Ischemic heart disease
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-02-21
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is a general concept that combines acute and chronic pathological processes with a similar pathogenesis. The key to the development of coronary heart disease is to disturb the coronary circulation, which results in a change in metabolic metabolism in the heart muscle. In other words, the myocardium requires more oxygen and nutrients than it enters with the available blood flow.
The course of IBS is divided into acute, in the form of myocardial infarction, and chronic, when the patient is bothered by periodic attacks of angina pectoris.
A special role in determining the variety and nature of the course of IHD is given to modern diagnostic methods. Consideration is given to patient complaints, objective research, laboratory findings and the results of instrumental methods. All this makes it possible to put the exact diagnosis and in the future to appoint an effective treatment. Otherwise, an unfavorable forecast is given.
Video: Ischemic heart disease - causes, diagnosis, treatment
Classification of coronary heart disease
The disease is considered in various categories, classifiers and open databases. But the most commonly used International Classification of Diseases of the 9th and 10th revisions. By ICD-10 IBS stands under I20-I25 font, and in ICD-9 - under 410-414.
According to Wikipedia, the term "ischemic heart disease" is similar to Latin. morbus ischaemicus cordis from dr.-grech.ἴσχω - "delay, hold back" and αἷμα - "blood".
The following clinical forms are distinguished in the IBS group:
- Stenocardia, which in turn is divided into unstable and stable, or angina tension.
- Myocardial infarction (primary).
- Myocardial infarction (repeated).
- Previously transferred myocardial infarction, which is expressed in postinfarction cardiosclerosis.
- Sudden coronary death, which can end with successful resuscitation and fatal outcome.
- Heart failure.
When the diagnosis is made, the clinical form of the disease must be indicated, for example: "IBS: stable angina II FC".Some clinical forms are considered in separate classifications, according to which the required designation is necessarily indicated in the final diagnosis.
Classification of unstable angina by Braunwald
| A - there is an external reason that intensifies ischemia. Secondary unstable angina | B - external causes of angina are absent. Primary unstable angina | C - occurs within 2 weeks after myocardial infarction. Postinfarction angina | |
| I - first-emerging, progressive angina, without rest angina | IA | IB | IC |
| II is a stenocardia of rest within a month, but not within the next 48 hours | IIA | IIB | IIC |
| III - Stenocardia of rest in the nearest | IIIA | IIIB | IIIC |
A - there is an external reason that intensifies ischemia. Secondary unstable angina B - external causes of angina are absent. Primary unstable angina C - occurs within 2 weeks after myocardial infarction. Postinfarction angina
I - first-emerging, progressive angina, without rest angina IA IB IC
II is a stenocardia of rest within a month, but not within the next 48 hours of IIA IIB IIC
III - rest angina within the next 48 hours IIIA IIIB IIIC
In addition to the classification given in the group of unstable angina pectoris, an early postinfarction SC is secreted, progressing and first emerged, as well as Printsmetal, or variant.
Classification of myocardial infarction is very voluminous and is considered in the stages of development, scale and anatomy of the lesions, the location of necrotic focal point, the course of the disease. In addition, more modern classifications, developed on the basis of general considerations of European, American and worldwide cardiology communities, operate.
Causes of coronary heart disease
The development of the disease is directly related to the lack of oxygen that enters the heart muscle. Because of oxygen starvation, the myocardium begins to lose its ability to perform its functions, and the more the site of the defeat, the stronger the clinic of the disease will be expressed. In some cases, blood circulation in coronary vessels stops so sharp that there is an acute oxygen deficiency with all the consequent consequences
Why does blood flow in coronary vessels stop? This may involve one or more pathological mechanisms:
- Atherosclerosis and thrombosis.
- Atherosclerosis of coronary vessels.
- Spasm of blood vessels.
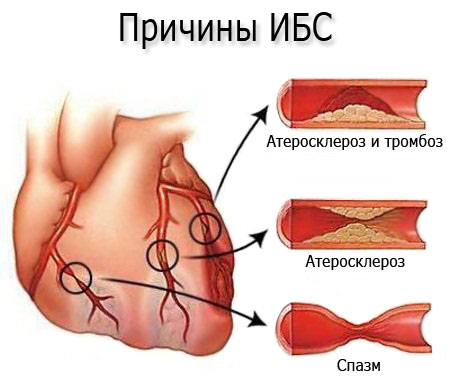
Also, there are so-called extravascular etiologic factors contributing to the development of IHD. In some cases, risk factors that contribute to the clinical picture of the slow-moving process play an important role.
Developmental factors
A key etiological factor in the development of coronary artery disease is atherosclerosis. With this pathology, the narrowing of the lumen of the coronary arteries is observed, because of which the needs of the myocardium in the blood supply do not coincide with the real possibilities of the bloodstream.
In atherosclerosis, specific plaques are formed, which in some cases overlap the lumen of the vessel by 80%. Then myocardial infarction develops, or, as a more "easy" option, angina.
Formation of an atherosclerotic plaque does not occur simultaneously. It may take months or even years to go. At the beginning, on the walls of the coronary vessels, low density lipoproteins are deposited, which begin to gradually affect the epithelium, located next to it.

Platelets and other shaped elements of blood accumulate at the site of the defeat, due to which the lumen of the vessel overlaps with the increasingly prominent part of the plaque. If the pathological education takes up to 50% of the lumen of the vessel, then the clinic of the disease is not sluggish or not expressed at all. Otherwise, the CHD develops in one or another clinical form.
Each coronary artery supplies blood to a specific area of the myocardium. The farther from its distal end is the region of the vessel affected by atherosclerosis, the more extensive it may be ischemia or necrosis. If the pathological process involves the mouth of the left coronary artery or the main trunk, then the most severe ischemia develops. Heart muscle.
In addition to the developmental factors lying inside the vessel, there are extravascular causes. First and foremost, it's arterial hypertension, which most often causes spasm of the coronary vessels. The formation of a coronary heart disease is facilitated by frequent and pronounced tachycardia, as well as hypertrophy of the myocardium. In the latter two cases, the need for cardiac muscle in oxygen sharply increases and with their dissatisfaction ischemia develops.
Risk factors
Modern scholars and leading clinicians have an important role in the development of coronary heart disease in predisposing circumstances. On their background, with a high probability, a pathological condition can develop with all the ensuing consequences. The risk factors for CHD in many respects are similar to those in atherosclerosis, which is due to the direct involvement of the atherosclerotic plaque in the partial or complete overlap of the lumen of the vessel.
Ischemic heart disease is associated with many risk factors (FD), so a sort of classification was required to streamline them for better perception.
- Biological Fr:
- Men are more likely to be ill than women.
- Older people are more likely to have atherosclerosis, and therefore higher probability of developing myocardial ischemia.
- Hereditary predispositions, which contribute to the development of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and, consequently, coronary heart disease.
2. Anatomical-physiological and metabolic FV:
- Diabetes mellitus, basically insulin-dependent type.
- Increased body weight and obesity.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Elevated levels of lipids in the blood (hyperlipidemia) or a violation of the percentage of different types of lipids (dyslipidemia).
3. Behavioral Fr:
- Improper nutrition.
- The presence of bad habits, especially smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Hypodynamia or excessive physical activity.
Muscular elastic hyperplasia of intima arteries, including coronary arteries, is another possible risk factor for the onset of CHD, but today it is in the process of study. Changes in blood vessels of the type of hyperplasia are already determined among children, so there are assumptions about promoting such a FV to the development of coronary arteritis at an older age. In addition, the role of the CDH13 gene and its mutation in the formation of ischemia is studied, but so far this assumption has not been fully proven.
Types of coronary heart disease
In patients with IBS, the most commonly defined clinical forms such as myocardial infarction and angina pectoris. Other species are not so frequent, and they are more complex in diagnostics. On the basis of this, the clinic and the course of the myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, sudden coronary death and postinfarction cardiosclerosis will be considered.
Myocardial infarction
A similar diagnosis can be established when there is confirmed a clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods of myocardial necrosis. It may be small or large, but regardless of it the patient should be sent as soon as possible to the department of intensive care and intensive care.
- Large-focal myocardial infarction is characterized by pathognomonic changes, which are determined on the ECG and in the course of laboratory diagnosis. Of particular importance is the increase in lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase and a number of other proteins in serum.
Such enzymes indicate the activity of the oxidation-reduction reaction that passes through the body. If normally these components are found only in the cells, then when they break down, the proteins pass into the blood, therefore, by their number, it is possible indirectly to judge the scale of necrosis.
- The small-basal myocardial infarction is often transplanted by legs, as the clinic may not be expressed, and changes in the ECG and in the analyzes are also not as critical as in the case of a large-centered MI.
Angina pectoris
The disease has a characteristic clinical sign - a back pain that may arise from any stress (physical or emotional). Pain can be felt like burning, heavy or severe discomfort, and often spreads through nerve fibers to other areas of the body (shoulder blade, lower jaw, left arm.
The duration of a stenocardia attack is usually 1-10 minutes, much less often - up to half an hour.
Another characteristic of the stenocardia trait is pain relief with nitroglycerin, which does not help with myocardial infarction. Also, painful sensations can go away on their own if an emotional or physical stimulus is eliminated.
Characteristics of individual forms of angina pectoris:
- The first occurrence of angina pectoris is quite variable in its course, so it is not immediately possible to accurately diagnose. As a rule, this usually takes up to three months. During this period, an observation of the patient's condition, the development of a disease that can progress into a stable or stable form is conducted.
- Stable angina - characterized by the appearance of pain sensations with a certain regularity. The severity of stable angina is determined by the functional classes, which corresponds to the FC necessarily indicated in the final diagnosis.
- Progressive angina - the intensity of pain attacks is growing quite rapidly, with the patient reducing resistance to physical and emotional stress. Such a form of angina is poorly controlled by nitroglycerin and in severe cases, administration of narcotic analgesics may be required.
Stenocardia occurs spontaneously, while not associated with any physical or emotional stimuli. Such a form of stenocardia is often determined at rest, at night or in the morning. A similar pathology is defined as spontaneous angina.
Sudden coronary death
The second clinical sign is the primary cardiac arrest. Her education is associated with electrical instability of the myocardium. Such a diagnosis is only displayed if there is no confirmation of the definition of another specific IHD. For example, the heart may stop due to myocardial infarction, and then indicate in the diagnosis of death from myocardial infarction.
The high risk of sudden coronary death is observed in those patients who have signs of contraction of a large number of coronary vessels on the coronary angiography. An unfavorable condition is the expansion of the left ventricle.Significantly increases the likelihood of sudden coronary death after a heart attack. Also, any myocardial ischemia, including without a pronounced painful sensation, can be considered as a danger due to abrupt cessation of cardiac activity.
Postinfarction cardiosclerosis
In clinical practice, this disease is considered to be a complication of a previous transmitted myocardial infarction. To produce such a diagnosis should be given at least 2 months. In some cases postinfarction cardiosclerosis is considered as an independent disease, but this should not be confirmed by the presence of angina, heart failure, etc. In addition, signs of focal or diffuse cardiosclerosis should be present in the ECG.
In relatively light cases, patients experience an interruption in the rhythm of the heart. The severe course of the illness is accompanied by shortness of breath, edema, heart pain, inability to withstand the burden, etc. The complexity of the pathology is that there is a more or less noticeable progression of the process, which can only hold on to time with competently selected therapy.
Video: Types and forms of ischemic heart disease
Diagnostics
Patients with coronary heart disease are involved with a cardiologist who, in the course of the initial treatment, is paying attention to clinical symptoms. In the IBS, the following typical complaints are distinguished:
- Pain for the sternum, which in most cases is associated with emotional and physical stress.
- Wrong work of the heart, which is accompanied by weakness and arrhythmia.
- Cataracts on the legs, indicating heart failure.
- Feeling of shortness of breath
Of considerable importance during the examination is the history of the disease. This is when the doctor asks for clarifying questions about the nature of the pain, its duration, etc. It also matters the amount of physical activity that the patient can withstand relatively calmly. For proper diagnosis, information on the effectiveness of various pharmacological agents, including nitroglycerin, should be obtained. Additionally, the risk factors are specified.
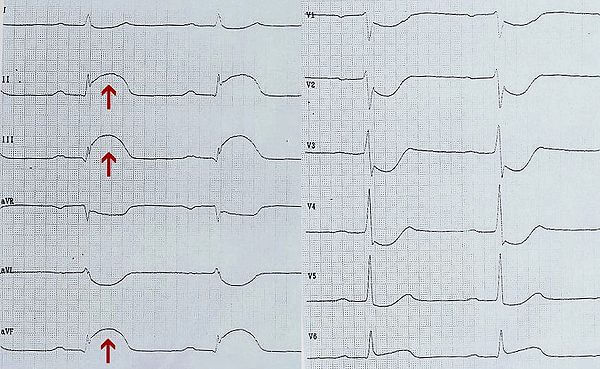
All patients with suspicion of coronary heart disease undergo electrocardiography . This indirect method of diagnosis can not accurately indicate how many cardiomyocytes died, but it uses myocardial functions such as automatism and conductive ability.
The following symptoms of myocardial infarction are noticeable on the ECG:
- The appearance of pathological Q, which in some leads is combined with a negative T wave.
- In acute myocardial infarction, the ST segment highlights and manifests itself in the form of a "sailfish" or "cat back" ..
- With myocardial ischemia, depression of the segment ST is noted.
- In the presence of scar in the myocardium for ECG, for two days and more, a negative tine T of weak severity and a pathological tooth Q is determined.
ECG is necessarily supplemented by conducting ultrasound of the heart. With this modern method of research, it is possible to evaluate in real time the state of the heart muscle, how much the cardiac contractility has suffered from heart attack, and whether there are abnormalities in the functioning of the valve apparatus. If necessary, echocardiography is combined with doplerography, which makes it possible to evaluate the potential of blood flow.
Laboratory studies are relevant for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction, as various biochemical parameters change during the development of the pathological process. First of all, protein fractions are determined, which are normally found only inside the cell, and after the destruction of cardiomyocytes enter the bloodstream. For example, in the first 8 hours after myocardial infarction, the level of creatine kinase increases, and in the first day - myoglobin. Trotonins are determined up to 10 days, also the amount of lactate dehydrogenase and aminotransferase is also significant.
With a violation of the structure of the myocardium, a nonspecific reaction is observed in the form of an increase in the concentration of AST and ALT, the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation (ESR) and the appearance of neutrophilic leukocytosis.
In patients with IHD, a lipid profile must be examined. For this purpose, indicators such as total cholesterol, triglycerides, high and low density lipoproteins, apolipoproteins and an index of atherogeny are determined.
Functional tests , combined with ECG recording, allow you to evaluate the potential of the cardiac muscle under physical stress. For early diagnosis of the disease, this is extremely important, since not all patients are at rest in clinical settings. A person can get loads in different ways. The most widespread - exercise bike. Also, a treadmill, walking on stairs and so on are often used.
Additional instrumental studies:
- CT-angiography (or angiography of coronary vessels) - is conducted for the purpose of obtaining X-rays with contrasting special substances vessels. The received images show blockage of arteries, their occlusion, and also the degree of passability.
- Holter monitoring is to register an ECG for a day or two, for which the patient wears a special device with him all the time. The study allows to determine not clearly expressed and hidden changes in cardiac activity, when the standard ECG can not record changes due to the rare occurrence of the attack.
- Intraperitoneal ECG - is performed in cases where changes to the standard ECG are not recorded, but there are clinical signs of the presence of additional focal points of excitation. An active electrode is introduced into the esophagus to study the electrical activity of the atrium and atrioventricular node.
CHD treatment
The treatment tactic is based on the classification of coronary heart disease, since each specific form of treatment has its own specific therapies. Despite this, there are common guidelines for the management of patients with coronary heart disease, which are as follows:
- Moderate physical stress is important in stabilizing patients with coronary heart disease, the higher the fictitious weight, the greater the need for oxygen, and because of the disturbed blood supply to the heart muscle, this only exacerbates the course of the disease by provoking new attacks. If the patient goes to the correction, then gradually the physical load increases.
- Dietary nutrition should be as good as possible for myocardium, so the amount of salt and volume of water decreases. In the determination of atherosclerosis from the diet, products such as smoked foods, pickles, animal fats are excluded. High-calorie and fatty foods are also not recommended. If the patient has obesity, then they are particularly careful about the calorie counting question, because the energy consumption should correspond to the energy coming from the food.
Medicinal therapy
Cardiologists in the United States were offered a treatment scheme abbreviated as "ABC". It is based on the use of drugs from the three pharmacological groups: antiplatelet, beta-blockers, statins (considered as hypocholesterolemic drugs). If a concomitant illness is defined as hypertension, then medicines are added to treat this pathology.
- Antiagregants - prevent the adhesion of erythrocytes and platelets, as well as their further adhesion to the inner wall of the vessel. As a result, blood rheology improves, the risk of developing blood clots decreases. Of the drugs of this group most often used ascaster, aspirin, also appointed clopidogrel.
- Beta-blockers - acting on the mechanism of stimulation of adrenoreceptors in myocardial cells, which leads to a decrease in the contractility of the heart. This, in turn, has a beneficial effect on the state and functioning of the organ.Drugs from this group are contraindicated in certain pulmonary diseases. Today, metoprolol, carvedilol, bisoprolol are most commonly used.
- Statins and fibrates - refer to anticholesterolemic drugs, since they contribute to slowing the growth of already existing atherosclerotic plaques and preventing the formation of new ones. To some extent, the severity of the course of an IHD attack can be alleviated. Most commonly, lovastatin, simvastatin, rosuvastatin, atorvastatin are prescribed from this group. Fibrates, among which fenofibrate is most well-known, can increase the level of high-density lipoprotein having anti-atherogenic significance.
Depending on the indications and the accompanying pathology, the patient can be prescribed nitrates (expand the venous channel and thus remove the load from the heart), anticoagulants (do not allow the formation of thrombi), diuretics (loop or thiazide). Antiarrhythmics in the form of amiodarone may also be prescribed for treating and preventing rhythm disorders.
Video: What drugs are used to treat coronary heart disease (CHD)?
Natural hypolipidemic remedies
In combination therapy, hypolipidemics such as aspirin and polycosanol may be used. The latter name is a general term for long-chain alcohols, which are made from plant waxes. Today, it is often determined in various nutritional supplements.
In the course of the application, polycosanol does not adversely affect coagulation, thus contributing to increased concentration of high density lipoproteins and a decrease in the fraction of "harmful" lipoproteins of low density. In addition, the substance has an antiplatelet effect.
Endovascular coronary angioplasty
An alternative to open surgical intervention. It is used in various forms of CHD, even in the case of progression of pathology and in order to prevent complications. This method combines coronary angioplasty and endovascular technology, often represented by transuminal and transdermal instruments.
For the expansion of spasmodic vessels, due to which ischemia of the myocardium, stenting is most often used, and, more rarely, balloon angioplasty. All manipulations are performed under the control of coronary angiography and X-ray examination. A large vessel is chosen to introduce the required instrumentation, mainly the femoral artery is given preference.
Video: Stenting of the coronary arteries
Surgical treatment
Under certain circumstances, coronary heart disease is not suitable for medical treatment. Then the variant of operative intervention, in particular, an aortocoronary bypass, is considered. The purpose of this technique is to combine coronary vessels with the aorta via an autograft (represented, basically, by a large subcutaneous vein).
Basic indications for surgical intervention in coronary heart disease:
- multiple lesions of the coronary vessels;
- Definition of stem stenosis in the area of the left coronary vessel;
- determination of mouth stenosis in the area of the right or left coronary vessel;
- Stenosis of the anterior coronary vessel, which is not susceptible to angioplasty.
Operative treatment can not be performed when the patient has multiple lesions of the peripheral coronary vessels that are diffuse. Also, the contractile capacity of the myocardium, the presence of heart failure in the stage of decompensation and postinfarction state, which is not more than 4 months, is considered as a contraindication.
Non-medicated treatment
Conservative therapy, if necessary, can be complemented by non-pharmacological effects, which also help to improve myocardial conditions.
The main methods of treatment of non-medical directions:
- Hirudotherapy - known as leech treatment. In the saliva of these creatures there are components with an anti-aggregate effect, which results in prevention of thrombotic events. It is difficult to judge the effectiveness of the method because it does not have the approval of the field of evidence-based medicine.
- Impulse-wave therapy of the heart - low-power shock waves are used to implement the technique. Under their action, new vessels begin to form in the myocardium, which significantly improves blood supply to the tissues. This is just as necessary to reduce the area of ischemia. The non-invasive method is most often used in the absence of the effectiveness of conservative and surgical treatment. According to some researchers, improvement of myocardial perfusion is observed in almost 60% of patients.
- Reinforced external counterpulsation - by the method of conduction is similar to internal counterpulsation. Refers to non-operating methods and is based on the work of special air cuffs that are put on the legs. Due to the sharp pumping of air from the cuff during the systole, pressure in the vascular bed decreases, which means that the heart load is removed. At the same time, during the diastole, the bloodstream, on the contrary, is intensely filled with blood, which makes it possible to improve the condition of the myocardium. After a long study in the US, the method has received approval and is now widely used in clinics.
Forecast
The conclusion on the development of the disease largely depends on the severity of the clinic and the severity of structural changes in the myocardium. In most cases, a relatively unfavorable prognosis is given, since it is impossible to reverse the disease regardless of the treatment being performed. The only therapy helps to improve the well-being of the patient, to make attacks less likely, in some cases it is possible to noticeably improve the quality of life. Without treatment, the disease progresses very rapidly and leads to a lethal outcome.
