Myocardial hypoxia: symptoms, causes and treatment
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-05-18
Acute myocardial hypoxia
This condition occurs when the oxygen supply to the heart muscle suddenly decreases. The cells do not have time to adapt to the changed conditions. They continue to metabolize, but it becomes incomplete, accumulate under-oxidized metabolites. With the preservation of hypoxia, the tissues of the heart muscle die.
Clinically, this condition is manifested by attacks of chest pain, an increase in their duration and intensity. In the future, myocardial infarction develops - necrosis of the heart muscle with loss of its contractile function.
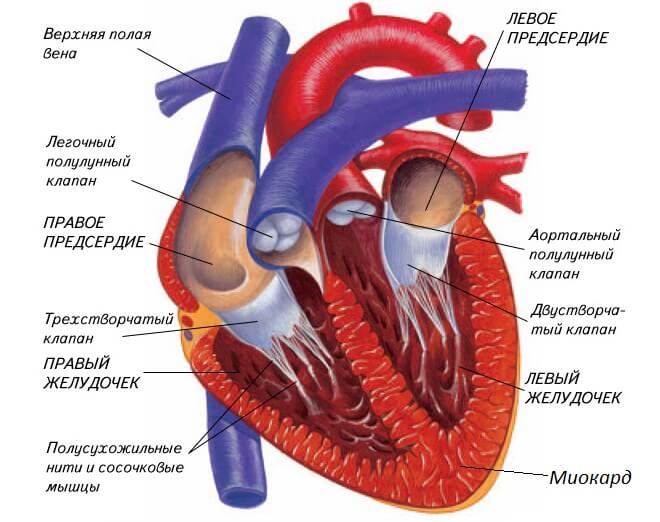
Possible reasons
Hypoxia of the myocardium can be caused by the following reasons:
- low oxygen content in atmospheric air;
- Diseases of the lungs with a violation in them of gas exchange;
- decrease in the amount of blood flowing through the myocardium due to pathology of the coronary arteries;
- deterioration of the ability of the blood to carry oxygen, for example, in case of carbon monoxide poisoning;
- violation of the utilization of oxygen by the cells themselves, for example, when poisoning with cyanides, heavy metals.
Under the influence of these processes, the amount of oxygen in all tissues of the body decreases. He responds with an adaptive response, as a result of which blood flow is redistributed to supply the vital organs - the brain and the heart.Therefore, acute myocardial hypoxia can occur only with significant, life-threatening effects.
An exception is acute hypoxia caused by local disturbance of blood supply in the pathology of the arteries of the heart.The main reason for this - atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels, complicated by the formation of a thrombus in the place of narrowing of the artery by a plaque. Clinically, this condition is accompanied by the development of unstable angina or myocardial infarction.
Video: Hypoxia - oxygen starvation
In addition, the cause of acute myocardial hypoxia can be a sudden spasm of the arteries of the heart due to the excess of vasoconstrictor substances (for example, adrenaline release during emotional or physical exertion) or in violation of the internal surface of the vessels (endothelial dysfunction), which leads to the development of variant (vasospastic) angina .
Effects of hypoxic processes in the heart muscle
For the normal operation of the heart, which provides blood circulation throughout the body, it is necessary to constantly supply oxygen to the myocardium. In acute hypoxia, it is disrupted, and with the imbalance between the needs of the heart and its supply, a cascade of cellular, biochemical and inflammatory reactions occurs, eventually causing the death of the cells of the heart muscle.
Necrosis of the myocardium and ventricular remodeling
The degree of damage to cells depends not only on the severity of the disturbance of the blood supply, but also on its duration, as well as the needs of the myocardium at this time. A significant loss of the ability of myocardial cells to contract can occur only a minute after the cessation of blood flow. The persistent hypoxia leads to irreversible damage to the heart muscle after 20-40 minutes, less often this period increases to several hours. The time of development of necrosis depends on a number of conditions, including the initial level of activity of the organism and the presence of collateral (by-pass, additional) coronary blood flow.
The cells that degrade as a result of acute hypoxia are destroyed, and in their place a connective (scar) tissue is formed.In this anatomical structure of the chambers of the heart can significantly change. The left ventricle, which performs the basic pump function, expands and acquires a spherical shape, its contractility decreases. This process is called ventricular remodeling, and it can be slowed down by proper treatment.
Reperfusion injury
Restoration of blood flow after an episode of acute myocardial hypoxia can cause further ischemic cell damage, which is called reperfusion. This process involves the interaction between free oxygen radicals remaining in the tissues after an episode of hypoxia, and calcium ions emerging from damaged myocardiocytes. As a result, microvessels that feed the myocardium are injured, cell damage increases, life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances occur. Measures to prevent reperfusion injury are unknown.
"Stunned" and "sleeping" myocardium
After acute myocardial hypoxia, its temporary disruption of function occurs. It develops if coronary blood flow has been disturbed for a short time (5 to 15 minutes), and persists for several hours or days after the elimination of oxygen deficiency. This condition is called a stunned myocardium.
A prolonged acute hypoxia causes a partial or complete violation of heart contractility - a "sleeping" myocardium. Such a process can be eliminated after a complete restoration of blood flow in the coronary arteries.
These disorders are caused by the breakdown during the course of oxygen starvation of important energy metabolites, for example, adenosine. It is necessary to ensure contractility of the muscle fibers of the heart.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of myocardial hypoxia depend on its severity and duration. This determines the degree of damage to cells, the possibility of their destruction and the reversibility of violations. Acute hypoxia can manifest itself by such changes:
- ischemia - a temporary, reversible condition, which is clinically expressed by the attack of angina pectoris;
- necrosis - an irreversible process, which is the basis of myocardial infarction.
The main symptom of angina pectoris is the pain behind the sternum.
| Symptoms | Characteristics of pain |
| Cause | Physical activity, usually walking or climbing stairs; food intake; smoking; exit to frost;intercourse |
| Duration | End of attack after 1 - 2 minutes after the termination of the load, the average duration of 2 - 5 minutes |
| Location: | The upper and middle part of the sternum, less often to the left of it, and also in the region of the stomach, left shoulder blade, left shoulder |
| Irradiation ("return") | Left arm, left shoulder, lower jaw, teeth, scapula |
| Character | Compressing, pressing, feeling of heaviness, less often "drilling" |
| Intensity of increase | Occurs gradually, can have different severity - from moderate to very strong; The time of cessation of pain is always much less than its development |
| The effect of nitroglycerin | Nitroglycerin helps for 1 to 3 minutes |
Other symptoms accompanying reversible acute myocardial hypoxia:
- fear of death;
- pallor of the skin, cold extremities;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- it is possible to increase blood pressure.
With more prolonged and / or severe acute hypoxia, which is manifested by unstable angina, the clinical manifestations intensify:
- Attacks of pain become more frequent, longer and more pronounced, appear with less stress or even at rest;
- there are sudden nocturnal episodes of arrhythmia, suffocation, severe weakness;
- the required amount of nitroglycerin tablets increases, its effectiveness decreases.
With sudden pronounced hypoxia, myocardial infarction develops. Its main symptoms are:
- very strong, wave-like pain behind the sternum, dilating, burning character;
- duration of an attack more than half an hour;
- absence of the effect of nitroglycerin;
- feeling of fear;
- instability of blood pressure, disturbances of the heart rhythm, dyspnea, choking;
- severe pallor of the skin, cold sweat.
This condition requires immediate medical attention.
Hypoxia in pregnant and newborns
In pregnant women, myocardial hypoxia occurs with a decrease in the level of oxygen in their blood. The main reasons for this condition are:
- embolism by amniotic fluid when they get into the mother's vessels;
- bronchial asthma;
- anemia;
- hyperventilation syndrome (dyspnea) with concomitant obesity;
- pericardial cardiomyopathy, which occurs at the end of pregnancy and leads to heart failure;
- pneumonia;
- pneumothorax;
- pulmonary embolism.
These conditions cause not only signs of oxygen deficiency in the mother, but also affect the fetus. Another cause of fetal hypoxia is fetoplacental insufficiency. With insufficient intake of oxygen in the blood of the child, his body compensates for the hypoxia of the tissues by the increase in cardiac contractions. This is the first sign of acute oxygen starvation of a child.
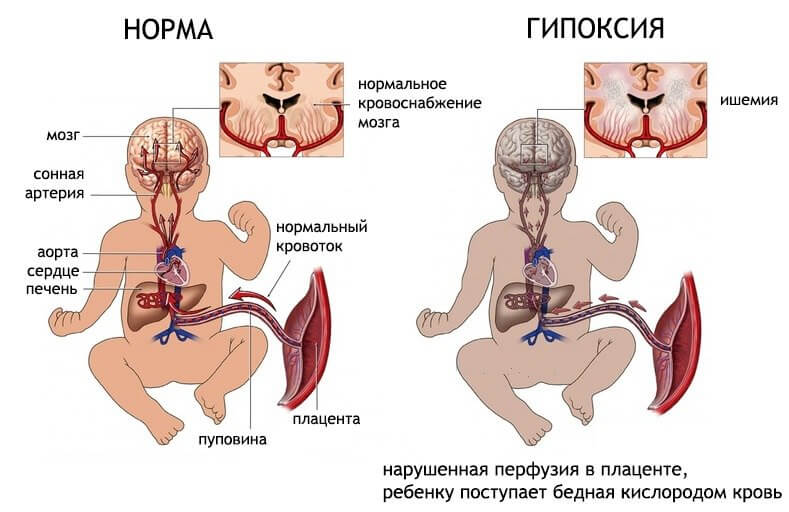
Hypoxia of newborns develops with malformations of the lungs, the pathology of labor (placental abruption, entanglement or prolapse of the umbilical cord during labor). At the same time, the brain and heart of the child suffer.For the prevention of this condition are used:
- purification of the respiratory tract of the newborn, stimulation of the first inspiration;
- correct management of birth, prevention of umbilical cord prolapse;
- control fetal heartbeat during labor, if necessary - emergency cesarean section;
- correction of respiratory disorders in the newborn (oxygen supply through the catheter, administration of surfactant preparations and other methods of treatment).
With continued myocardial hypoxia, the heart of a newborn quickly loses its ability to adapt by increasing heart rate.Develops acute heart failure - a life-threatening condition.
Video: Hypoxia of the fetus
How hypoxia manifests itself on the ECG
Electrocardiographic manifestations of acute myocardial hypoxia depend on the changes that it caused. With reversible disturbances, temporary signs of ischemia appear. The development of myocardial infarction is accompanied by successive changes in the ECG, which allow to determine the prescription, localization and depth of necrosis of the heart muscle.

Manifestations of short-term acute hypoxia:
- the horizontal displacement of the ST segment below the isoelectric line ("depression") by 1 mm or more;
- the appearance of a deep negative ("coronary") T wave in one or more leads, usually pectorals;
- transient disturbances of the heart rhythm (extrasystole, paroxysmal tachycardia) and blockade.
After the restoration of the blood flow, these changes disappear, the ECG returns to the initial parameters.
Stages of myocardial infarction on the ECG:
| Name | Duration | Symptoms |
| Ischemic | Up to 30 minutes | The appearance of a high pointed spike T |
| Damage | Up to 3 days | Short-term shift of the ST segment below the isoline, followed by its ascent and merging with the T wave;a characteristic monophasic curve is recorded on the ECG |
| Sharp | Up to 3 weeks | Formation of deep dilated Q wave;possibly the disappearance of the Rwave, the formation of a negative T wave while maintaining the STsegment elevation above the isoline |
| Subacute | About a month after the onset of an infarction | Return of the ST segment to an isoline, a decrease in the depth of the negative tooth T |
| Scarring | Usually throughout the whole subsequent life | Deep widened Q tooth with disappearance of manifestations of ischemia ( ST and T changes) |
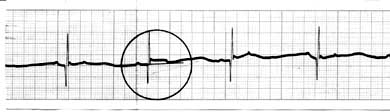
The heart is supplied with several large arteries, so myocardial hypoxia usually affects only part of it. Depending on the localization of the above changes, the cardiologist can determine the localization of the pathological process:
| Affected artery | Type of infarction | Modified leads |
| Right coronary | Lower | II, III, aVF |
| Anterior interventricular | Anteroposterior | V1, V2 |
| The distal (terminal) branch of the anterior interventricular artery | Anterior-apical | V3, V4 |
| Envelope | Anteroposterior | I, aVL, V5, V6 |
| Left coronary | Front | I, II, aVL, V1 - V6 |
How to treat acute myocardial hypoxia?
Talking about the treatment of hypoxia is not entirely correct, because it is not a disease. In clinical manifestations of myocardial hypoxia, therapy is prescribed for the disease that caused it, primarily angina pectoris or myocardial infarction.
The main method of treatment of acute short-term hypoxia of the myocardium is the intake of nitroglycerin. This drug expands coronary vessels, restoring normal blood flow to the affected area of the myocardium. With stable angina this allows you to quickly eliminate oxygen deficiency.
If acute myocardial hypoxia led to the development of a heart attack, surgical (percutaneous angioplasty) and medication (thrombolysis) methods of treatment are used. Their goal is to restore the blood supply to the affected area and prevent the spread of necrosis to the surrounding tissues of the heart.
The incidence and mortality from myocardial infarction is significantly reduced if patients or witnesses of an attack quickly recognize the disease and call an "An ambulance". It is very important to properly organize cardiac care in the regions, which allows performing cardiosurgical interventions in the first hours after the development of the disease. If these conditions are met in 2017, the death rates from heart attack after hospitalization in many areas of Russia are equal to the European data.
Traditional methods of treatment
Eliminate short-term hypoxia of the myocardium will help stop physical activity and warming the body. With severe damage to cells, it is impossible to restore their vital functions without medical assistance.
In chronic hypoxia, in order to normalize metabolic processes in the heart, in addition to drugs, you can use:
- a mixture of grated garlic and honey;
- infusion of motherwort, chamomile and hawthorn;
- infusion of lemon balm, valerian, caraway, mistletoe;
- oat broth.
Chronic hypoxia of the myocardium
This is a condition in which the heart muscle constantly receives an insufficient amount of oxygen. The body adapts to these conditions, a network of additional cardiac vessels - collaterals is formed, the metabolic rate in the cells varies.However, with prolonged hypoxia, the compensatory possibilities are gradually depleted, heart failure develops.
What can cause hypoxic changes in the heart?
The causes of chronic hypoxia are the same as acute. The main one is ischemic heart disease, which develops as a result of atherosclerotic lesion of the walls of the coronary arteries. Other causes of chronic cardiac hypoxia may include:
- lung diseases (COPD, emphysema and others), accompanied by respiratory failure;
- cardiovascular disorders, especially in diabetes mellitus;
- pathology of the thyroid gland (hypo- and hyperthyroidism);
- anemia;
- systemic connective tissue diseases and vasculitis damaging the vascular wall.
With all these conditions, it is recommended to observe not only a specialist (endocrinologist, hematologist, rheumatologist), but also a cardiologist.
Diagnosis of myocardial hypoxia
In addition to clinical manifestations, myocardial hypoxia is accompanied by changes in the work of the heart, which are recorded with the help of additional research methods:
- ECG;
- exercise ECG-test (veloergometry, treadmill test), revealing ischemic changes in physical activity;
- daily monitoring of the ECG, which helps in the diagnosis of vasospastic angina and the detection of rhythm disturbances;
- Coronary angiography revealing signs of arteriosclerosis;
- Echocardiography, showing violations of local contractility, areas of "sleeping" and "stunned" myocardium, signs of heart failure;
- computer angiography of the coronary arteries.
To determine the cause of hypoxia, general and biochemical blood tests, determination of the lipid spectrum, markers of myocardial damage (troponins), hormonal status are used.
Prevention of myocardial hypoxia
To reduce the risk of myocardial hypoxia, it is necessary to eliminate its causes:
- in time to treat diseases of the lungs, blood, endocrine organs;
- avoid intensive physical exertion without prior preparation;
- reduce stress;
- more to be in the open air;
- to struggle with excess weight, smoking;
- observe an antiatherosclerotic diet with reduced carbohydrates or animal fats.
Conclusion
Hypoxia of the myocardium accompanies many diseases, but its main cause is ischemic heart disease. Acute hypoxia is often accompanied by angina attacks or the development of myocardial infarction, chronic heart failure is typical. The cardiologist conducts diagnostics and correction of consequences of this pathological process. Diet, medication, cardiosurgical interventions are used.
