Functional tachycardia
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-14
Functional tachycardia refers to disregulatory rhythm disturbances, which in most cases are not able to lead to significant hemodynamic disorders. The term is often used in clinical practice when a person has signs of tachycardia, but there is no organic heart disease.
The main difference between a functional tachycardia and an organic, capable of causing a hemodynamic disorder, is a short course of attacks and the restoration of a normal rhythm in a relaxed environment.
The diagnostic of functional tachycardia uses the same methods as in the case of pathological rhythm disturbances.Also, before the diagnosis is made, it is important to study the general condition of the person, the presence or absence of a concomitant pathology of the heart. Since the emergence of functional tachycardia is possible at any age, athletes, pregnant women, it is important not to miss the pathology, which, unlike functional tachycardia, can endanger the health of the patient.
Video Tachycardia during pregnancy
Functional tachycardia description
From the point of view of physiology, all arrhythmias can be divided into two large groups:
- Organic - develop on the background of cardiovascular diseases. Often associated with dysfunction of the valve apparatus, disturbances of the coronary circulation, myocarditis and changes in the functioning of the conducting pathways of the heart. Also, this group includes those arrhythmias that are associated with intoxication of the body or the wrong medication.
- Functional - their occurrence is independent of heart disease. Often the appearance of such arrhythmias is associated with a disorder of regulation of the autonomic nervous system. Therefore, such a violation is often called disregulatory.
In most cases, functional tachycardias are due to neurogenic pathology or diseases of the central nervous system.
Some forms of rhythm disturbance are not functional, but they are not pathological:
- Sinus arrhythmia is a compensatory disturbance of the rhythm, which maintains a normal minute volume of blood circulation with insufficient hemodynamics.
- Slow substitute rhythms - arise to prevent a heart stop while reducing the sinus node's automatism.
Physicians most often use the notion of functional tachycardia in cases where there is no evidence of organic heart disease, but the heartbeat arises and may even give the patient an inconvenience.
Symptoms of functional tachycardia
It manifests itself as sinus arrhythmia, when there is a slight increase in the frequency of cardiac contractions relative to the age norm. Attacks of tachycardia may occur suddenly, then talk about paroxysmal form of rhythm disturbance, or the heartbeat gradually increases and the same images stop. In such cases, a diagnosis of functional sinus tachycardia is established.
Depending on the nature of the functional tachycardia, the following vegetative disorders may occur:
- weakness;
- noise in the ears;
- feeling of heat;
- dizziness;
- feeling of chilliness;
- cold brushes and feet.
The degree of severity of violations of the autonomic system often depends not on the functional tachycardia, but on the activity of the sympathetic department of the nervous system. Therefore, attention is often focused not on how dangerous the functional tachycardia is, but on the underlying disease that provokes the development of rhythm disturbance.
If during the examination symptoms such as shortness of breath, gallstone rhythm, and enlargement of the heart are determined, the patient is concerned not with functional but with an organic tachycardia.
Causes of functional tachycardia
Most of the cases associated with functional tachycardia are considered from the point of view of the state of the central and peripheral nervous system. Various diseases of this part of the body can cause not only functional tachycardia, but also more severe violations of the heart rhythm.
Common causes of functional tachycardia:
- neurosis;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- vegetative dystonia;
- attacks of panic attacks;
- sympathic-adrenal crises;
- long-lasting depression.
Other causes of functional tachycardia development may be emotional or physical stress, elevated body temperature, and the presence of harmful habits.
Types / photos of functional tachycardia
Violation of the rhythm is most often expressed in the following forms: functional sinus tachycardia and functional supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia. Other species are not so often found or can not be considered functional at all, if you take, for example, trembling or fibrillation.
Functional sinus tachycardia
The origin of the pathology is mainly due to increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system. Most often, this form of rhythm disturbance is diagnosed with thyrotoxicosis, as well as dysfunction of higher neuromuscular regulation.

Sinus tachycardia can occur with various extracardial diseases: thyrotoxicosis, neurogenic disorders. It is often found in children and adolescents, as well as in pregnant women and during hormonal failures, when, for some reason, compensatory mechanisms for the circulation of blood in normal volume are triggered.
Nadjulyodochkovaya paroxysmal tachycardia
In most cases, the disorder is due to neurogenic disorders. An important feature of the occurrence of paroxysms is their launch by extrasystolic contraction. At the same time, patients often feel a push in the cardiac region and then the appearance of such sensation as the "roar of the heart".
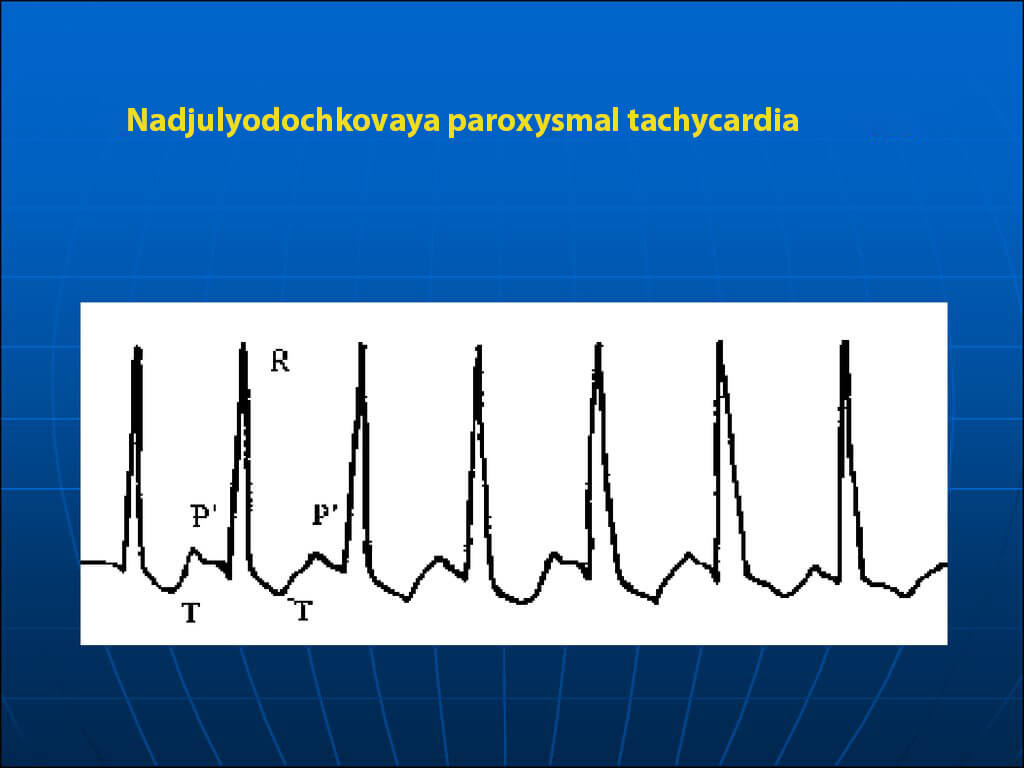
The disease can be complicated by half-awkward and faint states. In some patients, the attack ends with appetite for defecation and abundant urination. Despite the severe course of the disease, hemodynamic disorders develop in rare cases.
Diagnosis of functional tachycardia
With functional sinus tachycardia of neurogenic origin, a change in rhythm is observed during the transition from one position to another. Also, the vagal test slows the heart rhythm, which is not detected in the case of, for example, sinus tachycardia with thyrotoxicosis.
Complaints of heart attacks are indications for the use of standard electrocardiography. In addition, serial ECG-diagnostics and Holter monitoring are required.
ECG signs with functional tachycardia:
- The rhythm is regular with heart rate of 100 beats per minute, with paroxysmal form can reach up to 200 beats;
- ventricular complex is narrow, without deformations of the usual form;
- with sinus tachycardia of functional origin, a monomorphic tooth P, which at high heart rate can be communicated with the tooth T, is observed, thus simulating paroxysmal tachycardia.
In setting accurate diagnosis often have to resort to load tests and vagal tests. In particular, in the case of sinus tachycardia, the vagal test slows the heart rate, which is not observed in the case of supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia.
Treatment and prevention of functional tachycardia
In most cases, treatment with functional tachycardia is not required. The appointment of antiarrhythmic drugs can be carried out in the case of a complicated clinical picture, when the emerging symptoms of the disease bring the patient tangible discomfort. It is also important to adhere to the recommendations of the doctor involved in the main disease, in which a functional tachycardia arose. This may be an endocrinological or neurological pathology, and it is important to have effective treatment here, which will not make such a complication as a functional tachycardia.
In the treatment of functional tachycardia, a method of psychotherapy is often used, which allows, in combination with medication exposure, to bring heart activity to the heart as quickly as possible.
Specific prevention of functional tachycardia does not exist. It all depends on the extracardiac disease with which the violation of the rhythm is associated. The only patient with emotional lability should be less exposed to stress that can provoke the development of rhythm disturbance. Regarding the cardiovascular system, it will never prevent proper nutrition, healthy lifestyle and moderate physical activity.
