Ischemic stroke
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-06-27
Ischemic stroke (AI) is a brain damage that occurs due to impaired cerebral circulation.Emerging against the background of the damage symptoms are characteristic for that part of the brain that does not receive in the required quantity of oxygen and nutrients.
There are several types of stroke, among which ischemic (up to 85% of cases), more rarely - hemorrhagic (up to 20% of cases). Thus, the ratio between hemorrhagic and ischemic types of stroke is 1: 4.
The stroke is diagnosed primarily in clinical manifestations, and only after the patient is admitted to a medical institution does it become possible to make an MRI, REG and other studies. With the timely provision of medical care, the prognosis is usually favorable, although often after a stroke complications occur that worsen the patient's quality of life.
Video: Ischemic stroke
Types
Ischemic stroke is a fairly common disease - about 85 people out of every 100 who have a stroke, this diagnosis is made. There are two different ways of developing AI.
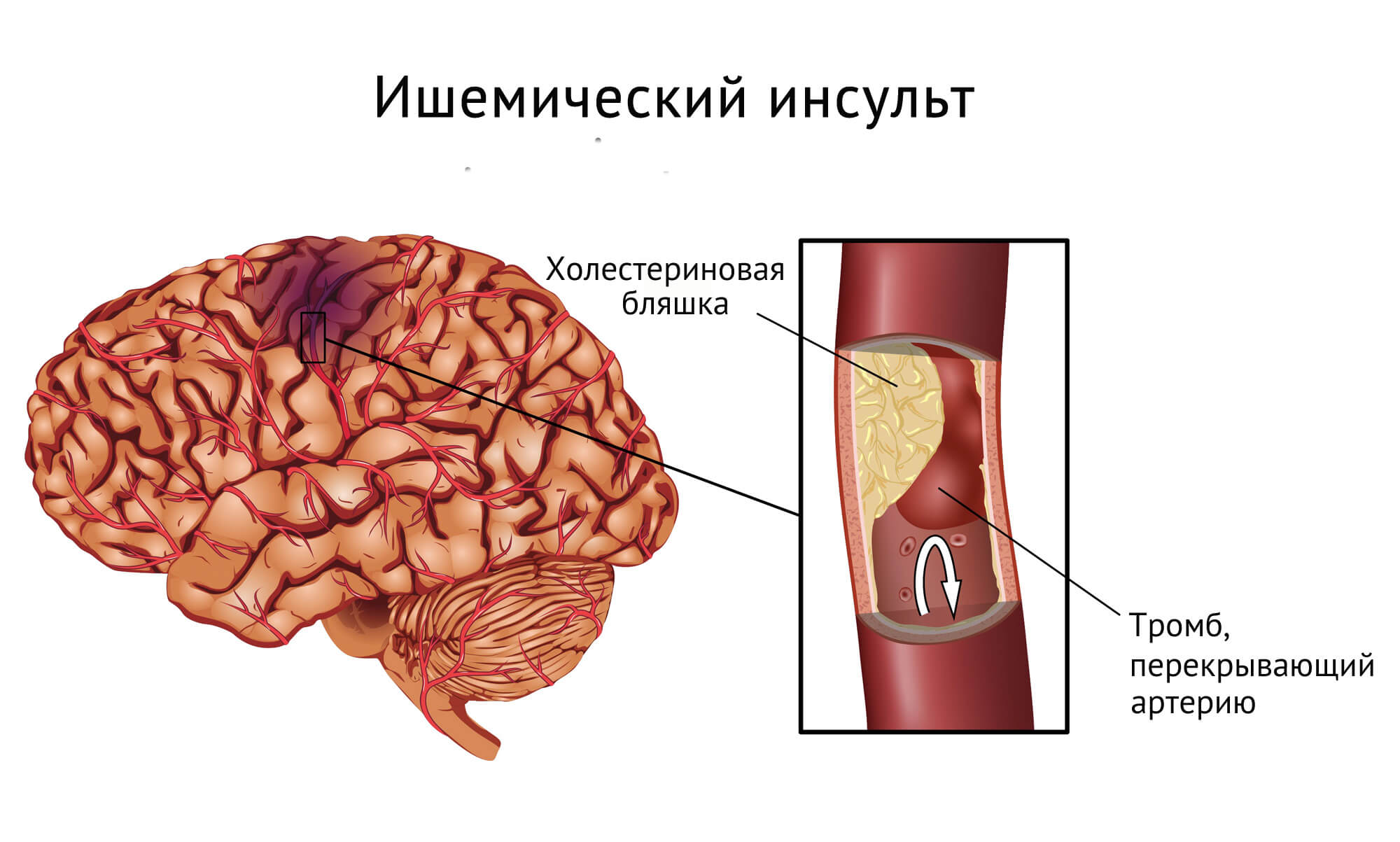
- Arterial thrombosis (also called thrombotic stroke or cerebral thrombosis). This is when a blood clot forms in the artery, as a result of which blood supply is blocked.
- Cerebral embolism (also known as embolic stroke). This is when a blood clot forms elsewhere in the body and, moving through the vessels to the brain, blocks them and disrupts the blood supply. A clot is usually formed in the heart or in one of the large arteries that supply the brain.
Depending on the current AI distinguish three degrees of severity:
- An easy degree is shown by insignificant displays of a cerebral infringement which approximately in a month completely pass or take place.
- The average degree - here more pronounced focal neurological symptoms than cerebral palsy.
- Severe degree - the patient is determined by severe cerebral disorders, which are often supplemented by weakness of consciousness, dislocation symptoms, etc.
Since the brain is supplied with various blood vessels, when one of them is clogged, AI develops with a certain localization that corresponds to the affected arterial basin:
- Brain arteries (anterior, middle and posterior).
- The main and vertebral arteries and vessels, which branch off from them.
- Internal carotid artery.
Causes
The development of AI is primarily associated with a clot of blood or the accumulation of fatty inclusions that block the flow of blood through the vessels of the brain. It is also often determined thromboembolism - this is when, for example, a thrombus forms in the heart cavity, which after entering the general bloodstream is entered with blood in the brain.
The likelihood of occurrence of an ischemic stroke is observed in people of African or Asian nationality. AI is also more often diagnosed in people after age 65, although the incidence of AI among middle-aged people has increased.
If an abnormal heartbeat, called atrial fibrillation, is determined, the patient is more likely to have an ischemic stroke.This is due to the fact that during a frequent irregular rhythm in the heart formed clots, often moving through the circulatory network of the brain.
The risk of blood clots increases markedly if the arteries are severely narrowed or fat deposits are determined inside them. A similar disorder is known as atherosclerosis and is more often detected in middle-aged and older people. Also, the formation of atherosclerosis, which leads to AI, contributes to:
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- poor physical activity;
- high cholesterol;
- overweight or obesity;
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- Pharby's disease.
Video: How does an ischemic stroke occur?
Symptoms
The disease usually manifests itself suddenly, within a few seconds or minutes. Sometimes the transient (transient) ischemic attack (TIA) develops, gradually turning into a full stroke.
A good way to remember the signs of an ischemic stroke is to use the FAST test (Face Arm Speech Test, which translates as "Face-Hand-Speech-Test").
- The face . If a person has a stroke, then the facial expression is broken, that is, for example, it becomes impossible to smile. Also, the corners of the mouth or eyes can drop down, most often on one side.
- Hand . When a person has a stroke, it is difficult to raise your arm and keep it in the extended position.
- Speech . A stroke patient often has a slurred speech or it is difficult to repeat the names of general purpose objects (chair, table, bed).
If a number of the person who is present has one or more of the above symptoms, or if you have had to note this yourself, you should immediately seek emergency care.
Other symptoms of AI depend on where the blood supply is disturbed in the brain. The explanation is simple - different areas of the brain are supplied with blood vessels, and they all receive blood through different arteries. Therefore, it can be determined:
- numbness on one side of the body;
- headache;
- feeling dizzy or unstable;
- feeling tired and weak;
- pain in the neck or face;
- double vision or other visual impairment;
- convulsive condition;
- feeling of heat or, conversely, chills;
- dry mouth;
- frequent palpitations.
These symptoms are often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Sometimes a brief syncope occurs.
Diagnostics
When a patient enters a medical institution, several tests are performed to find out what type of stroke has developed and how much the brain has suffered. This will help the doctor make an individually selected treatment plan.
Methods of diagnosis:
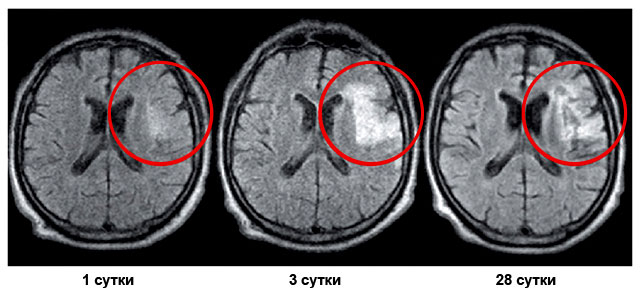
- Computer tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows you to make brain scans, which makes it possible to determine the type of stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) with the most accurate localization.
- An electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to record the rhythm and electrical activity of the heart, which allows you to find out the accompanying diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Blood tests to measure the level of cholesterol, blood sugar and blood coagulability.
Later, other ways of diagnosing the heart and blood vessels can be carried out to find out what caused the development of ischemic stroke. In particular, they may include:
- Ultrasonic scanning of carotid arteries in the neck.
- Angiography to conduct a detailed assessment of blood supply to the brain.
Treatment and rehabilitation
Medication Therapy
With AI, the following drugs can be prescribed:
- Alteplase - a drug helps to destroy blood clots and helps restore blood flow in the brain. The patient, as a rule, should use the remedy not later than four and a half hours after the onset of the attack, and then the symptoms begin to come to naught, but the earlier, the better. Alteplase is not suitable for everyone, therefore it is necessary to consult a doctor.
- Antiplatelet drugs, such as aspirin, can reduce the risk of blood clots after a stroke.
- Anticoagulant drugs such as heparin or warfarin can also prevent the formation of thrombi.
The attending physician may prescribe some other medicines that help control blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar.
Surgical effects
In some cases, surgery is necessary to reduce the risk of a recurrence. In particular, such surgical intervention as carotid endarterectomy can be performed to remove blood clots and fat deposits from one of the carotid arteries in the neck.
Rehabilitation
Stroke can damage the brain. Since this body controls all actions and sensations, it may happen that it will be necessary to retrain skills and abilities or learn to adapt to new ways of doing household affairs. Such activities aimed at restoring the patient after AI are known as rehabilitation after a stroke.
The best recovery occurs in the first weeks and months after a stroke. But even after a longer period of time, improvement of the general condition and restoration of lost skills can continue.
A multidisciplinary team of professionals participates in the development of the rehabilitation program, which designs a rehabilitation scheme according to the needs of the particular patient. The team can include physiotherapists, speech and language therapists, ophthalmologists and psychologists, cardiologists and nurses. Their joint work helps patients to become as fit as possible for everyday life.
Complications
Ischemic stroke can be very severe and cause long-term disruption in the brain. Sometimes frustration of brain activity can lead to death.
Complications of ischemic stroke may be as follows:
- weakness or paralysis, often on one side of the body;
- difficulty swallowing;
- problems with sleep;
- speech disorder, reading and writing;
- problems with the perception of visual images (can be double vision, fuzzy vision, etc.);
- memory disorder and concentration of attention;
- obstructed management of movement of the bladder and intestines (incontinence or constipation);
- sexual dysfunction;
- changes in personality and behavior;
- anxiety and depression;
- pain, often in one or both shoulders;
- seizures in the form of seizures.
If a person can not move because of complications of ischemic stroke, then he becomes helpless and may even be in danger. In particular, the constant lying causes:
- deep vein thrombosis (DVT);
- contractures (when the arms, legs become so tight that they are difficult to straighten).
Near the bed patients must necessarily be a nurse / nurse or someone from the family who can conduct appropriate care.
Prevention
The risk of developing a stroke can be significantly reduced if you practice the following recommendations:
- Stop smoking because even with passive smoking, blood pressure rises and there is a risk of developing atherosclerosis, hypertension.
- You need to eat healthy food and reduce the daily intake of fats and salt. Too much fatty food in the diet can lead to inflammation of the arteries, and excessive amounts of salt help increase blood pressure.
- It is worth doing more permissible exercises to keep yourself healthy.
- It is important to drink less alcohol, as this can increase blood pressure and the likelihood of fat deposits in the arteries. Also, lovers of alcoholic beverages increase the risk of atrial fibrillation.
Frequently asked Questions
Can aspirin prevent ischemic stroke?
Aspirin is a medical drug from the pharmacological group of antiplatelet agents, so it promotes blood thinning, which prevents the formation of blood clots. However, the drug may increase the risk of bleeding, for example in the stomach or intestines.
If a patient has never had a stroke, the benefits of taking aspirin may not outweigh the risks of his continued use. It is more important to make changes in your lifestyle, for example, improve nutrition and do more exercise, give up alcohol and smoking. Aspirin should be taken only when the doctor recommended it.
How long do people stay in the hospital?
Surely it is difficult to say, because much depends on how seriously the stroke has gone and how well the recovery process is going. The average stay in the hospital is 17 days.
Before leaving the hospital, patients often undergo a commission consisting of physicians of various specializations, which includes: a physiotherapist, a social worker, a speech and language therapist, etc. These specialists evaluate the patient's condition from different angles, after which the need for his stay in hospital conditions.
Can ischemic stroke be transmitted by heredity?
The risk of developing a stroke is significantly increased if one of the relatives had an earlier case. But this does not mean that a stroke will necessarily occur. First of all, the probability of developing an attack depends on factors that can not be changed (for example, age, race and family predisposition), as well as the way of life that leads a person.
Are TIA and ischemic stroke the same?
Transient ischemic attacks (TIA) are also known as "mini-strokes". Like strokes, they happen when the blood supply to the brain is broken, but with TIA, ischemia takes a very short time.
With TIA, a clot blocks the blood vessel; but unlike ischemic stroke, it resolves relatively quickly. The disease causes symptoms similar to a stroke, but usually they do not last more than 24 hours. In fact, most TIAs last less than an hour.
In some people, TIA develops before ischemic stroke - usually a couple of days before the stroke, so if any of the symptoms listed above are noted, it is important to seek medical help. TIA should be treated as a warning that the risk of stroke is very high. This harbinger allows you to get the necessary help in a timely manner.
