Extrasystolic arrhythmia
Author Ольга Кияница
2017-11-10
Modern diagnostic methods, and first and foremost electrocardiography, allow to determine the most minor violations of the cardiac rhythm. Extrasystolic arrhythmia refers precisely to this group of diseases, when extraordinary arises between normal heart contractions. This can be facilitated by even insignificant stresses and experiences. In the childhood of such disturbances a huge amount, therefore, extrasystole is determined not only in adults or in old age, but also in children.
Episodic extrasystoles are often found in practically healthy people and in the absence of subjective arrhythmias intolerance, they do not require specific treatment.
The subject of extrasystole was repeatedly touched by many scholars. Various groups of patients have been observed and in the course of studies, it has been found that healthy people have up to 100 extrasystoles a day. But there are severe forms of extrasystolic arrhythmia, so how dangerous is the disease will be described below.
Video: Cardiac Arrhythmia
Description of extrasystolic arrhythmia
Normally, the heart muscle is reduced at similar intervals. In the electrocardiogram, this is displayed as a sinus rhythm with substantially identical teeth separated by an isoline. When extrasystoles, an extraordinary contraction of the entire heart or of its individual cells occurs, which is marked on the ECG as a tooth, unlike the rest.
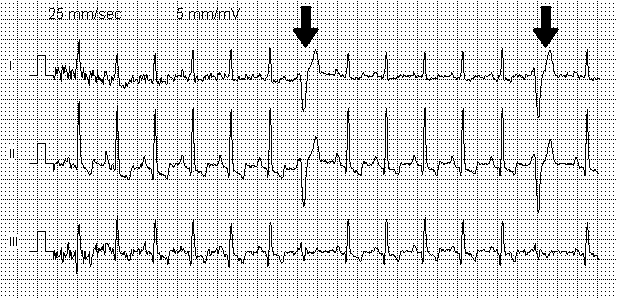
Extrasystoles are most often an ineffective heart contraction, since diastole does not normally fill the blood with body chambers.
There are several mechanisms for the emergence of extrasystole. The first one is cyclic, or reentry, when the electric pulse is transmitted over the fibers and stumbles to an obstruction in the form of a scar or ischemic area. The signal returns and re-cuts.
There is a second mechanism - the formation of an ectopic focal point. This occurs for various reasons, and the resulting area begins to send minor impulses that are recorded on the ECG as extrasystoles.
Symptoms of extrasystolic arrhythmia
In most cases, patients do not complain about the emergence of extrasystole. An extraordinary contraction can be felt as a fleeting impulse in the heart that does not cause significant discomfort.
Extrasystole is manifested by the following general symptoms:
- tangible interruptions in cardiac activity ("fading", "turning over" of the heart);
- feeling of weakness and fast fatigability;
- irritability and anxiety appear;
- sweating increases;
- headaches and dizziness;
- it becomes difficult to breathe.
Extrasystolic arrhythmia often acts as a marker for other diseases, so interruptions in the heart often combine with the characteristics inherent in another pathology:
- With vegetosocial dystonia - it is anxiety, irritability, feeling of fear, which is associated with increased activity of the parasympathetic department of the nervous system;
- With osteochondrosis, it is pain in the problem zone of the spine (most often it is neck, thoracic department);
- when overeating is a feeling of discomfort in the chest and heaviness in the abdomen, which is due to the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on the heart, especially if a person has bitten and took a horizontal position;
Extrasystolic arrhythmia may also develop during pregnancy, especially in those cases where, before conception, a woman has had cardiovascular disease, thyroid problems, or respiratory system. In the absence of subjective intolerance of interruptions, the treatment of extrasystole is not required.
Causes of extrasystolic arrhythmia
Determination of the cause of the development of extrasystole is necessary for the effective treatment and prognosis of the disease. This is especially important in the case of severe forms of the disease, which have a large impact on the general condition of the patient.

Functional causes of extrasystolic arrhythmia
Much depends on external factors, when, for example, smoking or drinking alcohol brings harm to the heart and other systems and organs. Stress situations and frequent fatigue also contribute to the emergence of extrasystoles. In such cases, the body is looking for additional possibilities, therefore, in the heart muscle there are areas generating an electrical impulse. As a result, heart failure is felt.
Hormonal disorders associated with dysfunction of the thyroid gland, pancreas, or climax, often provoke the appearance of extrasystole. At the same time there may be not only interruptions in cardiac activity, but also tides, rapid heartbeat.
The increase in temperature against the background of infectious diseases very often contributes to the development of extrasystolic arrhythmia. For such cases, the formation of ectopic foci is typical, when the heart does not cope with increased stress.
Organic factors of the appearance of extrasystolic arrhythmia
Failure of cardiac activity mainly occurs in the context of ischemic heart disease. This applies to both myocardial infarction, cardiosclerosis and angina pectoris. In these diseases, the structure of the myocardium changes, because of which the electrical impulse can not normally pass through the conducting paths.
Cardiovascular failure, most often chronic, is second only to the organic causes of the development of extrasystoles.The heart muscle begins to contract poorly when dilatation (stretching) of the ventricles, so there is a violation of the rhythm.
Heart defects and infectious heart disease also play an important role in the emergence of extraordinary contractions.Endocarditis and myocarditis are characterized by inflammation in the tissues of the heart. Insufficiency or stenosis of some valves leads to hemodynamic disorders. As a result, compensatory mechanisms develop in the form of extrasystoles.
Types / photos of extrasystolic arrhythmia
There are several forms of the disease:
- supraventricular extrasystole;
- ventricular extrasystole.
The most unfavorable is ventricular extrasystolic arrhythmia. What is such a pathology dangerous? First and foremost, there is a high probability of complications in the form of ventricular fibrillation. Therefore, patients with this ailment are observed at the cardiologist and receive antiarrhythmic treatment.
Najyludochkovaya extrasystole
Arises due to organic changes in the atrium or atrioventricular septum. Characterized by the appearance of an ectopic focus that generates extraordinary impulses. Another name for the pathological condition is supraventricular extrasystolic arrhythmia.

Allocate the following forms of supraventricular extrasystole depending on.
- localization of the ectopic focal point - atrial and atrioventricular;
- the number of foci - monotropic (single) and polythytic (two or more focuses);
- appearance time - early (appear in the phase of atrial contraction), late (appear in the phase of contraction of the ventricles or during diastole) and interpolated (determined in the interim period - between the reductions of the atrium and the ventricles);
- Frequencies occurring in one minute are paired (two at the same time), single (no more than five extrasystoles), multiple (from five extrasystoles and more), group (several extrasystoles are formed in a row).
Ventricular extrasystolic arrhythmia
A common type of rhythm disturbance associated with dysfunction of the conducting system of the ventricles.Depending on the localization of the pathological process, they differ in extrasystole:
- right ventricular;
- left ventricular
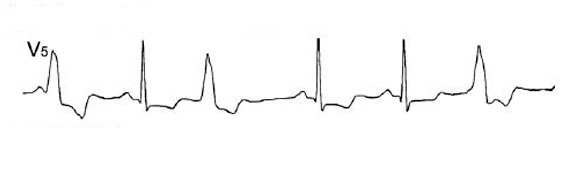
The disease is characterized by extensive variability, therefore, to simplify the diagnosis and the appointment of effective treatment, ventricular extrasystolic arrhythmias are divided into classes:

Daily ECG monitoring is used to determine the grade of ventricular extrasystoles.
Class I extrasystoles are considered not to be harmful to health, the other five are accompanied by hemodynamic disorders to a lesser or greater degree. Launching a similar pathology is dangerous, as ventricular fibrillation may develop.
Subfamilies of arrhythmia
- Benign, in which there is no organic damage to the heart muscle. With her such a dangerous complication, as a sudden stop of the heart, does not threaten.
- Potentially malignant extrasystole. Characterized by the presence of initial hemodynamic disorders due to the presence of organic changes in the heart of varying degrees of severity. The risk of cardiac arrest in this case increases several times.
- Maliciously running extrasystole. It is a violation of the rhythm, which is associated with the emergence of a large number of extrasystoles. There are serious damage to the heart tissue and persistent hemodynamic disorders. The probability of mortality is very high.
Diagnosis of extrasystolic arrhythmia
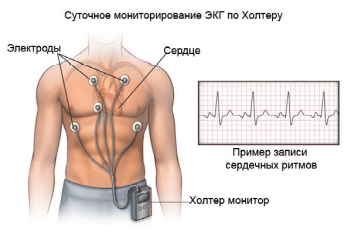
In all forms of cardiac abnormalities, the patient is referred to an electrocardiogram . This research method determines different types of extrasystoles. The pairs are shown on the electrocardiogram as untimely, closely spaced contractions between evenly moving correct teeth. Similarly, group and multiple extrasystoles are seen, alternating between normal abbreviations one after another. Uniform extrasystoles are difficult to see on a small tape, removed for no more than 5 minutes, so they are used to determine Holter monitoring (daily ECG).
Daily ECG monitoring is another way to determine extrasystolic arrhythmia. Suitable for a more thorough assessment of the patient's condition, as well as for the determination of individual extraordinary contractions. Method of conducting: during the day the patient removes the ECG, while it moves and spends time as usual. After the doctor evaluates the result of the control for the presence of pathology and its degree of severity.
Treatment of extrasystolic arrhythmia
In the first place, provocative factors are eliminated, or their impact on the patient diminishes. Further, the treatment tactic depends on the form and severity of the main and additional diseases.

- Uniform extrasystoles, which do not cause anxiety, do not require correction.
- Neurogenic extrasystole is treated with the help of organizing the correct day, psychotherapy, sedatives in the form of diazepam and valerian tincture.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed for marked clinical signs (heart failure, shortness of breath, heart pain), with the appearance of an early ventricular extrasystole, polythyroid and group extrasystory on an electrocardiogram, in the presence of cardiosclerosis after an infarction.
- Extrasystolic arrhythmia of classes IV and V can be corrected by means of defibrillator and cardioverter installation.
- Implantation of an artificial rhythm driver is indicated in the ineffectiveness of medication therapy.
Antiarrhythmic drugs (beta-blockers) are not prescribed in the presence of a patient's tendency to hypotension or uncommon heart rhythm.
Prevention of extrasystolic arrhythmia
It is based on a series of activities that can be attributed to virtually all cardiovascular diseases.

- the diet should be balanced and maximally saturated with foods useful for the heart (apples, pomegranates, nuts, avocados, seeds, salmon, salmon, olive oil and flaxseed oil);
- physical activity must be moderate and alternate with rest;
- if necessary, you must regularly take medications prescribed by your doctor;
- physiotherapy with the advice of a doctor will help to strengthen the cardiac muscle;
- it is necessary to refuse harmful habits (smoking, alcohol) and to avoid stressful situations.
Video: Audible heart beat - extrasystoles / PVC and sinus beats
Similar articles

Among all arrhythmias, extrasystoles are the most common. Other known names of pathology are ectopic strokes, premature strokes, premature atrium or ventricular complexes. Their occurrence is associated with premature contraction of the heart. Most often they do not pose a health hazard, but in some cases, the course of the underlying disease worsens.
Extrasystole is the most common type of rhythm disturbance that can be observed not only in patients with cardiac pathology, but also in completely healthy people. The essence of this phenomenon boils down to the fact that some parts of the heart contract out of their turn, which leads to the formation of arrhythmia. Most often, patients older than 50 years suffer from extrasystole. Violation of the rhythm can intensify after physical and psychoemotional loads, as well as after consuming alcohol-containing and caffeine-containing beverages.

In one of the forms of arrhythmia, namely extrasystoles, not all drugs can be used. The best option is the appointment of a cardiologist, but even the most sick should be aware of what drugs can be taken with cardiac arrhythmia. As a result, a more thorough treatment course will be achieved.

Сколь срочно и необходимо может быть назначение бисопролола в дозе 5 или 10 мг, если перед наступлением экстрасистолии было злоупотребление алкоголем в течении 3 дней и давление поднималось до 160/100? После этого был прекращен прием алкоголя на фоне тяжести в сердце и затрудненного дыхания, которое так же связано со сломанной носовой перегородкой, в следствии чего человек сильно храпит во сне, и носовое дыхание часто бывает затруднено (так же во время сна); ртом он при этом не дышит.
После этого принимался энтэросгель 1 день и после трехдневного приема панангина 2 раза в день давление снизилось до 120/85 и 130/90, но экстрасистолы на кардиограмме не часто но сохраняются.
Meow, в первую очередь нужно пройти обследования, назначенные доктором, только потом принимается решение о назначении бисопролола или другого бета-адреноблокатора. Как правило, при нечастых экстрасистолиях достаточно придерживаться здорового образа жизни, чтобы поддерживать нормальное состояние. И, конечно, нужно обратиться к врачу-отоларингологу, чтобы вылечить поломанную носовую перегородку.