Medical magazine Arrhythmia center
The unique structure of the heart allows him to work throughout human life, generating electrical impulses on his own in cardiac cells - cardiomyocytes.
In the ordinary state, cardiac activity is practically not felt. If there are organic or functional disorders, a cardiovascular disease occurs. Timely treatment can prevent negative consequences, but how and when should you go to the doctor?
Our portal on the health of your heart provides detailed information about cardiovascular diseases.
- How and why do heart diseases develop?
- What factors contribute to their occurrence?
- When should I see a doctor?
- What modern methods of diagnosis and treatment are offered by medicine?
Answers to these questions and many others you will find on the pages of our website.
Why does the heart ache?
Unfortunately, cardiovascular diseases account for 31% of all deaths recorded in the world. Presenting a vast group of pathological conditions, are defined in young and old, in the able-bodied population and in newborns.
Types of cardiovascular diseases:
- Ischemic heart disease (CHD), which includes sudden coronary death, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, cardiosclerosis
- Essential hypertension (hypertension)
- Cerebrovascular disorders, including strokes, encephalopathies
- Arrhythmias
- Heart defects (congenital and acquired)
- Heart failure
- Inflammatory and infectious lesions, expressed in myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis
- The pathology of the veins, represented by varicose enlargement, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis
- Diseases of peripheral circulation.
We set out to provide the most interesting and useful materials about such diseases as arrhythmia, tachycardia and bradycardia. It is these pathological conditions that are most often determined in the population, in adults and in children. To know how they are manifested and how to deal with them, see our website.
What is an arrhythmia?
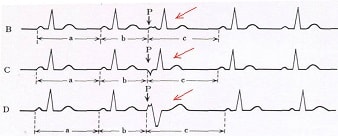
The term "arrhythmia" is similar to the Greek word ἀρρυθμία, which in translation means irregularity, lack of rhythm. Under the arrhythmia understand the activity of the heart different from the normal sinus rhythm. In a normal and quiet state, the number of heartbeats in adults is 60-90 times per minute. In the presence of functional or organic disorders there is an arrhythmia manifested by the following types of heartbeat:
- more frequent - a tachycardia;
- slowed - bradycardia;
- irregular - fibrillation;
- premature contraction - by type of extrasystole.

The degree of severity of rhythm disturbance may not be a direct indication of the severity of the underlying disease.
Causes of arrhythmia
In some cases, arrhythmia is seen as a natural reaction of the body to external stimuli: a bite of insects, physical or emotional stress, acute respiratory viral infection with high fever, copious eating or wearing tight clothes. After eliminating the root cause, the rhythm comes back to normal.
In pathological situations, arrhythmia develops as an independent disease, or, more characteristic of a rhythm disorder, occurs against the background of the pathology of the heart or other organs and systems. This may be thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, arterial hypertension, cardiosclerosis. Also, hormonal restructuring in the body, which is especially pronounced in adolescents, pregnant women, during menopause, can cause arrhythmia.
 Stress
Stress
 SMOKING
SMOKING
 ALCOHOL
ALCOHOL
 INCORRECT FOOD
INCORRECT FOOD
What are arrhythmias?
All arrhythmias are divided into groups, united by violations of the function of the heart. Disturbed disorder of automatism, excitability, conductivity of the whole body or its departments. Each group includes a number of specific diseases, which are characterized by a common mechanism of development of rhythm disturbance. Some forms of arrhythmia do not pose a threat to human health, so they may not require medical treatment if they arise. Other arrhythmias are associated with organic heart lesions, so timely medical attention should be provided when detecting them.
Arrhythmias that present a life threat are often associated with severe physical illnesses. For example, this form of arrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation, occurs against ischemic heart disease, cardiac malformations, or chronic heart failure. In patients without a pathology of the heart, fibrillation does not occur. At the same time, the severity of arrhythmia can not be judged by the dynamics of the development of the underlying disease.