This study can show if the heart size is enlarged or if fluid in the lungs is determined.
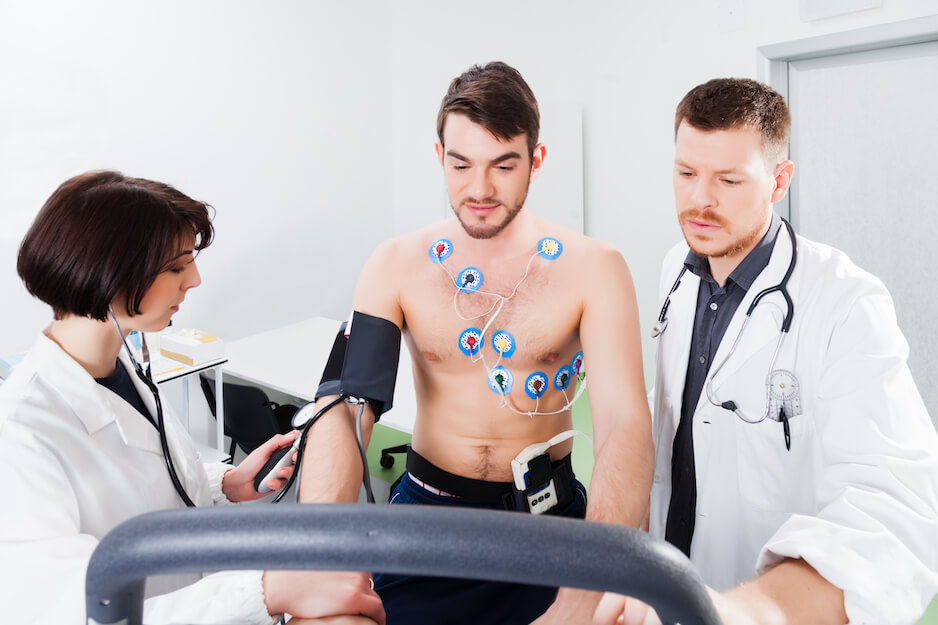
- An ECG is a simple diagnostic method that registers the electrical activity of the heart. Shows how quickly the heart beats and what is its rhythm (normal or irregular). The ECG also records the power and time of electrical signals when they pass through each heart chamber.
- Holter monitoring. The patient is offered a small portable device that records the electrical activity of the heart while the person is doing his daily work for 24 or 48 hours.
- Echocardiography (echocardiography) is a test that uses sound waves to create a moving heart image. The monitor shows the work of the organ, its size and shape. There are several types of echocardiography, including a study with a load. This study is conducted like a stress test. Stress chocardiography may show a decrease in blood flow to the heart, as well as signs of coronary heart disease. Another type of echocardiogram is a transesophageal study that gives an idea of deep heart defects.
- Stress test.Some heart problems are easier to diagnose when the body is working under load. In the course of stress testing, the patient is trained or taken medication, which helps to intensify the heartbeat. This type of test can be combined with a scan of the heart, echocardiogram and positron emission tomography of the heart.
Diagnostic procedures
To confirm the diagnosis, one or more medical procedures may be required to confirm the diagnosis or prepare the patient for surgery. These studies may include cardiac catheterization, coronary angiography, or myocardial biopsy.
- Catheterization of the heart. This procedure allows you to determine the blood pressure and blood flow in the chambers of the heart. It also makes it possible to collect blood samples and to assess the condition of the arteries of the heart using an X-ray image. During the catheterization of the heart, a long, thin flexible tube, called a catheter, is placed in the blood vessel of the hands or in the groin (upper part of the thigh) or neck and directed to the heart.
- Ischemic angiography. This procedure is often combined with cardiac catheterization. During the study, the dye, which can be seen on the X-ray image, is injected into the coronary arteries, which explains hemodynamics of the heart and blood vessels. The paint can also be inserted directly into the heart chambers. This allows the doctor to study the cardiac output.
- Myocardial biopsy. During this procedure, the doctor takes a small portion of the heart muscle. For this purpose, catheterization of the heart is performed. Subsequently, the biopsy of the heart muscle is studied under a microscope, resulting in visible changes in the cells. Myocardial biopsy is used to diagnose some types of cardiomyopathy.
- Genetic testing. Certain types of cardiomyopathy are observed in families. If a test shows that a person has a chance to become ill, a doctor may start treatment at an early stage of the disease when the medicine works best, to find the disease from the parents, brothers and sisters or other family members of the patient.
Treatment
In the presence of cardiomyopathy, which is not manifested by symptoms or symptoms, treatment is often not prescribed. Sometimes, extensive cardiomyopathy, which develops suddenly, may disappear by itself. In other cases, in the presence of cardiomyopathy, treatment is required, which depends on the type of disease, the severity of the symptoms, the accompanying complications, as well as the age and general health of the patient.
Cardiomyopathy treatment may include:
- Changing lifestyle
- Use of medication
- Passage of non-surgical procedures
- Surgical effects
- Implantation of the device
- Heart transplantation
The main goals of cardiomyopathy treatment include:
- Control of clinical manifestations so that the patient has a normal quality of life
- Managing predisposing factors that cause or contribute to the disease
- Prevention of complications and the risk of sudden cardiac arrest
Changing lifestyle
To improve the general condition of the patient it is useful to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Practicing healthy eating
- Keep body weight within acceptable limits
- Avoid stressful situations
- To have an active lifestyle
- Refuse to smoke
Use of medication
Different medicines are used to treat cardiomyopathy. In particular, drugs are prescribed for:
- Restoration of electrolyte balance in the body. Electrolytes are required to maintain a level of fluid and an acid-base balance within acceptable limits. They also participate in the work of muscles and nerve fibers. Disturbance in the concentration of electrolytes can be a sign of dehydration (lack of fluid in the body), as well as heart failure, high blood pressure or other diseases. In order to regulate the balance of electrolytes, blockers of aldosterone are often used.
- Normalizing the heart rate. Antiarrhythmic drugs help prevent arrhythmia, as they adjust the heart to a normal rhythm.
- Blood Pressure Reduction. ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers are used to effectively lower blood pressure.
- Prevention of thrombus formation.For this purpose anticoagulants are most often prescribed.uch drugs are especially indicated in the presence of advanced cardiomyopathy.
- Reducing the inflammatory process. A similar task is achieved with the help of drugs from the group of corticosteroids.
- Removing excess sodium. Mostly used diuretics and cardiac glycosides, which remove sodium from the body and reduce the amount of fluid in the blood.
- Slow heart rate. Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers and digoxin are used. hese drug groups are also used to lower blood pressure.
Drugs prescribed by a doctor should be taken regularly. Do not change the dosage of the drug or pass the dose if the doctor has not spoken about it.
Video Dilatational cardiomyopathy. Symptoms, Symptoms and Treatment Methods
Surgical effects
Doctors use several types of surgical interventions to treat cardiomyopathy. Septal myectomy, device implantation, or heart transplant depending on the readings.
- Septic myectomy
The presented operation is carried out in the open heart. It is used to treat people with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy to eliminate severe manifestations. Assigned to young patients in the absence of the effect of the medication taken, as well as those patients who are badly helped by medications.
During surgery, the surgeon removes part of the thickened partition, which protrudes into the left ventricle. It improves hemodynamics of the heart and the general system of blood supply. After removal, the myocardium does not grow. If necessary, the surgeon can also simultaneously restore or replace the mitral valve. Septic
Myectomy is often carried out successfully and allows you to return to normal life without symptoms.
- Implantation of the device
Surgeons can install several types of devices in the heart to improve function and symptom relief, including:
- Device for resynchronizing heart therapy. With its help, the contractions of the left and right ventricles of the heart are coordinated.
- Cardioverter defibrillator. Helps to control life-threatening arrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac arrest. This small device is implanted into the chest or abdomen and connected to the heart through special wiring. If there is a dangerous change in the heart rate, then an electrical signal is sent to the myocardium, helping to restore normal heartbeat.
- Auxiliary device for the left ventricle . Helps the heart to pump blood throughout the body. Can be used for long-term therapy or short-term treatment of people waiting for a heart transplant.
- Pacemaker . This small device is placed under the skin on the chest or abdomen to control various forms of arrhythmia. The device's operation is based on the generation of electrical impulses, which makes the heart beat at normal speed.
Heart transplantation
For this operation, the surgeon replaces the sick heart of a healthy person, taken from a deceased donor. Heart transplantation is the last method of treating people with heart failure, which is often a complication of cardiomyopathy. In such cases, the condition of the patient is so serious that all treatments other than heart transplants can not be successful.
Non-surgical procedures
Doctors can use non-surgical methods for the ablation type for alcohol treatment of cardiomyopathy. During this procedure, the doctor inserts a solution from ethanol through the tube into a small artery that supplies blood to the thickened area of the heart muscle. Alcohol kills cells, resulting in a thickened myocardium compressed to more normal sizes. After this procedure blood flows more freely through the ventricle, which improves the clinical picture.
Forecast
The prognostic conclusion for cardiomyopathy depends on many different components, including:
- The cause and type of cardiomyopathy
- How well does the body react to the treatment
- The severity and severity of the clinical picture
The emergence of cardiac failure in the KMP often indicates a long-term (chronic) course of the disease. Over time, the condition may worsen. Some people develop severe cardiac insufficiency that requires surgical intervention. In the extreme case, medications, surgery and other treatments can no longer help.
Prevention
It is almost impossible to prevent the development of hereditary cardiomyopathy. Nevertheless, measures can be taken to reduce the risk of diseases or conditions that may lead to cardiomyopathy or complicate its course. In particular, prevention of coronary heart disease, high blood pressure and myocardial infarction should be performed.
If necessary, the doctor can advise to bring changes in the habitual way of life. More often recommend:
- Avoid using alcohol and drugs
- Getting enough sleep and rest
- Adhere to a healthy heart for nutrition
- Exercise enough physical activity
- Do not give way to stress
- Quit smoking
Cardiomyopathy may be caused by the underlying disease or condition. If you take his treatment at an early stage of development, then you can prevent complications of KMP. For example, it is important to monitor high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol and diabetes in a timely manner:
Video About the most important: Cardiomyopathy
Similar articles
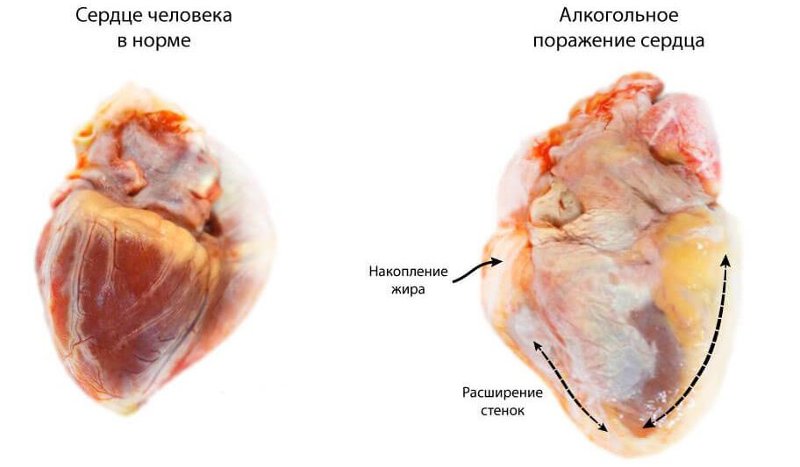
Every year, the number of patients increases in alcoholic cardiomyopathy. This pathological condition is still known as an alcoholic heart, alcohol myocardial dystrophy, "beer heart" or "bull's heart". The more pronounced the signs of the disease, the more critical the state of health of the patient, therefore, it is extremely important to pay attention to the disturbance in time, which will allow for adequate treatment.
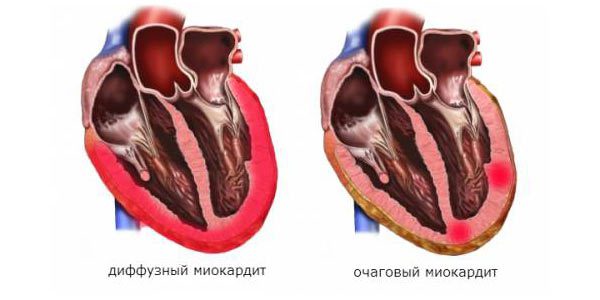
Heart disease can be associated with non-inflammatory pathological processes, which lead to equally difficult consequences, in particular to dyshormonal cardiomyopathy. If a patient has been examined and conducted medical treatment in a timely manner, then the prognostic conclusion is most often favorable.

The disease can develop as early as 30-35 years and help to reduce the quality of life of the patient. In 10-20% of cases, the disease is transmitted by inheritance. In some patients, hemodynamic disturbances are so pronounced that it is threatened by a cardiac arrest. With timely treatment, the prognostic value can be improved.
